Howell-Jolly bodies are composed of DNA, usually left from the nucleus, that appears as a round, dark-staining inclusion in the cytoplasm of red blood cells. Howell-Jolly bodies can be found in various conditions including splenectomy and anemia.
Remnants of erythrocyte nuclei, nuclear fragments, or aggregates of chromosomes are called:
he last choice in this question is false. Rocky mountain spotted fever is NOT geographically restricted to the Rocky mountain region. In fact, according to the CDC, this disease is widely distributed east of the Rocky Mountains and also occurs in limited areas on the Pacific Coast.
Which one of the following statements is false?
A hospital chief operating officer is responsible for
A laboratory scientist is working the night shift at a local hospital when the power goes out. What is the course of action to continue to provide laboratory results?
Drawing a lavendar stopper tube before an SST tube can cause a falsely:
Question options:
P. vivax characteristically displays Schuffner's dots and often enlarged RBCs along with brownish granules. P. vivax can also have 12-24 merozoies in each cell, actually filling the entire RBC. This parasite also has very irreglar shapes often referred to as "Ameboid".
P. falciparum and P. malariae do not display Shuffner's dots, therefore could not be the correct choice.
P. ovale does display Shuffner's dots in all stages, but characteristically has about 8-12 merozoites in rosettes or irregular clusters inside the RBC. Also, P. ovale characteristically shows enlarged, ovoid RBCs with fimbriated edges.
Identify the parasite of a patient with suspected malaria who demonstrates the following findings on a blood smear:
- Enlarged RBCs, some with fine brownish granules
- > 15 parasites in some cells
- Ameboid structures
- Schuffner's dots
An employer who fails to provide sufficient personal protective equipment (PPE) for employees may be fined by the:
Allergen-specific IgE, synthesized in response to allergens, becomes fixed to receptors on cellular membranes, especially those of basophils. If these receptor-bound IgE molecules are aggregated on re-exposure to specific allergen, both mast cells and basophils produce mediators that result in the allergic response. IgE-antigen interaction at the cell surface causes degranulation of cells and release of substances including: histamine, SRS-A, platelet activator, a kallikrein, and an eosinophil chemotactic factor. Basophils are the principal cells that bind IgE antibody while their number of receptor sites is proportional to serum IgE levels. Eosinophils are drawn to the site by the basophil chemotaxis mechanism, but are not the main cell which binds the IgE antibody.
Immunology
The mediator cells that bind MOST to IgE antibodies are:
The two main areas of the clinical laboratory are:
MCH is the average weight of hemoglobin in the average red blood cell. The value is expressed in picograms (10-12 grams).
Hematology
Hemoglobin (g/100ml) x 10 / RBC count (millions/mm3) is the formula for calculating:
Rapid vascular constriction, not dilation, immediately occurs when there is vascular injury in order to constrict the amount of blood that escapes the vessels; ultimately preventing massive loss of blood.
Primary hemostatic processes resulting from vascular damage include all of the following EXCEPT:
Standard precautions should be followed:
L/S ratio <2.0 indicates an increased risk of respiratory distress syndrome (RDS) at delivery. L/S ratio <1.5 indicates a very high risk of developing RDS.
Which of the following statements regarding the L/S ratio is TRUE?
The correct answer is highlighted below
A ratio of 2:1 or greater usually indicates adequate pulmonary surfactant to prevent respiratory distress syndrome (RDS)
A ratio of 1.5:1 indicates fetal lung maturity in pregnancies associated with diabetes mellitus.
Sphingomyelin levels increase during the 3rd trimester causing the L/S ratio to fall slightly during the last two weeks of gestation.
A phosphatidylglycerol (PG) spot indicates the presence of meconium in the amniotic fluid
Lecithin is in direct ratio with sphingomyelin
Heparin contamination is characterized by an elevation in the aPTT test and can also cause an increased PT test as well. Reptilase time tests are used to elimate the effects of heparin contamination as the reagents and method are resistant to the effects of antithrombin III, unlike the PT and aPTT tests. Therefore, it would be expected that a patient sample containing pre-analytical heparin contamination will show an increased aPTT (and sometimes PT as well) while showing a normal reptilase time.
