An infection preventionist is reviewing practices in a facility's food preparation department. Which of the following practices should be revised?
Thawing meat at room temperature
Using a cutting board to cut vegetables
Maintaining hot food at 145° F (62.7° C) during serving
Discarding most perishable food within 72 hours
Thawing raw meat at room temperature is a major food safety violation because it allows bacteria to multiply rapidly within the temperature danger zone (40–140°F or 4.4–60°C). Meat should always be thawed in the refrigerator, under cold running water, or in a microwave if cooked immediately.
Why the Other Options Are Incorrect?
B. Using a cutting board to cut vegetables – This is safe as long as proper cleaning and sanitation procedures are followed.
C. Maintaining hot food at 145°F (62.7°C) during serving – 145°F is an acceptable minimum temperature for certain meats like beef, fish, and pork.
D. Discarding most perishable food within 72 hours – Many perishable foods, especially leftovers, should be discarded within 3 days, making this an appropriate practice.
CBIC Infection Control Reference
The APIC guidelines emphasize that raw meat should never be thawed at room temperature due to the risk of bacterial growth and foodborne illness.
Which of the following factors increases a patient’s risk of developing ventilator-associated pneumonia (VAP)?
Hypoxia
Nasogastric tube
Acute lung disease
In-line suction
Ventilator-associated pneumonia (VAP) is a type of healthcare-associated pneumonia that occurs in patients receiving mechanical ventilation for more than 48 hours. The Certification Board of Infection Control and Epidemiology (CBIC) emphasizes identifying risk factors for VAP in the "Prevention and Control of Infectious Diseases" domain, aligning with the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) guidelines for preventing ventilator-associated events. The question requires identifying which factor among the options increases a patient’s risk of developing VAP, based on evidence from clinical and epidemiological data.
Option B, "Nasogastric tube," is the correct answer. The presence of a nasogastric tube is a well-documented risk factor for VAP. This tube can facilitate the aspiration of oropharyngeal secretions or gastric contents into the lower respiratory tract, bypassing natural defense mechanisms like the epiglottis. The CDC’s "Guidelines for Preventing Healthcare-Associated Pneumonia" (2004) and studies in the American Journal of Respiratory and Critical Care Medicine (e.g., Kollef et al., 2005) highlight that nasogastric tubes increase VAP risk by promoting microaspiration, especially if improperly managed or if the patient has impaired gag reflexes. This mechanical disruption of the airway’s protective barriers is a direct contributor to infection.
Option A, "Hypoxia," refers to low oxygen levels in the blood, which can be a consequence of lung conditions or VAP but is not a primary risk factor for developing it. Hypoxia may indicate underlying respiratory compromise, but it does not directly increase the likelihood of VAP unless associated with other factors (e.g., prolonged ventilation). Option C, "Acute lung disease," is a broad term that could include conditions like acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS), which may predispose patients to VAP due to prolonged ventilation needs. However, acute lung disease itself is not a specific risk factor; rather, it is the need for mechanical ventilation that elevates risk, making this less direct than the nasogastric tube effect. Option D, "In-line suction," involves a closed-system method for clearing respiratory secretions, which is designed to reduce VAP risk by minimizing contamination during suctioning. The CDC and evidence-based guidelines (e.g., American Thoracic Society, 2016) recommend in-line suction to prevent infection, suggesting it decreases rather than increases VAP risk.
The CBIC Practice Analysis (2022) and CDC guidelines prioritize identifying modifiable risk factors like nasogastric tubes for targeted prevention strategies (e.g., elevating the head of the bed to reduce aspiration). Option B stands out as the factor most consistently linked to increased VAP risk based on clinical evidence.
References:
CBIC Practice Analysis, 2022.
CDC Guidelines for Preventing Healthcare-Associated Pneumonia, 2004.
Kollef, M. H., et al. (2005). The Impact of Nasogastric Tubes on VAP. American Journal of Respiratory and Critical Care Medicine.
American Thoracic Society Guidelines on VAP Prevention, 2016.
When implementing a multimodal strategy (or bundle) for improving hand hygiene, the infection preventionist should focus on Calculator
signage for hand hygiene reminders.
cost effectiveness of hand hygiene products.
availability of gloves in the patient care area
institutional assessment of significant barriers.
When implementing a multimodal strategy (or bundle) for hand hygiene, the infection preventionist should first assess barriers to compliance before implementing solutions.
Step-by-Step Justification:
Understanding Barriers First:
Identifying barriers (e.g., lack of access to sinks, high workload, or poor compliance culture) is critical for effective intervention.
APIC Guidelines on Hand Hygiene Improvement:
Strategies must be tailored based on the institution's specific challenges.
Why Other Options Are Incorrect:
A. Signage for hand hygiene reminders:
Signage alone is insufficient without addressing systemic barriers.
B. Cost-effectiveness of hand hygiene products:
While important, cost analysis comes after identifying compliance barriers.
C. Availability of gloves in the patient care area:
Gloves do not replace hand hygiene and may lead to lower compliance.
CBIC Infection Control References:
APIC/JCR Workbook, "Hand Hygiene Compliance and Institutional Barriers".
APIC Text, "Hand Hygiene Improvement Strategies".
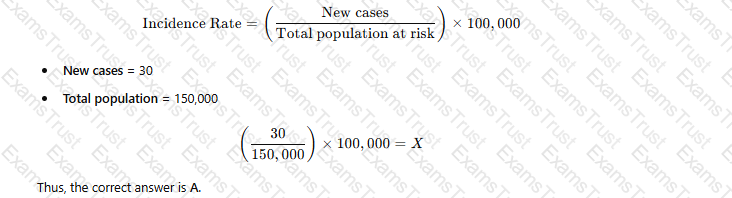
A city has a population of 150.000. Thirty new cases of tuberculosis (TB) were diagnosed in the city last year. These now cases brought the total number of active TB cases in the city last year to 115. Which of the following equations represents the incidence rate tor TB per 100.000 in that year?
(30 ÷ 150.000) x 100.000 = X
(30÷ 150.000) x 100 = X
(115 ÷ 150.000) x 100.000 - X
(115 ÷ 100.000) x 100 = X
The incidence rate is calculated using the formula:
 A white paper with black text
AI-generated content may be incorrect.
A white paper with black text
AI-generated content may be incorrect.
Why the Other Options Are Incorrect?
B. (30 ÷ 150,000) × 100 = X – Incorrect multiplier (should be 100,000 for standard incidence rate).
C. (115 ÷ 150,000) × 100,000 = X – 115 represents total cases (prevalence), not incidence.
D. (115 ÷ 100,000) × 100 = X – Uses the wrong denominator and multiplier.
CBIC Infection Control Reference
APIC defines the incidence rate as the number of new cases per population unit, typically per 100,000 people.
What is the correct order of steps for reprocessing critical medical equipment?
Clean, sterilize, disinfect
Disinfect, clean, sterilize
Disinfect, sterilize
Clean, sterilize
The correct answer is D, "Clean, sterilize," as this represents the correct order of steps for reprocessing critical medical equipment. According to the Certification Board of Infection Control and Epidemiology (CBIC) guidelines, critical medical equipment—items that enter sterile tissues or the vascular system (e.g., surgical instruments, implants)—must undergo a rigorous reprocessing cycle to ensure they are free of all microorganisms, including spores. The process begins with cleaning to remove organic material, debris, and soil, which is essential to allow subsequent sterilization to be effective. Sterilization, the final step, uses methods such as steam, ethylene oxide, or hydrogen peroxide gas to achieve a sterility assurance level (SAL) of 10⁻⁶, eliminating all microbial life (CBIC Practice Analysis, 2022, Domain III: Infection Prevention and Control, Competency 3.3 - Ensure safe reprocessing of medical equipment). Disinfection, while important for semi-critical devices, is not a step in the reprocessing of critical items, as it does not achieve the sterility required; it is a separate process for non-critical or semi-critical equipment.
Option A (clean, sterilize, disinfect) is incorrect because disinfecting after sterilization is unnecessary and redundant, as sterilization already achieves a higher level of microbial kill. Option B (disinfect, clean, sterilize) reverses the logical sequence; cleaning must precede any disinfection or sterilization to remove bioburden, and disinfection is not appropriate for critical items. Option C (disinfect, sterilize) omits cleaning and incorrectly prioritizes disinfection, which is insufficient for critical equipment requiring full sterility.
