How much should each pass of the transducer overlap the previous path during a weld scan?
A welding engineer or inspector should be notified when a weld has failed a weld quality test more than how many times in order to help determine the cause of the test failure?
In magnetic particle examination, the yoke is placed parallel to the weld to detect cracks:
The simplest weldability tests are those that evaluate:
Which of the following is a practical solution that could prevent or reduce lack of fusion in carbon steel during the weld process?
When welding using the GTAW process, which of the following best describes the appearance of a transverse crack on a radiograph?
Eddy current can be used to measure the:
What increases when a welder increases the amperage?
Hardenability of a steel can be an indirect indicator of:
One limitation of a shielded metal arc welding (SMAW) process is that:
What is(are) the most appropriate action(s) to prepare an in-service carbon steel piping system that has been in caustic service for welding?
What is the purpose of the IQI?
Which welding process produces a fast-freezing weld pool and is generally suited for joining thin sections or root passes?
Which term is used to describe a groove melted into the base metal adjacent to the weld toe or weld root and left unfilled by weld metal?
Which of the following statements is true?
For design purposes, the maximum usefulness of a weldment under test is based upon the:
A four-digit designation for a SMAW electrode under AWS classification uses the third digit to define the:
Refer to the following diagram:
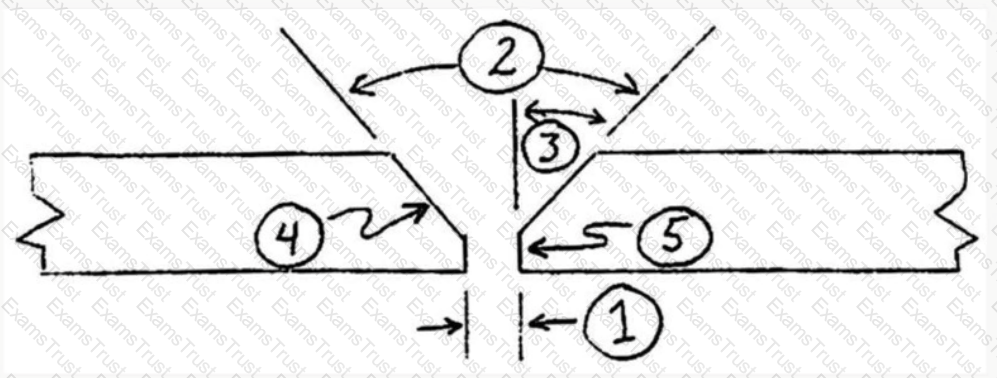
Item#4 represents:
Which of the following has the lowest range of welding currents and electrode diameters associated with the GMAW process?
A “mill certificate" is a/an:
For SMAW welding, the last number of the electrode identification identifies:
Which of the following can result from residual magnetism left in a partially completed weld?
The deflection of an arc from its normal path that is a result of magnetic forces is referred to as:
Hot tapping and in-service welding should be carried out only with:
Crater cracks typically occur:
A-number groupings are based upon the:
Which of the following is an important aspect of a qualified WPS?
To reduce the possibility of cracking, which of the following maximum hardness levels is required for weldments in wet H2S service?
P-numbers are based on which of the following?
Remote examination of welds may use aids such as telescopes, borescopes, fiberscopes, cameras, or other suitable instruments provided they have:
What is a discontinuity?
Heating a round bar to an elevated temperature and then quenching one end is a test method to determine:
Which of the following is used to determine the soundness and ductility of a groove weld?