A specimen drawn from an indwelling catheter that was contaminated by heparin would be indicated by:
The laboratory employee with an 2-year associate degree who performs clinical testing is the:
Waived tests are those considered to have an insignificant risk of erroneous results. Which of the following is NOT an example of a waived test?
Which of the procedures listed below will increase the platelet concentration in the preparation of Platelets?
Western blot analysis is frequently utilized as the confirmatory method of HIV detection.
Which of the following assays is routinely used for confirmation of HIV infections:
Spirochetes such as Borrelia and Treponemes are best visualized using darkfield microscopy. Borrelia, which causes Relapsing fever, can be visualized under darkfield microscopy of wet preps of peripheral blood. Treponema can be visualized by darkfield microscopy of early primary lesions, and aspirates of affected lymph nodes.
Which of the following organisms is best visualized by use of a darkfield microscope:
Where can one find guidance on the minimum performance standards for clinical laboratories?
The agency within Department of Health and Human Services (DHHS) responsible for implementing CLIA'88 is:
% concentration (expressed as a proportion or ratio) x volume needed = mass of reagent to use
So... 10% (w/v) solution of sodium hydroxide x 200 mL needed = 20 grams of sodium hydroxide
How many grams of sodium hydroxide are required to prepare a 200 ml solution of a 10% (weight per volume) solution? (Atomic weights: Na = 23; 0 = 16; H = 1)
Listeria monocytogenes is the correct answer. The motility agar is showing motility at the top of the tube, but not deeper; typical of this catalase-positive, gram positive bacillus. Streptococcus agalactiae would be catalase negative and a coccus. Erysipelothrix rhusiopathiae would be H2S-positive and catalase negative. Escherichia coli is a gram negative bacillus.

This Gram-positive bacillus grew as a diffusely beta-hemolytic colony from a newborn. It was catalase positive and had tumbling motility on a hanging drop preparation. This is how it appeared on triple sugar iron agar and motility medium. What is the most likely diagnosis?
Alkaline over acid, or K/A, in TSI reactions is associated with the fermatation of glucose alone and the utilization of peptone.
Which of the following sugars has been fermented by a gram-negative rod that has produced an alkaline slant and an acid butt on triple sugar iron agar (TSI).?
Provide the equivalent measurement for 1000 milligrams.
Question options:
PCT usually rises within 3-6 hours of infection. CRP also increases rapidly following infection, but is not as specific for infection as PCT. A rise in CRP could also occur with SIRS. Lactic acid is usually used to detect and monitor impaired circulation and tissue oxygenation in critically ill patients.
Chemistry
Of the three laboratory tests that are listed, which has proven to be most effective for early differentiation of systemic inflammatory response syndrome (SIRS) from sepsis due to its increase following infection and higher specificity?
Escherichia coli and Klebsiella pneumoniae are two good quality control choices for the indole test. E. coli is indole positive, while K. pneumoniae is indole negative. A positive reaction is noted when there is a red layer at the top of the tube after the addition of Kovács reagent, while the negative result is a lack of color change in the top of the tube after the addition of Kovács reagent.
Which one of the following combinations of organisms would be appropriate positive and negative controls to verify the specific test functions listed?
As magnification DECREASES, the opening of the iris diaphragm will...
Serum separator tubes should not be used for:
Question options:
Pluripotential stem cells are ultimately capable of differentiating into all types of leukocytes.
Hematology
Pluripotential stem cells are capable of producing which of the following:
A combination of (nonselective) 5% sheep blood and (selective) MacConkey agars is sufficient for the recovery of the pathogenic microorganisms that are most commonly encountered in urinary tract infections (UTIs). MacConkey is the selective culture medium that is most commonly used to inhibit growth of gram-positive organisms (most UTIs are caused by gram-negative organisms).