The focus on cleaning followed by sterilization aligns with CBIC’s emphasis on evidence-based reprocessing protocols to prevent healthcare-associated infections (HAIs), ensuring that critical equipment is safe for patient use (CBIC Practice Analysis, 2022, Domain III: Infection Prevention and Control, Competency 3.4 - Implement environmental cleaning and disinfection protocols). This sequence is supported by standards such as AAMI ST79, which outlines the mandatory cleaning step before sterilization to ensure efficacy and safety.
References: CBIC Practice Analysis, 2022, Domain III: Infection Prevention and Control, Competencies 3.3 - Ensure safe reprocessing of medical equipment, 3.4 - Implement environmental cleaning and disinfection protocols. AAMI ST79:2017, Comprehensive guide to steam sterilization and sterility assurance in health care facilities.
Which of the following is included in an effective respiratory hygiene program in healthcare facilities?
Community educational brochures campaign
Mask availability at building entrance and reception
Separate entrance for symptomatic patients and visitors
Temperature monitoring devices at clinical unit entrance
An effective respiratory hygiene program in healthcare facilities aims to reduce the transmission of respiratory pathogens, such as influenza, COVID-19, and other droplet- or airborne infectious agents, by promoting practices that minimize the spread from infected individuals. The Certification Board of Infection Control and Epidemiology (CBIC) emphasizes the importance of such programs within the "Prevention and Control of Infectious Diseases" domain, aligning with guidelines from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). The CDC’s "Guideline for Isolation Precautions" (2007) and its respiratory hygiene/cough etiquette recommendations outline key components, including source control, education, and environmental measures to protect patients, visitors, and healthcare workers.
Option B, "Mask availability at building entrance and reception," is a core element of an effective respiratory hygiene program. Providing masks at entry points ensures that symptomatic individuals can cover their mouth and nose, reducing the dispersal of respiratory droplets. This practice, often referred to as source control, is a primary strategy to interrupt transmission, especially in high-traffic areas like entrances and receptions. The CDC recommends that healthcare facilities offer masks or tissues and no-touch receptacles for disposal as part of respiratory hygiene, making this a practical and essential inclusion.
Option A, "Community educational brochures campaign," is a valuable adjunct to raise awareness among the public about respiratory hygiene (e.g., covering coughs, hand washing). However, it is an external strategy rather than a direct component of the facility’s internal program, which focuses on immediate action within the healthcare setting. Option C, "Separate entrance for symptomatic patients and visitors," can enhance infection control by segregating potentially infectious individuals, but it is not a universal requirement and depends on facility resources and design. The CDC suggests this as an optional measure during outbreaks, not a standard element of every respiratory hygiene program. Option D, "Temperature monitoring devices at clinical unit entrance," is a useful screening tool to identify febrile individuals, which may indicate infection. However, it is a surveillance measure rather than a core hygiene practice, and its effectiveness is limited without accompanying interventions like masking.
The CBIC Practice Analysis (2022) and CDC guidelines prioritize actionable, facility-based interventions like mask provision to mitigate transmission risks. The availability of masks at key entry points directly supports the goal of respiratory hygiene by enabling immediate source control, making Option B the most appropriate answer.
References:
CBIC Practice Analysis, 2022.
CDC Guideline for Isolation Precautions: Preventing Transmission of Infectious Agents in Healthcare Settings, 2007.
What question would be appropriate for an infection preventionist to ask when reviewing the discussion section of an original article?
Was the correct sample size and analysis method chosen?
Could alternative explanations account for the observed results?
Is the study question important, appropriate, and stated clearly?
Are criteria used to measure the exposure and the outcome explicit?
When reviewing the discussion section of an original article, an infection preventionist must focus on critically evaluating the interpretation of the study findings, their relevance to infection control, and their implications for practice. The discussion section typically addresses the meaning of the results, compares them to existing literature, and considers limitations or alternative interpretations. The appropriate question should align with the purpose of this section and reflect the infection preventionist's need to assess the validity and applicability of the research. Let’s analyze each option:
A. Was the correct sample size and analysis method chosen?: This question pertains to the methodology section of a research article, where the study design, sample size, and statistical methods are detailed. While these elements are critical for assessing the study's rigor, they are not the primary focus of the discussion section, which interprets results rather than re-evaluating the study design. An infection preventionist might ask this during a review of the methods section, but it is less relevant here.
B. Could alternative explanations account for the observed results?: The discussion section often explores whether the findings can be explained by factors other than the hypothesized cause, such as confounding variables, bias, or chance. This question is highly appropriate for an infection preventionist, as it encourages a critical assessment of whether the results truly support infection control interventions or if other factors (e.g., environmental conditions, patient factors) might be responsible. This aligns with CBIC's emphasis on evidence-based practice, where understanding the robustness of conclusions is key to applying research to infection prevention strategies.
C. Is the study question important, appropriate, and stated clearly?: This question relates to the introduction or background section of an article, where the research question and its significance are established. While important for overall study evaluation, it is not specific to the discussion section, which focuses on interpreting results rather than revisiting the initial question. An infection preventionist might consider this earlier in the review process, but it does not fit the context of the discussion section.
D. Are criteria used to measure the exposure and the outcome explicit?: This question is relevant to the methods section, where the definitions and measurement tools for exposures (e.g., a specific intervention) and outcomes (e.g., infection rates) are described. The discussion section may reference these criteria but focuses more on their implications rather than their clarity. This makes it less appropriate for the discussion section specifically.
The discussion section is where authors synthesize their findings, address limitations, and consider alternative explanations, making option B the most fitting. For an infection preventionist, evaluating alternative explanations is crucial to ensure that recommended practices (e.g., hand hygiene protocols or sterilization techniques) are based on solid evidence and not confounded by unaddressed variables. This critical thinking is consistent with CBIC's focus on applying research to improve infection control outcomes.
References:
CBIC Infection Prevention and Control (IPC) Core Competency Model (updated 2023), Domain I: Identification of Infectious Disease Processes, which emphasizes critical evaluation of research evidence.
CBIC Examination Content Outline, Domain V: Management and Communication, which includes assessing the validity of research findings for infection control decision-making.
Which of the following activities will BEST prepare a newly hired infection preventionist to present information at the facility’s orientation program?
Observing other departments’ orientation presentations
Meeting with the facility’s leadership
Reviewing principles of adult learning
Administering tuberculin skin tests to orientees
The correct answer is C, "Reviewing principles of adult learning," as this activity will best prepare a newly hired infection preventionist to present information at the facility’s orientation program. According to the Certification Board of Infection Control and Epidemiology (CBIC) guidelines, effective education delivery, especially for healthcare professionals during orientation, relies on understanding adult learning principles (e.g., andragogy), which emphasize learner-centered approaches, relevance to practice, and active participation. Reviewing these principles equips the infection preventionist (IP) to design and deliver content that addresses the specific needs, experiences, and motivations of the audience—such as new staff learning infection control protocols—enhancing engagement and retention (CBIC Practice Analysis, 2022, Domain IV: Education and Research, Competency 4.1 - Develop and implement educational programs). This preparation ensures the presentation is tailored, impactful, and aligned with the goal of promoting infection prevention behaviors.
Option A (observing other departments’ orientation presentations) can provide insights into presentation styles or facility norms, but it is less focused on the IP’s specific educational role and may not address the unique content of infection prevention. Option B (meeting with the facility’s leadership) is valuable for understanding organizational priorities and gaining support, but it is more about collaboration and context-setting rather than direct preparation for presenting educational material. Option D (administering tuberculin skin tests to orientees) is a clinical task related to TB screening, not a preparatory activity for designing or delivering an educational presentation.
The focus on reviewing adult learning principles aligns with CBIC’s emphasis on evidence-based education strategies to improve infection control practices among healthcare personnel (CBIC Practice Analysis, 2022, Domain IV: Education and Research, Competency 4.2 - Evaluate the effectiveness of educational programs). This approach enables the IP to effectively communicate critical information, such as hand hygiene or isolation protocols, during the orientation program.
References: CBIC Practice Analysis, 2022, Domain IV: Education and Research, Competencies 4.1 - Develop and implement educational programs, 4.2 - Evaluate the effectiveness of educational programs.
During an outbreak of ventilator-associated pneumonia (VAP), the infection preventionist should FIRST:
Review adherence to ventilator bundle elements.
Implement preemptive antibiotic therapy in all ventilated patients.
Isolate all ventilated patients in negative pressure rooms.
Perform bacterial cultures from ventilator circuits.
Reviewing compliance with VAP prevention bundles (e.g., head-of-bed elevation, oral care, sedation breaks) is the first step in outbreak control.
Preemptive antibiotics (B) are not recommended due to antibiotic resistance risks.