Eosin methylene blue (EMB) is a selective agar that also inhibits the growth of gram-positive organisms. Therefore, using only a combination of MacConkey and EMB would prevent the detection of a gram-positive organism, if this were the cause of the infection.
Chocolate agar or other enriched media may be needed in addition to blood and MacConkey if a more fastidious organism is suspected.
Thayer-Martin would be used specifically for recovery of Neisseria gonorrhoeae. Thayer-Martin (or Modified Thayer-Martin) inhibits other microorganisms and allows the selective recovery of both N. gonorrhoeae and N. meningitidis.
Microbiology
Which culture agar combinations below will usually be sufficient for MOST routine urine culture investigations?
On the red cell membrane, there is a bicarbonate / chloride exchanger. This exchanger allows for bicarbonate to leave the red cells while chloride is allowed inside.
In blood, bicarbonate leaves the red blood cell and enters the plasma through an exchange mechanism with:
The National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute initiated the National Cholesterol Education Program (NCEP) in 1985. The goal was to reduce the number of Americans with elevated cholesterol and thus reduce illnesses and deaths in the United States due to coronary heart disease. Three adult treatment panels have been published since then with clinical practice guidelines for managing cholesterol levels in adults.
The most recent panel, Adult Treatment Panel III (ATP III), was published in 2001 and updated in 2004. The NCEP: ATP III also includes criteria for the diagnosis of metabolic syndrome.
Select the set of laboratory assays that are utilized in the NCEP: ATP III criteria for metabolic syndrome diagnosis.
Amniotic fluid bilirubin is increased in association with the severity of hemolytic diseases of the newborn. As red blood cells lyse during these conditions, bilirubin builds up as a byproduct of the red cell destruction. The more red blood cells that are being destroyed in the baby, the more increased the bilirubin level will become.
Which one of the following tests BEST correlates with the severity of hemolytic disease of the newborn (HDN).
Immunoassay is the most common technique that is used by clinical laboratories for therapeutic drug monitoring.
Most of the drugs commonly assessed with TDM can be measured on analytical platforms which utilize antibodies (in some form) for detection. Antibodies can be developed that recognize drugs. Although most drugs are much too small to evoke an immune response, scientists can conjugate drugs to immunogenic proteins to produce antibodies that recognize drug-specific epitopes.
Which of the following is the most common technique that is used by clinical laboratories for therapeutic drug monitoring?
Provide the equivalent measurement for 4 milligrams.
Which advancement in clinical science occurred during the second half of the twentieth century?
Francisella is slow growing on primary isolation culture media and produces poorly-staining coccobacilli on Gram stain. Because Francisella tularensis is included on the list of bioterrorism agents, suspicious isolates should be referred immediately to a public health laboratory in lieu of attempting an in-laboratory identification.
One of the BIGGEST problems with isolating Francisella is that these organisms:
Convert the following temperature from Fahrenheit to Celsius
102 degrees F
Heinz bodies occur as the result of denaturation and precipitation of hemoglobin, and are often attached to the red cell membrane. They require staining with crystal violet or methyl violet to be visible. They may be seen in thalassemia, with unstable hemoglobins, or during a hemolytic episode in G6PD deficiency.
Hematology
The intracellular precipitates seen in the RBCs in this illustration is termed:
A test with high specificity accurately detects the absence of disease. The more specific a test is, the fewer false-positive results will occur. A test with high sensitivity accurately identifies the presence of disease. The more sensitive a test, the fewer false-negative results it produces. In the case stated in this question, the immunoassay has high specificity, so it has few false-positives and will accurately detect those individuals who do not have the disease or condition that is being tested for. However, the test has low sensitivity, so it may not identify all individuals who actually have the disease; it may produce many false-negative results.
The accuracy of an immunoassay is its ability to discriminate between results that are true positives and results that are true negatives. Two parameters of test accuracy are specificity and sensitivity. Which of these statements apply to an immunoassay with high specificity, but low sensitivity?
Glucagon and epinephrine promote glycogenolysis, conversion of glycogen to glucose, which increases plasma glucose.
Cortisol along with glucagon increases gluconeogenesis, formation of glucose from noncarbohydrates which also raises plasma glucose concentration.
Chem
Which of the following hormones increases plasma glucose concentration by converting glycogen to glucose? Please select all correct answers
If your reactions are strong at immediate spin (3+) and then get weaker at AHG (w+), it could mean the presence of a strong cold antibody.
Cold antibodies tend to be IgM and their optimum phase for reactivity is immediate spin. Incubation and washing of the sample may cause the agglutination that occurred at room temperature to break down. This would appear as a weaker reaction at AHG.
If the reaction strengths varied in each panel cell then that could be an indication that there are multiple antibodies present.
Your screen cells are 3+ at immediate spin and weak (W)+ at AHG. Your auto control is negative for both phases. Some of your antibody panel cells are 3+ at immediate spin and negative at AHG. What should you suspect?
Only non-self antigens can be immunogenic. Self antigens are normally recognized by the immune system as part of the host, so an immune response does not normally occur. Non-self antigens are immunogenic since they have the potential to cause an immune response.
For a substance to be immunogenic it must be:
The parents will each give one of their ABO genes, so the possibilities are as follows:
AB, AO, AB, AO = 50% chance of A blood type, 50% chance of AB blood type
Blood Bank
If parents have the blood group genotypes AA and BO, what is the possibility of having a child with a blood type of A?
Serum calcitonin is normally produced by the C cells of the thyroid. It functions to reduce serum calcium by inhibiting release of calcium from bone. It is a peptide with a molecular weight of 3400, and has a half life of approximately 12 minutes. It is characteristically elevated in medullary carcinoma of the thyroid. Since medullary carcinoma often occurs as an autosomal disorder, family members of patients with this condition should be screened for serum calcitonin.
Serum calcitonin is typically elevated in which of the following conditions:
1 SD = 68.3%, 2 SD = 95.5%, 3 SD = 99.7
As defined by a Gaussian distribution curve, what percentage of values would be expected to fall within two standard deviations of the mean:
Joint pain is a common early symptom of HH. Cirrhosis of the liver, cardiomyopathy, and diabetes are late symptoms of HH.
What is a common early symptom of hereditary hemochromatosis (HH)?
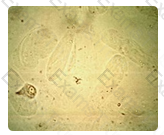
Ammonium biurate crystalsare typically round, irregularly spiked and yellow-brown in color.
A microscopic examination of a normal urine pH 8.0 shows 2+ yellow-brown thorny spheres which are MOST probably:
Provide the equivalent measurement for one pint.
Vitamin K dependent factors are those that require Vitamin K for their synthesis in the liver. Vitamin K is an important factor to gamma-glutamyl carboxylase which adds a carboxyl group to glutamic acid residues on factors II, VII, IX and X, as well as Protein S, Protein C. In adding the gamma-carboxyl group to glutamate residues on the immature clotting factors Vitamin K is itself oxidized. Deficiency of Vitamin K due to malabsorption, liver disease, etc. may contribute to bleeding disorders because clotting factor maturation depends on Vitamin K.
Which of these coagulation factors are referred to as "vitamin-K dependent?"
Convert the following temperature from Celsius to Fahrenheit
8 degrees C
A quality control program is to be set up for the following tests:
Phenylalanine deaminase (PAD)
Indole production
Voges-Proskauer (V-P)
Which pair of stock culture organisms would be MOST suitable to verify the performance of these three tests?
Plasma concentrations of creatinine are used to assess renal function. Creatinine clearance is based on the serum creatinine level and is used to measure glomerular filtration rate, or GFR.
An increased serum level of which of the following analytes is MOST commonly associated with decreased glomerular filtration?