Negative pressure rooms (C) are not required for VAP.
Ventilator circuit cultures (D) do not guide patient management.
CBIC Infection Control References:
APIC Text, "VAP Prevention Measures," Chapter 11.
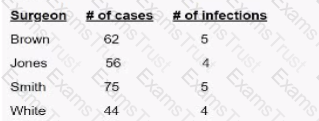
Surgical site infection (SSI) data for the previous quarter reveal the following numbers. The surgeon with the highest infection rate is Doctor
Brown
Jones.
Smith
White
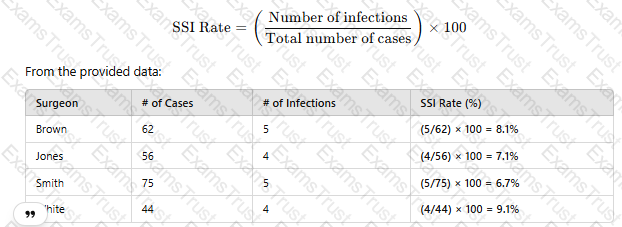
To determine which surgeon has the highest surgical site infection (SSI) rate, use the following formula:
 A screenshot of a report
AI-generated content may be incorrect.
A screenshot of a report
AI-generated content may be incorrect.
Since Dr. White has the highest SSI rate at 9.1%, the correct answer is D. White.
CBIC Infection Control Reference
SSI rates are calculated using infection count per total procedures and reported as percentage values.
Following an outbreak of Hepatitis A, the water supply is sampled. A high count of which of the following isolates would indicate that the water was a potential source?
Coliforms
Pseudomonads
Legionella
Acinetobacter
Coliform bacteria are indicators of fecal contamination in water, making them a critical measure of water safety. Hepatitis A is a virus primarily transmitted via the fecal-oral route, often through contaminated food or water.
Step-by-Step Justification:
Fecal Contamination and Hepatitis A:
Hepatitis A virus (HAV) spreads through ingestion of water contaminated with fecal matter. High coliform counts indicate fecal contamination and increase the risk of HAV outbreaks.
Use of Coliforms as Indicators:
Public health agencies use total coliforms and Escherichia coli (E. coli) as primary indicators of water safety because they signal fecal pollution.
Waterborne Transmission of Hepatitis A:
Hepatitis A outbreaks have been traced to contaminated drinking water, ice, and improperly treated wastewater. Coliform detection signals a need for immediate action.
Why Other Options Are Incorrect:
B. Pseudomonads:
Pseudomonads (e.g., Pseudomonas aeruginosa) are environmental bacteria but are not indicators of fecal contamination.
C. Legionella:
Legionella species cause Legionnaires' disease through inhalation of contaminated aerosols, not through fecal-oral transmission.
D. Acinetobacter:
Acinetobacter species are opportunistic pathogens in healthcare settings but are not indicators of waterborne fecal contamination.
CBIC Infection Control References:
APIC Text, "Water Systems and Infection Control Measures".
APIC Text, "Hepatitis A Transmission and Waterborne Outbreaks".
Which of the following operating suite design features is LEAST important for the prevention of infection?
Type of floor material
Positive pressure air handling
Placement of sinks for surgical scrubs
Control of traffic and traffic flow patterns
The correct answer is A, "Type of floor material," as it is the least important operating suite design feature for the prevention of infection compared to the other options. According to the Certification Board of Infection Control and Epidemiology (CBIC) guidelines, the design of operating suites plays a critical role in infection prevention, particularly for surgical site infections (SSIs). While the type of floor material (e.g., vinyl, tile, or epoxy) can affect ease of cleaning and durability, its impact on infection prevention is secondary to other design elements that directly influence air quality, hygiene practices, and personnel movement (CBIC Practice Analysis, 2022, Domain III: Infection Prevention and Control, Competency 3.5 - Evaluate the environment for infection risks). Modern flooring materials are generally designed to be non-porous and easily disinfected, mitigating their role as a primary infection risk factor when proper cleaning protocols are followed.
Option B (positive pressure air handling) is highly important because it prevents the influx of contaminated air into the operating suite, reducing the risk of airborne pathogens, including those causing SSIs. This is a standard feature in operating rooms to maintain a sterile environment (AORN Guidelines for Perioperative Practice, 2023). Option C (placement of sinks for surgical scrubs) is critical for ensuring that surgical staff can perform effective hand and forearm antisepsis, a key step in preventing SSIs by reducing microbial load before surgery. Option D (control of traffic and traffic flow patterns) is essential to minimize the introduction of contaminants from outside the operating suite, as excessive or uncontrolled movement can increase the risk of airborne and contact transmission (CDC Guidelines for Environmental Infection Control in Healthcare Facilities, 2019).
The relative unimportance of floor material type stems from the fact that infection prevention relies more on consistent cleaning practices and the aforementioned design features, which directly address pathogen transmission routes. This aligns with CBIC’s focus on evaluating environmental risks based on their direct impact on infection control (CBIC Practice Analysis, 2022, Domain III: Infection Prevention and Control, Competency 3.4 - Implement environmental cleaning and disinfection protocols).
References: CBIC Practice Analysis, 2022, Domain III: Infection Prevention and Control, Competencies 3.4 - Implement environmental cleaning and disinfection protocols, 3.5 - Evaluate the environment for infection risks. AORN Guidelines for Perioperative Practice, 2023. CDC Guidelines for Environmental Infection Control in Healthcare Facilities, 2019.
Which of the following infectious diseases is associated with environmental fungi?
Listeriosis
Hantavirus
Mucormycosis
Campylobacter
The correct answer is C, "Mucormycosis," as it is the infectious disease associated with environmental fungi. According to the Certification Board of Infection Control and Epidemiology (CBIC) guidelines, mucormycosis is caused by fungi belonging to the order Mucorales, which are commonly found in the environment, including soil, decaying organic matter, and contaminated water. These fungi can become opportunistic pathogens, particularly in immunocompromised individuals, leading to severe infections such as rhinocerebral, pulmonary, or cutaneous mucormycosis (CBIC Practice Analysis, 2022, Domain I: Identification of Infectious Disease Processes, Competency 1.1 - Identify infectious disease processes). Environmental exposure, such as inhalation of fungal spores or contact with contaminated materials, is a primary mode of transmission, making it directly linked to environmental fungi.
Option A (Listeriosis) is caused by the bacterium Listeria monocytogenes, typically associated with contaminated food products (e.g., unpasteurized dairy or deli meats) rather than environmental fungi. Option B (Hantavirus) is a viral infection transmitted through contact with rodent excreta, not fungi, and is linked to environmental reservoirs like rodent-infested areas. Option D (Campylobacter) is a bacterial infection caused by Campylobacter species, often associated with undercooked poultry or contaminated water, and is not related to fungi.
The association of mucormycosis with environmental fungi underscores the importance of infection prevention strategies, such as controlling environmental contamination and protecting vulnerable patients, which aligns with CBIC’s focus on identifying and mitigating risks from infectious agents in healthcare settings (CBIC Practice Analysis, 2022, Domain III: Infection Prevention and Control, Competency 3.2 - Implement measures to prevent transmission of infectious agents). This knowledge is critical for infection preventionists to guide environmental cleaning and patient care protocols.
References: CBIC Practice Analysis, 2022, Domain I: Identification of Infectious Disease Processes, Competency 1.1 - Identify infectious disease processes; Domain III: Infection Prevention and Control, Competency 3.2 - Implement measures to prevent transmission of infectious agents.
Which of the following BEST demonstrates the effectiveness of a program targeted at reducing central-line associated bloodstream infections (CLABSIs) in an intensive care unit (ICU)?
A 25% decrease in the length of stay in the ICU related to CLABSIs
A 25% reduction in the incidence of CLABSIs over 6 months
A 30% decrease in total costs related to treatment of CLABSIs over 12 months
A 30% reduction in the use of antibiotic-impregnated central catheters over 6 months
Evaluating the effectiveness of a program to reduce central-line associated bloodstream infections (CLABSIs) in an intensive care unit (ICU) requires identifying the most direct and relevant measure of success. The Certification Board of Infection Control and Epidemiology (CBIC) emphasizes outcome-based assessment in the "Performance Improvement" and "Surveillance and Epidemiologic Investigation" domains, aligning with the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) guidelines for infection prevention. The primary goal of a CLABSI reduction program is to decrease the occurrence of these infections, with secondary benefits including reduced length of stay, costs, and resource use.