The Western Blot Assay is used as a confirmatory test for which of the following:
Beta-thalassemia major, also known as Cooley's anemia, has inherited two genes for beta thalassemia without a normal beta-chain gene. This disease is assoicated with a marked deficiency in beta chain production and in the production of normal Hb A. These patients exhibit increased amounts of iron due to the mutliple transfusions that keep them alive. There is also a striking increase in hemoglobin F and an elevation in hemoglobin A2.
Hematology
A 5-year-old African American child with hepato-splenomegaly and skeletal abnormalities has the following lab results:
WBC = 4,800/cu.mm
20 NRBC/100 WBC
RBC = 2.70 X 106
HGB = 6.2 g/dL
Many target cells
Marked hypochromasia, anisocytosis & poikilocytosis
Serum Iron = 200 µg/dL (elevated)
Sickle Solubility = negative
Hemoglobin F = elevated
What is the PROBABLE cause of these findings?
All of the following activities are associated with platelets EXCEPT:
The thrombin time (TT) involves the addition thrombin to platelet poor plasma to stimulate the clotting process. It reflects ability of the patient to convert fibrinogen to fibrin but is also sensitive to the presence of inhibitors that may be present in the plasma, like heparin. Therefore, it can be used to measure the effects of heparin on a coagulation sample.
This assay would be used to help rule-out heparin contamination in a coagulation sample:
Medical ethics
Match each of the following definitions associated with heart disease and heart failure to the term that it defines.
1. Congestive heart failure
2. Infarction
3. Ischemia
4. Angina
The FTA-ABS is used to confirm that a positive non-treponemal test like RPR is not the result of a biological false positive, which occur in about 1 to 10 percent of the population.
A positive RPR test and a negative FTA-ABS test is most likely the result of:
Abrupt change in temperature is one of the risk factors in which a sickling event may occur.
Dehydration, hypoxia, and physical exertion, rather than excessive intake of fluids, inhaling oxygen, and sedentary lifestyle, are all additional risk factors in which sickling events may occur.
Which of these could cause a sickling event?
Provide the equivalent measurement for 1 centimeter.
Question options:
Troponin is potentially more specific for myocardial damage than CK-MB and stays elevated longer. It may eventually replace CK-MB as the standard marker of myocardial damage. In addition, troponin T has been known to be elevated in the setting of even mild degrees of renal failure. Troponin and CK-MB both tend to rise approximately 3 hours after a MI (hence why the correct answer is "A", since it is false); however, troponins can stay elevated up to 2 weeks as CK-MB tends to return to baseline around 36 hours.
Chemistry
Which of the following statements is FALSE regarding troponin?
Since hemoglobin is measured spectrophotometrically on hematology analzyers, interference from lipemia or icteric specimens can lead to decreased light detected and measured through the sample and therefore inaccurate hemoglobin results occur.
On an electronic cell counter, hemoglobin determination may be falsely elevated caused by the presence of:
Skeletal deformations result from the increased erythropoiesis that occurs in beta thalassemia major. Children with beta thalassemia intermedia may demonstrate some facial bone deformity, however this is not common. Beta thalassemia minor rarely causes any physical signs or symptoms and beta thalassemia minima is completely asymptomatic.
Skeletal deformations are most commonly present in which of the following beta thalassemias?
Which EBV markers would be MOST likely positive for an individual who had infectious mononucleosis 9 years ago?
The antiglobulin test may be omitted from the serological crossmatch if the patient's antibody screen is negative and there is no history of detection of unexpected antibodies.
Blood Bank
What must be true for the antiglobulin phase of the serologic crossmatch to be omitted (i.e., immediate spin crossmatch is done)? Please select all correct answers
These are tyrosine crystals

Urinalysis & Other Body Fluids
True or false? Cystine crystals are present on this slide.
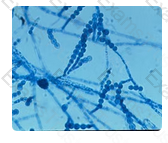
The microscopic features shown here represent Scopulariopsis species. In most instances, particularly if a patient does not have underlying immunologic or hematologic disease, Scopulariopsis species should be considered a contaminant when recovered from a sputum specimen. However, if there is clinical or X-ray evidence of mycotic pulmonary infection, additional daily induced sputum specimens should be obtained.