Option B, "A 25% reduction in the incidence of CLABSIs over 6 months," is the best demonstration of effectiveness. The incidence of CLABSIs—defined by the CDC as the number of infections per 1,000 central line days—directly measures the program’s impact on the targeted outcome: preventing bloodstream infections associated with central lines. A 25% reduction over 6 months indicates a sustained decrease in infection rates, providing clear evidence that the intervention (e.g., improved insertion techniques, maintenance bundles, or staff education) is working. The CDC’s "Guidelines for the Prevention of Intravascular Catheter-Related Infections" (2017) and the National Healthcare Safety Network (NHSN) protocols prioritize infection rate reduction as the primary metric for assessing CLABSI prevention programs.
Option A, "A 25% decrease in the length of stay in the ICU related to CLABSIs," is a secondary benefit. Reducing CLABSI-related length of stay can improve patient outcomes and bed availability, but it is an indirect measure dependent on infection incidence. A decrease in length of stay could also reflect other factors (e.g., improved discharge planning), making it less specific to program effectiveness. Option C, "A 30% decrease in total costs related to treatment of CLABSIs over 12 months," reflects a financial outcome, which is valuable for justifying resource allocation. However, cost reduction is a downstream effect of decreased infections and may be influenced by variables like hospital pricing or treatment protocols, diluting its direct link to program success. Option D, "A 30% reduction in the use of antibiotic-impregnated central catheters over 6 months," indicates a change in practice but not necessarily effectiveness. Antibiotic-impregnated catheters are one prevention strategy, and reducing their use could suggest improved standard practices (e.g., chlorhexidine bathing), but it could also increase infection rates if not offset by other measures, making it an ambiguous indicator.
The CBIC Practice Analysis (2022) and CDC guidelines emphasize that the primary measure of a CLABSI prevention program’s success is a reduction in infection incidence, as it directly addresses patient safety and the program’s core objective. Option B provides the most robust and specific evidence of effectiveness over a defined timeframe.
References:
CBIC Practice Analysis, 2022.
CDC Guidelines for the Prevention of Intravascular Catheter-Related Infections, 2017.
NHSN CLABSI Surveillance Protocol, 2021.
Essential knowledge, behaviors, and skills that an individual should possess and demonstrate to practice in a specific discipline defines which of the following?
Certification
Competence
Knowledge
Training
The correct answer is B, "Competence," as it defines the essential knowledge, behaviors, and skills that an individual should possess and demonstrate to practice in a specific discipline. According to the Certification Board of Infection Control and Epidemiology (CBIC) guidelines, competence encompasses the integrated application of knowledge, skills, and behaviors required to perform effectively in a professional role, such as infection prevention and control. Competence goes beyond mere knowledge or training by including the ability to apply these attributes in real-world scenarios, ensuring safe and effective practice (CBIC Practice Analysis, 2022, Domain IV: Education and Research, Competency 4.3 - Assess competence of healthcare personnel). This holistic definition is critical in healthcare settings, where demonstrated competence—through actions like proper hand hygiene or outbreak management—directly impacts patient safety and infection prevention outcomes.
Option A (certification) refers to a formal recognition or credential (e.g., CIC certification) that validates an individual’s qualifications, but it is an outcome or process rather than the definition of the underlying abilities. Option C (knowledge) represents the theoretical understanding or factual basis of a discipline, which is a component of competence but not the full scope that includes behaviors and skills. Option D (training) involves the education or instruction provided to develop skills and knowledge, serving as a means to achieve competence rather than defining it.
The focus on competence aligns with CBIC’s emphasis on ensuring that healthcare personnel are equipped to meet the demands of infection prevention through a combination of education, practice, and evaluation (CBIC Practice Analysis, 2022, Domain IV: Education and Research, Competency 4.2 - Evaluate the effectiveness of educational programs). This definition supports the development of professionals who can adapt and perform effectively in dynamic healthcare environments.
References: CBIC Practice Analysis, 2022, Domain IV: Education and Research, Competencies 4.2 - Evaluate the effectiveness of educational programs, 4.3 - Assess competence of healthcare personnel.
Which of the following is the BEST strategy for reducing bloodstream infections associated with central venous catheters?
Routine replacement of central lines every 7 days.
Use of chlorhexidine-impregnated dressings.
Daily blood cultures for patients with central lines.
Use of povidone-iodine instead of chlorhexidine for skin antisepsis.
Chlorhexidine-impregnated dressings reduce central line-associated bloodstream infections (CLABSI) by preventing bacterial colonization.
Routine catheter replacement (A) increases insertion risks without reducing infections.
Daily blood cultures (C) are unnecessary and lead to false positives.
Povidone-iodine (D) is less effective than chlorhexidine for skin antisepsis.
CBIC Infection Control References:
APIC Text, "CLABSI Prevention Measures," Chapter 10.
To understand how their hospital-acquired infection rates compare to other health care settings, an infection preventionist (IP) plans to use benchmarking.
Which of the following criteria is important to ensure accurate benchmarking of surveillance data?
Data collectors are trained on how to collect data
Collecting data on a small population lo ensure accuracy of data collection
Denominator rates are selected based on an organizational risk assessment
Using case definitions that are adjusted for the patient population being studied
Benchmarking compares infection rates across healthcare facilities. For accurate benchmarking, case definitions must be standardized and adjusted for patient demographics, severity of illness, and other risk factors.
Why the Other Options Are Incorrect?
A. Data collectors are trained on how to collect data – Training is necessary, but it does not directly ensure comparability between facilities.
B. Collecting data on a small population – A larger sample size increases accuracy and reliability in benchmarking.
C. Denominator rates selected based on an organizational risk assessment – Risk assessment is important, but standardized case definitions are critical for comparison.
CBIC Infection Control Reference
According to APIC, accurate benchmarking relies on using standardized case definitions that account for differences in patient populations.
Which of the following represents a class II surgical wound?
Incisions in which acute, nonpurulent inflammation are seen.
Incisional wounds following nonpenetrating (blunt) trauma.
Incisions involving the biliary tract, appendix, vagina, and oropharynx.
Old traumatic wounds with retained devitalized tissue.
Surgical wounds are classified by the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) into four classes based on the degree of contamination and the likelihood of postoperative infection. This classification system, detailed in the CDC’s Guidelines for Prevention of Surgical Site Infections (1999), is a cornerstone of infection prevention and control, aligning with the Certification Board of Infection Control and Epidemiology (CBIC) standards in the "Prevention and Control of Infectious Diseases" domain. The classes are as follows:
Class I (Clean): Uninfected operative wounds with no inflammation, typically closed primarily, and not involving the respiratory, alimentary, genital, or urinary tracts.
Class II (Clean-Contaminated): Operative wounds with controlled entry into a sterile or minimally contaminated tract (e.g., biliary or gastrointestinal), with no significant spillage or infection present.
Class III (Contaminated): Open, fresh wounds with significant spillage (e.g., from a perforated viscus) or major breaks in sterile technique.
Class IV (Dirty-Infected): Old traumatic wounds with retained devitalized tissue or existing clinical infection.
Option A, "Incisions in which acute, nonpurulent inflammation are seen," aligns with a Class II surgical wound. The presence of acute, nonpurulent inflammation suggests a controlled inflammatory response without overt infection, which can occur in clean-contaminated cases where a sterile tract (e.g., during elective gastrointestinal surgery) is entered under controlled conditions. The CDC defines Class II wounds as those involving minor contamination without significant spillage or infection, and nonpurulent inflammation fits this category, often seen in early postoperative monitoring.
Option B, "Incisional wounds following nonpenetrating (blunt) trauma," does not fit the Class II definition. These wounds are typically classified based on the trauma context and are more likely to be considered contaminated (Class III) or dirty (Class IV) if there is tissue damage or delayed treatment, rather than clean-contaminated. Option C, "Incisions involving the biliary tract, appendix, vagina, and oropharynx," describes anatomical sites that, when surgically accessed, often fall into Class II if the procedure is elective and controlled (e.g., cholecystectomy), but the phrasing suggests a general category rather than a specific wound state with inflammation, making it less precise for Class II. Option D, "Old traumatic wounds with retained devitalized tissue," clearly corresponds to Class IV (dirty-infected) due to the presence of necrotic tissue and potential existing infection, which is inconsistent with Class II.
The CBIC Practice Analysis (2022) emphasizes the importance of accurate wound classification for implementing appropriate infection prevention measures, such as antibiotic prophylaxis or sterile technique adjustments. The CDC guidelines further specify that Class II wounds may require tailored interventions based on the observed inflammatory response, supporting Option A as the correct answer. Note that the phrasing in Option A contains a minor grammatical error ("inflammation are seen" should be "inflammation is seen"), but this does not alter the clinical intent or classification.