If Scopulariopsis species or any other hyaline mold is recovered from two or more successive specimens, its potential as a pathogenic agent should be considered. Scopulariopsis species have been reported as the agents of pulmonary fungus ball infections in patients with preexistent cavities and as a cause of pneumonia in patients with leukemia.
Invasive pulmonary disease by this agent has not been reported.
The fungus illustrated in this photomicrograph was recovered from an induced sputum specimen from a 74 year old man with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. This isolate is most likely:
The body of a tapeworm is composed of successive segments known as proglottids. Each mature proglottid has both male and female reproductive structures.
What is the anatomical feature of a tapeworm that possesses both male and female reproductive structures?
This is the total magnification of the high dry objective lens.
Mode is defined as the number that occurs most frequently in a set of numbers.
The value that occurs most frequently in a set of results or values would be termed:
Chain-of-Custody procedures must be followed for
What component is indicated for patients who receive directed donations from immediate family members to prevent transfusion-associated graft versus host disease (TA-GVHD)?
Clostridium difficile is a gram-positive, spore-forming bacilli. The remaining organisms will all stain gram-negative on direct smear or smears made from culture.
Which of the following organisms are gram-positive?
A phlebotomist has just performed a venipuncture on a patient. How would the phlebotomist dispose of the used needle?
Which of the following organizations has developed standards to maintain the performance of the clinical laboratory at the highest standards for quality care?
First, determine the number of WBC's from the hemocytometer as follows:
WBC count = (dilution ratio x # of cells counted x 10) / (# mm2 area counted)
Then: WBC count = (20 x 100 x 10) / (8) = 2500 WBC/mm3 (or 2500 WBC/uL or 2.5 x 103 WBC/uL)
Next, to find the WBC count per liter, multiply the WBC count/uL by the number of uL/L (there are 106 uL/L)
So: (2.5 x 103 WBC/uL) x (106 uL/L) = 2.5 x 109 WBC/L
Hematology
A 1:20 dilution is made for a manual WBC count. The four corner squares on both sides of a hemocytometer are counted. A TOTAL of 100 cells are counted in that area. What is the white blood cell count in terms of a liter (? x 10^9/L)?
To prevent blood from clotting the specimen must be:
What are the certification requirements for clinical laboratory professionals?
Molarity x Molecular Weight x Volume = Grams
Molecular Weight (aka Formula Weight) =
2(1) + 32 + 4(16) = 98
So, 4 x 98 x 0.2L = 78.4g
What weight of H2SO4 is contained in 200 ml of a 4 molar H2SO4 solution? (Atomic weight: H= 1; S = 32; 0 = 16)
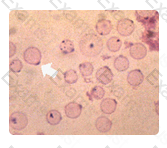
The intended response is "transfusion dimorphism". The microcytic, hypochromic erythrocytes suggests iron deficiency anemia. Interspersed among these cells are normocytic, normochromic erythrocytes suggesting two populations of red cells following transfusion. This was a case of severe iron deficiency treated with red cell transfusions and iron supplement.
The condition most likely associated with the peripheral blood picture in the photograph is:
Small, dense LDL is most likely to interact with arterial walls, leading to deposition of cholesterol, and initiating or worsening atherosclerosis. Small, dense LDL is associated with more than a three-fold increase in the risk of coronary heart disease.
Large, buoyant LDL is less atherogenic than small, dense LDL.
The LDL phenotype A is normal. It is the so called 'B' pattern that is associated with increased risk.
Which of the following is most likely to interact with arterial walls, leading to deposition of cholesterol, and initiating or worsening atherosclerosis?
Incompatiblity involving the ABO blood group system can cause the most severe type of transfusion reaction.
The cause of the most severe life-threatening hemolytic transfusion reactions is:
Which of the following genotypes cause beta thalassemia minor?