References:
CBIC Practice Analysis, 2022.
CDC Guidelines for Prevention of Surgical Site Infections, 1999.
A patient has a draining sinus at the site of a left total hip arthroplasty. A culture from the sinus tract reveals four organisms. Which of the following specimens is optimal for identifying the eliologic agent?
Blood
Wound drainage
Joint aspirate
Sinus tract tissue
The optimal specimen for identifying the etiologic agent in a prosthetic joint infection (PJI) is a joint aspirate (synovial fluid). This is because:
It provides direct access to the infected site without contamination from external sources.
It allows for accurate microbiologic culture, Gram stain, and leukocyte count analysis.
Why the Other Options Are Incorrect?
A. Blood – Blood cultures may help detect hematogenous spread but are not the best sample for identifying localized prosthetic joint infections.
B. Wound drainage – Wound cultures often contain contaminants from surrounding skin flora and do not accurately reflect joint space infection.
D. Sinus tract tissue – Cultures from sinus tracts often represent colonization rather than the primary infecting organism.
CBIC Infection Control Reference
APIC guidelines confirm that joint aspirate is the most reliable specimen for diagnosing prosthetic joint infections.
The infection preventionist (IP) collaborates with the Intravenous Therapy team to select the best antiseptic for use during the insertion of an intravascular device for adults. For a patient with no contraindications, what antiseptic should the IP suggest?
Chlorhexidine
Povidone-iodine
Alcohol
Antibiotic ointment
The selection of an appropriate antiseptic for the insertion of an intravascular device (e.g., peripheral or central venous catheters) is a critical infection prevention measure to reduce the risk of catheter-related bloodstream infections (CRBSIs). The Certification Board of Infection Control and Epidemiology (CBIC) emphasizes evidence-based practices in the "Prevention and Control of Infectious Diseases" domain, which includes adhering to guidelines for aseptic technique during invasive procedures. The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) provides specific recommendations for skin antisepsis, as outlined in the "Guidelines for the Prevention of Intravascular Catheter-Related Infections" (2017).
Option A, chlorhexidine, is the preferred antiseptic for skin preparation prior to intravascular device insertion in adults with no contraindications. Chlorhexidine, particularly in a 2% chlorhexidine gluconate (CHG) with 70% isopropyl alcohol solution, is recommended by the CDC due to its broad-spectrum antimicrobial activity, residual effect (which continues to kill bacteria after application), and superior efficacy compared to other agents in reducing CRBSI rates. Studies cited in the CDC guidelines demonstrate that chlorhexidine-based preparations significantly lower infection rates compared to povidone-iodine or alcohol alone, making it the gold standard for this procedure when tolerated by the patient.
Option B, povidone-iodine, is an alternative antiseptic that can be used for skin preparation. It is effective against a wide range of microorganisms and is often used when chlorhexidine is contraindicated (e.g., in patients with chlorhexidine allergy). However, its efficacy is less persistent than chlorhexidine, and it requires longer drying time, which can be a limitation in busy clinical settings. The CDC considers povidone-iodine a second-line option unless chlorhexidine is unavailable or unsuitable. Option C, alcohol (e.g., 70% isopropyl or ethyl alcohol), has rapid bactericidal activity but lacks a residual effect, making it less effective for prolonged protection during catheter dwell time. It is often used as a component of chlorhexidine-alcohol combinations but is not recommended as a standalone antiseptic for intravascular device insertion. Option D, antibiotic ointment, is not appropriate for skin preparation during insertion. Antibiotic ointments (e.g., bacitracin or mupirocin) are sometimes applied to catheter sites post-insertion to prevent infection, but their use is discouraged by the CDC due to the risk of promoting antibiotic resistance and fungal infections, and they are not classified as antiseptics for initial skin antisepsis.
The CBIC Practice Analysis (2022) supports the adoption of CDC-recommended practices, and the 2017 CDC guidelines explicitly state that chlorhexidine-based preparations with alcohol should be used for skin antisepsis unless contraindicated. For a patient with no contraindications, the infection preventionist should suggest chlorhexidine to optimize patient safety and align with best practices.
References:
CBIC Practice Analysis, 2022.
CDC Guidelines for the Prevention of Intravascular Catheter-Related Infections, 2017.
Which of the following procedures has NOT been documented to contribute to the development of postoperative infections in clean surgical operations?
Prolonged preoperative hospital stay
Prolonged length of the operations
The use of iodophors for preoperative scrubs
Shaving the site on the day prior to surgery
Postoperative infections in clean surgical operations, defined by the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) as uninfected operative wounds with no inflammation and no entry into sterile tracts (e.g., gastrointestinal or respiratory systems), are influenced by various perioperative factors. The Certification Board of Infection Control and Epidemiology (CBIC) emphasizes identifying and mitigating risk factors in the "Prevention and Control of Infectious Diseases" domain, aligning with CDC guidelines for surgical site infection (SSI) prevention. The question focuses on identifying a procedure not documented as a contributor to SSIs, requiring an evaluation of evidence-based risk factors.
Option C, "The use of iodophors for preoperative scrubs," has not been documented to contribute to the development of postoperative infections in clean surgical operations. Iodophors, such as povidone-iodine, are antiseptic agents used for preoperative skin preparation and surgical hand scrubs. The CDC’s "Guideline for Prevention of Surgical Site Infections" (1999) and its 2017 update endorse iodophors as an effective method for reducing microbial load on the skin, with no evidence suggesting they increase SSI risk when used appropriately. Studies, including those cited by the CDC, show that iodophors are comparable to chlorhexidine in efficacy for preoperative antisepsis, and their use is a standard, safe practice rather than a risk factor.
Option A, "Prolonged preoperative hospital stay," is a well-documented risk factor. Extended hospital stays prior to surgery increase exposure to healthcare-associated pathogens, raising the likelihood of colonization and subsequent SSI, as noted in CDC and surgical literature (e.g., Mangram et al., 1999). Option B, "Prolonged length of the operations," is also a recognized contributor. Longer surgical durations are associated with increased exposure time, potential breaches in sterile technique, and higher infection rates, supported by CDC data showing a correlation between operative time and SSI risk. Option D, "Shaving the site on the day prior to surgery," has been documented as a risk factor. Preoperative shaving, especially with razors, can cause microabrasions that serve as entry points for bacteria, increasing SSI rates. The CDC recommends avoiding shaving or using clippers immediately before surgery to minimize this risk, with evidence from studies like those in the 1999 guideline showing higher infection rates with preoperative shaving.
The CBIC Practice Analysis (2022) and CDC guidelines focus on evidence-based practices, and the lack of documentation linking iodophor use to increased SSIs—coupled with its role as a preventive measure—makes Option C the correct answer. The other options are supported by extensive research as contributors to SSI development in clean surgeries.
References:
CBIC Practice Analysis, 2022.
CDC Guideline for Prevention of Surgical Site Infections, 1999, updated 2017.
Mangram, A. J., et al. (1999). Guideline for Prevention of Surgical Site Infection. Infection Control and Hospital Epidemiology.
Which of the following processes is essential for endoscope reprocessing?
Intermediate level disinfection and contact time
Pre-cleaning, leak testing, and manual cleaning
Inspection using a borescope and horizontal storage
Leak testing, manual cleaning, and low level disinfection
The correct answer is B, "Pre-cleaning, leak testing, and manual cleaning," as these processes are essential for endoscope reprocessing. According to the Certification Board of Infection Control and Epidemiology (CBIC) guidelines, proper reprocessing of endoscopes is critical to prevent healthcare-associated infections (HAIs), given their complex design and susceptibility to microbial contamination. The initial steps of pre-cleaning (removing gross debris at the point of use), leak testing (ensuring the endoscope’s integrity to prevent fluid ingress), and manual cleaning (using enzymatic detergents to remove organic material) are foundational to the reprocessing cycle. These steps prepare the endoscope for high-level disinfection or sterilization by reducing bioburden and preventing damage, as outlined in standards such as AAMI ST91 (CBIC Practice Analysis, 2022, Domain III: Infection Prevention and Control, Competency 3.3 - Ensure safe reprocessing of medical equipment). Failure at this stage can compromise subsequent disinfection, making it a non-negotiable component of the process.
Option A (intermediate level disinfection and contact time) is an important step but insufficient alone, as intermediate-level disinfection does not achieve the high-level disinfection required for semi-critical devices like endoscopes, which must eliminate all microorganisms except high levels of bacterial spores. Option C (inspection using a borescope and horizontal storage) includes valuable quality control (inspection) and storage practices, but these occur later in the process and are not essential initial steps; vertical storage is often preferred to prevent damage. Option D (leak testing, manual cleaning, and low level disinfection) includes two essential steps (leak testing and manual cleaning) but is inadequate because low-level disinfection does not meet the standard for endoscopes, which require high-level disinfection or sterilization.
The emphasis on pre-cleaning, leak testing, and manual cleaning aligns with CBIC’s focus on adhering to evidence-based reprocessing protocols to ensure patient safety and prevent HAIs (CBIC Practice Analysis, 2022, Domain III: Infection Prevention and Control, Competency 3.4 - Implement environmental cleaning and disinfection protocols). These steps are mandated by guidelines to mitigate risks associated with endoscope use in healthcare settings.
References: CBIC Practice Analysis, 2022, Domain III: Infection Prevention and Control, Competencies 3.3 - Ensure safe reprocessing of medical equipment, 3.4 - Implement environmental cleaning and disinfection protocols. AAMI ST91:2015, Flexible and semi-rigid endoscope processing in health care facilities.
In a retrospective case-control study, the initial case group is composed of persons
with the disease
without the disease.
with the risk factor under investigation
without the risk factor under investigation
In a retrospective case-control study, cases and controls are selected based on disease status. The case group is composed of individuals who have the disease (cases), while the control group consists of individuals without the disease. This design allows researchers to look back in time to assess exposure to potential risk factors.
Step-by-Step Justification:
Selection of Cases and Controls:
Cases: Individuals who already have the disease.
Controls: Individuals without the disease but similar in other aspects.
Direction of Study:
A retrospective study moves backward from the disease outcome to investigate potential causes or risk factors.
Data Collection:
Uses past medical records, interviews, and laboratory results to determine past exposures.
Common Use:
Useful for studying rare diseases since cases have already occurred, making it cost-effective compared to cohort studies.
Why Other Options Are Incorrect:
B. without the disease: (Incorrect) This describes the control group, not the case group.
C. with the risk factor under investigation: (Incorrect) Risk factors are identified after selecting cases and controls.
D. without the risk factor under investigation: (Incorrect) The study investigates whether cases had prior exposure, not whether they lacked a risk factor.
CBIC Infection Control References:
APIC Text, Chapter on Epidemiologic Study Design.
A patient with suspected active tuberculosis is being transferred from a mental health facility to a medical center by emergency medical services. Which of the following should an infection preventionist recommend to the emergency medical technician (EMT)?
Place a surgical mask on both the patient and the EMT.
Place an N95 respirator on both the patient and the EMT.
Place an N95 respirator on the patient and a surgical mask on the EMT.
Place a surgical mask on the patient and an N95 respirator on the EMT.
Active tuberculosis (TB) is an airborne disease transmitted through the inhalation of droplet nuclei containing Mycobacterium tuberculosis. Effective infection control measures are critical during patient transport to protect healthcare workers, such as emergency medical technicians (EMTs), and to prevent community spread. The Certification Board of Infection Control and Epidemiology (CBIC) emphasizes the use of appropriate personal protective equipment (PPE) and source control as key strategies in the "Prevention and Control of Infectious Diseases" domain, aligning with guidelines from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC).
For a patient with suspected active TB, the primary goal is to contain the infectious particles at the source (the patient) while ensuring the EMT is protected from inhalation exposure. Option C, placing an N95 respirator on the patient and a surgical mask on the EMT, is the most appropriate recommendation. The N95 respirator on the patient serves as source control by filtering the exhaled air, reducing the dispersion of infectious droplets. However, fitting an N95 respirator on the patient may be challenging, especially in an emergency setting or if the patient is uncooperative, so a surgical mask is often used as an alternative source control measure. For the EMT, a surgical mask provides a basic barrier but does not offer the same level of respiratory protection as an N95 respirator. The CDC recommends that healthcare workers, including EMTs, use an N95 respirator (or higher-level respiratory protection) when in close contact with a patient with suspected or confirmed active TB, unless an airborne infection isolation room is available, which is not feasible during transport.
Option A is incorrect because placing a surgical mask on both the patient and the EMT does not provide adequate respiratory protection for the EMT. Surgical masks are not designed to filter small airborne particles like those containing TB bacilli and do not meet the N95 standard required for airborne precautions. Option B is impractical and unnecessary, as placing an N95 respirator on both the patient and the EMT is overly restrictive and logistically challenging, especially for the patient during transport. Option D reverses the PPE roles, placing the surgical mask on the patient (insufficient for source control) and the N95 respirator on the EMT (appropriate for protection but misaligned with the need to control the patient’s exhalation). The CBIC and CDC guidelines prioritize source control on the patient and respiratory protection for the healthcare worker, making Option C the best fit.
This recommendation is consistent with the CBIC’s emphasis on implementing transmission-based precautions (CDC, 2005, Guideline for Preventing the Transmission of Mycobacterium tuberculosis in Healthcare Settings) and the use of PPE tailored to the mode of transmission, as outlined in the CBIC Practice Analysis (2022).
References:
CBIC Practice Analysis, 2022.
CDC Guideline for Preventing the Transmission of Mycobacterium tuberculosis in Healthcare Settings, 2005.
A team was created to determine what has contributed to the recent increase in catheter associated urinary tract infections (CAUTIs). What quality tool should the team use?
Gap analysis
Fishbone diagram
Plan, do, study, act (PDSA)
Failure mode and effect analysis (FMEA)
The correct answer is B, "Fishbone diagram," as this is the most appropriate quality tool for the team to use when determining what has contributed to the recent increase in catheter-associated urinary tract infections (CAUTIs). According to the Certification Board of Infection Control and Epidemiology (CBIC) guidelines, the fishbone diagram, also known as an Ishikawa or cause-and-effect diagram, is a structured tool used to identify and categorize potential causes of a problem. In this case, the team needs to explore the root causes of the CAUTI increase, which could include factors such as improper catheter insertion techniques, inadequate maintenance, staff training gaps, or environmental issues (CBIC Practice Analysis, 2022, Domain II: Surveillance and Epidemiologic Investigation, Competency 2.2 - Analyze surveillance data). The fishbone diagram organizes these causes into categories (e.g., people, process, equipment, environment), facilitating a comprehensive analysis and guiding further investigation or intervention.
Option A (gap analysis) is useful for comparing current performance against a desired standard or benchmark, but it is more suited for identifying deficiencies in existing processes rather than uncovering the specific causes of a recent increase. Option C (plan, do, study, act [PDSA]) is a cyclical quality improvement methodology for testing and implementing changes, which would be relevant after identifying causes and designing interventions, not as the initial tool for root cause analysis. Option D (failure mode and effect analysis [FMEA]) is a proactive risk assessment tool used to predict and mitigate potential failures in a process before they occur, making it less applicable to analyzing an existing increase in CAUTIs.
The use of a fishbone diagram aligns with CBIC’s emphasis on using data-driven tools to investigate and address healthcare-associated infections (HAIs) like CAUTIs, supporting the team’s goal of pinpointing contributory factors (CBIC Practice Analysis, 2022, Domain II: Surveillance and Epidemiologic Investigation, Competency 2.3 - Identify risk factors for healthcare-associated infections). This tool’s visual and collaborative nature also fosters team engagement, which is essential for effective problem-solving in infection prevention.
References: CBIC Practice Analysis, 2022, Domain II: Surveillance and Epidemiologic Investigation, Competencies 2.2 - Analyze surveillance data, 2.3 - Identify risk factors for healthcare-associated infections.
A nurse exposed to pertussis develops a mild cough 14 days later. What is the recommended action?
Continue working with a surgical mask.
Exclude from patient care until five days after starting antibiotics.
Initiate post-exposure prophylaxis only if symptoms worsen.
Conduct serologic testing before deciding on work restrictions.
The CDC recommends exclusion of healthcare workers with pertussis until completing at least five days of antibiotic therapy.
CBIC Infection Control References:
APIC-JCR Workbook, "Occupational Health Considerations," Chapter 10
An infection preventionist (IP) encounters a surgeon at the nurse’s station who loudly disagrees with the IP’s surgical site infection findings. The IP’s BEST response is to:
Report the surgeon to the chief of staff.
Calmly explain that the findings are credible.
Ask the surgeon to speak in a more private setting to review their concerns.
Ask the surgeon to change their tone and leave the nurses’ station if they refuse.
The scenario involves a conflict between an infection preventionist (IP) and a surgeon regarding surgical site infection (SSI) findings, occurring in a public setting (the nurse’s station). The IP’s response must align with professional communication standards, infection control priorities, and the principles of collaboration and conflict resolution as emphasized by the Certification Board of Infection Control and Epidemiology (CBIC). The “best” response should de-escalate the situation, maintain professionalism, and facilitate a constructive dialogue. Let’s evaluate each option:
A. Report the surgeon to the chief of staff: Reporting the surgeon to the chief of staff might be considered if the behavior escalates or violates policy (e.g., harassment or disruption), but it is an escalation that should be a last resort. This action does not address the immediate disagreement about the SSI findings or attempt to resolve the issue collaboratively. It could also strain professional relationships and is not the best initial response, as it bypasses direct communication.
B. Calmly explain that the findings are credible: Explaining the credibility of the findings is important and demonstrates the IP’s confidence in their work, which is based on evidence-based infection control practices. However, doing so in a public setting like the nurse’s station, especially with a loud disagreement, may not be effective. The surgeon may feel challenged or defensive, potentially worsening the situation. While this response has merit, it lacks consideration of the setting and the need for privacy to discuss sensitive data.
C. Ask the surgeon to speak in a more private setting to review their concerns: This response is the most appropriate as it addresses the immediate need to de-escalate the public confrontation and move the discussion to a private setting. It shows respect for the surgeon’s concerns, maintains professionalism, and allows the IP to review the SSI findings (e.g., data collection methods, definitions, or surveillance techniques) in a controlled environment. This aligns with CBIC’s emphasis on effective communication and collaboration with healthcare teams, as well as the need to protect patient confidentiality and maintain a professional atmosphere. It also provides an opportunity to educate the surgeon on the evidence behind the findings, which is a key IP role.
D. Ask the surgeon to change their tone and leave the nurses’ station if they refuse: Requesting a change in tone is reasonable given the loud disagreement, but demanding the surgeon leave if they refuse is confrontational and risks escalating the conflict. This approach could damage the working relationship and does not address the underlying disagreement about the SSI findings. While maintaining a respectful environment is important, this response prioritizes control over collaboration and is less constructive than seeking a private discussion.
The best response is C, as it promotes a professional, collaborative approach by moving the conversation to a private setting. This allows the IP to address the surgeon’s concerns, explain the SSI surveillance methodology (e.g., NHSN definitions or CBIC guidelines), and maintain a positive working relationship, which is critical for effective infection prevention programs. This strategy reflects CBIC’s focus on leadership, communication, and teamwork in healthcare settings.
References:
CBIC Infection Prevention and Control (IPC) Core Competency Model (updated 2023), Domain V: Management and Communication, which stresses effective interpersonal communication and conflict resolution.
CBIC Examination Content Outline, Domain V: Leadership and Program Management, which includes collaborating with healthcare personnel and addressing disagreements professionally.
CDC Guidelines for SSI Surveillance (2023), which emphasize the importance of clear communication of findings to healthcare teams.
An infection preventionist should collaborate with a public health agency in primary prevention efforts by:
Conducting outbreak investigations.
Performing surveillance for tuberculosis through tuberculin skin test.
Promoting vaccination of health care workers and patients.
Offering blood and body fluid post-exposure prophylaxis.
Primary prevention focuses on preventing the initial occurrence of disease or injury before it manifests, distinguishing it from secondary (early detection) and tertiary (mitigation of complications) prevention. The Certification Board of Infection Control and Epidemiology (CBIC) emphasizes the "Prevention and Control of Infectious Diseases" domain, which includes collaboration with public health agencies to implement preventive strategies, aligning with the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) framework for infection prevention. The question requires identifying the activity that best fits primary prevention efforts.
Option C, "Promoting vaccination of health care workers and patients," is the correct answer. Vaccination is a cornerstone of primary prevention, as it prevents the onset of vaccine-preventable diseases (e.g., influenza, hepatitis B, measles) by inducing immunity before exposure. The CDC’s "Immunization of Health-Care Personnel" (2011) and "General Recommendations on Immunization" (2021) highlight the role of vaccination in protecting both healthcare workers and patients, reducing community transmission and healthcare-associated infections. Collaboration with public health agencies, which often oversee vaccination campaigns and supply distribution, enhances this effort, making it a proactive primary prevention strategy.
Option A, "Conducting outbreak investigations," is a secondary prevention activity. Outbreak investigations occur after cases are identified to control spread and mitigate impact, focusing on containment rather than preventing initial disease occurrence. The CDC’s "Principles of Epidemiology in Public Health Practice" (3rd Edition, 2012) classifies this as a response to an existing problem. Option B, "Performing surveillance for tuberculosis through tuberculin skin test," is also secondary prevention. Surveillance, including tuberculin skin testing, aims to detect latent or active tuberculosis early to prevent progression or transmission, not to prevent initial infection. The CDC’s "Guidelines for Preventing the Transmission of Mycobacterium tuberculosis" (2005) supports this as a screening tool. Option D, "Offering blood and body fluid post-exposure prophylaxis," is tertiary prevention. Post-exposure prophylaxis (e.g., for HIV or hepatitis B) is administered after potential exposure to prevent disease development, focusing on mitigating consequences rather than preventing initial exposure, as outlined in the CDC’s "Updated U.S. Public Health Service Guidelines" (2013).
The CBIC Practice Analysis (2022) and CDC guidelines prioritize vaccination as a primary prevention strategy, and collaboration with public health agencies amplifies its reach. Option C best reflects this preventive focus, making it the correct choice.
References:
CBIC Practice Analysis, 2022.
CDC Immunization of Health-Care Personnel, 2011.
CDC General Recommendations on Immunization, 2021.
CDC Principles of Epidemiology in Public Health Practice, 3rd Edition, 2012.
A 17-year-old presents to the Emergency Department with fever, stiff neck, and vomiting. A lumbar puncture is done. The Gram stain shows Gram negative diplocooci. Presumptive identification of the organism is
Haemophilus influenzae
Neisseria meningitidis
Listeria monocytogenes
Streptococcus pneumoniae
The Gram stain showing Gram-negative diplococci in cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) is characteristic of Neisseria meningitidis, a leading cause of bacterial meningitis in adolescents and young adults.
Step-by-Step Justification:
Gram Stain Interpretation:
Gram-negative diplococci in CSF strongly suggest Neisseria meningitidis.
Classic Symptoms of Meningitis:
Fever, stiff neck, and vomiting are hallmark signs of meningococcal meningitis.
Neisseria meningitidis vs. Other Bacteria:
Haemophilus influenzae (Option A) → Gram-negative coccobacilli.
Listeria monocytogenes (Option C) → Gram-positive rods.
Streptococcus pneumoniae (Option D) → Gram-positive diplococci.
CBIC Infection Control References:
APIC Ready Reference for Microbes, "Neisseria meningitidis and Meningitis".
Which of the following community-acquired infections has the greatest potential public health impact?
Cryptosporidium enteritis
Fifth disease (parvovirus B-19)
Clostridial myositis (gas gangrene)
Cryptococcal meningitis
The correct answer is A, "Cryptosporidium enteritis," as it has the greatest potential public health impact among the listed community-acquired infections. According to the Certification Board of Infection Control and Epidemiology (CBIC) guidelines, the public health impact of an infection is determined by factors such as its transmissibility, severity, population at risk, and potential for outbreaks. Cryptosporidium enteritis, caused by the protozoan parasite Cryptosporidium, is a waterborne illness that spreads through contaminated water or food, leading to severe diarrhea, particularly in immunocompromised individuals. Its significant public health impact stems from its high transmissibility in community settings (e.g., via recreational water or daycare centers), the difficulty in eradicating the oocysts with standard chlorination, and the potential to cause large-scale outbreaks affecting vulnerable populations, such as children or the elderly (CBIC Practice Analysis, 2022, Domain I: Identification of Infectious Disease Processes, Competency 1.3 - Apply principles of epidemiology). This is exemplified by notable outbreaks, such as the 1993 Milwaukee outbreak affecting over 400,000 people.
Option B (Fifth disease, caused by parvovirus B-19) is a viral infection primarily affecting children, causing a mild rash and flu-like symptoms. While it can pose risks to pregnant women (e.g., fetal anemia), it is generally self-limiting and has limited community-wide transmission potential, reducing its public health impact. Option C (clostridial myositis, or gas gangrene, caused by Clostridium perfringens) is a severe but rare infection typically associated with traumatic wounds or surgery, with limited person-to-person spread, making its public health impact low due to its sporadic nature. Option D (cryptococcal meningitis, caused by Cryptococcus neoformans) primarily affects immunocompromised individuals (e.g., those with HIV/AIDS) and is not highly transmissible in the general community, confining its impact to specific at-risk groups rather than the broader population.
The selection of Cryptosporidium enteritis aligns with CBIC’s focus on identifying infections with significant epidemiological implications, enabling infection preventionists to prioritize surveillance and control measures for diseases with high outbreak potential (CBIC Practice Analysis, 2022, Domain II: Surveillance and Epidemiologic Investigation, Competency 2.1 - Conduct surveillance for healthcare-associated infections and epidemiologically significant organisms). This is supported by CDC data highlighting waterborne pathogens as major public health concerns (CDC Parasites - Cryptosporidium, 2023).
References: CBIC Practice Analysis, 2022, Domain I: Identification of Infectious Disease Processes, Competency 1.3 - Apply principles of epidemiology; Domain II: Surveillance and Epidemiologic Investigation, Competency 2.1 - Conduct surveillance for healthcare-associated infections and epidemiologically significant organisms. CDC Parasites - Cryptosporidium, 2023.
What method of evaluation will BEST identify a staff member’s competency with reprocessing medical devices?
Verbalize the importance of reprocessing.
Demonstrate the appropriate sterilization procedure.
Describe the facility’s sterilization policies and procedures.
Obtain a score of 100% on a post-test following a reprocessing course.
The correct answer is B, "Demonstrate the appropriate sterilization procedure," as this method of evaluation will best identify a staff member’s competency with reprocessing medical devices. According to the Certification Board of Infection Control and Epidemiology (CBIC) guidelines, competency in reprocessing medical devices—such as cleaning, disinfection, and sterilization—requires not only theoretical knowledge but also the practical ability to perform the tasks correctly and safely. Demonstration allows the infection preventionist (IP) to directly observe the staff member’s hands-on skills, adherence to protocols (e.g., AAMI ST79), and ability to handle equipment, ensuring that the reprocessing process effectively prevents healthcare-associated infections (HAIs) (CBIC Practice Analysis, 2022, Domain IV: Education and Research, Competency 4.3 - Assess competence of healthcare personnel). This method provides tangible evidence of proficiency, as it tests the application of knowledge in a real or simulated setting, which is critical for ensuring patient safety.
Option A (verbalize the importance of reprocessing) assesses understanding and awareness, but it is a theoretical exercise that does not confirm the ability to perform the task, making it insufficient for evaluating competency. Option C (describe the facility’s sterilization policies and procedures) tests knowledge of guidelines, which is a component of competence but lacks the practical demonstration needed to verify skill execution. Option D (obtain a score of 100% on a post-test following a reprocessing course) measures theoretical knowledge and retention, but a perfect score does not guarantee practical ability, as it does not assess hands-on performance or problem-solving under real conditions.
The focus on demonstration aligns with CBIC’s emphasis on assessing competence through observable performance, ensuring that staff can reliably reprocess devices to maintain a sterile environment (CBIC Practice Analysis, 2022, Domain III: Infection Prevention and Control, Competency 3.3 - Ensure safe reprocessing of medical equipment). This method supports a comprehensive evaluation, aligning with best practices for training and competency assessment in healthcare settings.
References: CBIC Practice Analysis, 2022, Domain III: Infection Prevention and Control, Competency 3.3 - Ensure safe reprocessing of medical equipment; Domain IV: Education and Research, Competency 4.3 - Assess competence of healthcare personnel. AAMI ST79:2017, Comprehensive guide to steam sterilization and sterility assurance in health care facilities.
Which of the following microorganisms does NOT cause gastroenteritis in humans?
Norovirus
Rhinovirus
Rotavirus
Coxsackievirus
Gastroenteritis, characterized by inflammation of the stomach and intestines, typically presents with symptoms such as diarrhea, vomiting, and abdominal pain. The Certification Board of Infection Control and Epidemiology (CBIC) emphasizes the identification of infectious agents in the "Identification of Infectious Disease Processes" domain, aligning with the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) guidelines on foodborne and enteric diseases. The question requires identifying the microorganism among the options that does not cause gastroenteritis, necessitating an evaluation of each pathogen’s clinical associations.
Option B, "Rhinovirus," is the correct answer as it does not cause gastroenteritis. Rhinoviruses are the primary cause of the common cold, affecting the upper respiratory tract and leading to symptoms like runny nose, sore throat, and cough. The CDC and WHO classify rhinoviruses as picornaviruses that replicate in the nasopharynx, with no significant evidence linking them to gastrointestinal illness in humans. Their transmission is primarily through respiratory droplets, not the fecal-oral route associated with gastroenteritis.
Option A, "Norovirus," is a well-known cause of gastroenteritis, often responsible for outbreaks of acute vomiting and diarrhea, particularly in closed settings like cruise ships or nursing homes. The CDC identifies norovirus as the leading cause of foodborne illness in the U.S., transmitted via the fecal-oral route. Option C, "Rotavirus," is a major cause of severe diarrheal disease in infants and young children worldwide, also transmitted fecal-orally, with the CDC noting its significance before widespread vaccination reduced its impact. Option D, "Coxsackievirus," a member of the enterovirus genus, can cause gastroenteritis, particularly in children, alongside other syndromes like hand-foot-mouth disease. The CDC and clinical literature (e.g., Mandell, Douglas, and Bennett’s Principles and Practice of Infectious Diseases) document its gastrointestinal involvement, though it is less common than norovirus or rotavirus.
The CBIC Practice Analysis (2022) and CDC guidelines on enteric pathogens underscore the importance of distinguishing between respiratory and gastrointestinal pathogens for effective infection control. Rhinovirus’s exclusive association with respiratory illness makes Option B the microorganism that does not cause gastroenteritis.
References:
CBIC Practice Analysis, 2022.
CDC Norovirus Fact Sheet, 2021.
CDC Rotavirus Vaccination Information, 2020.
Mandell, Douglas, and Bennett’s Principles and Practice of Infectious Diseases, 9th Edition, 2019.
A hospital experiencing an increase in catheter-associated urinary tract infections (CAUTI) implements a quality improvement initiative. Which of the following interventions is MOST effective in reducing CAUTI rates?
Routine urine cultures for all catheterized patients every 48 hours.
Implementing nurse-driven protocols for early catheter removal.
Replacing indwelling urinary catheters with condom catheters for all male patients.
Using antibiotic-coated catheters in all ICU patients.
Nurse-driven catheter removal protocols have been shown to significantly reduce CAUTI rates by minimizing unnecessary catheter use.
Routine urine cultures (A) lead to overtreatment of asymptomatic bacteriuria.
Condom catheters (C) are helpful in certain cases but are not universally effective.
Antibiotic-coated catheters (D) have mixed evidence regarding their effectiveness.
CBIC Infection Control References:
APIC Text, "CAUTI Prevention Strategies," Chapter 10.
Assume the mean age of onset for patients with tuberculosis (TB) is 62 years, with one standard deviation of 5 years, and the age of onset follows a normal distribution. What is the percentage of patients expected to have the age of onset ranging from 57 to 67 years?
34%
68%
95%
99%
To determine the percentage of patients with an age of onset ranging from 57 to 67 years, we need to apply the properties of a normal distribution. In a normal distribution, the mean represents the central point, and the standard deviation defines the spread of the data. Here, the mean age of onset is 62 years, and the standard deviation is 5 years. The range of 57 to 67 years corresponds to one standard deviation below the mean (62 - 5 = 57) to one standard deviation above the mean (62 + 5 = 67).
In a normal distribution, approximately 68% of the data falls within one standard deviation of the mean (i.e., between μ - σ and μ + σ, where μ is the mean and σ is the standard deviation). This is a well-established statistical principle, often referred to as the 68-95-99.7 rule (or empirical rule) in statistics. Specifically, 34% of the data lies between the mean and one standard deviation above the mean, and another 34% lies between the mean and one standard deviation below the mean, totaling 68% for the range spanning one standard deviation on both sides of the mean.
Let’s verify this:
The lower bound (57 years) is exactly one standard deviation below the mean (62 - 5 = 57).
The upper bound (67 years) is exactly one standard deviation above the mean (62 + 5 = 67).
Thus, the range from 57 to 67 years encompasses the middle 68% of the distribution.
Option A (34%) represents the percentage of patients within one standard deviation on only one side of the mean (e.g., 62 to 67 or 57 to 62), not the full range. Option C (95%) corresponds to approximately two standard deviations from the mean (62 ± 10 years, or 52 to 72 years), which is wider than the given range. Option D (99%) aligns with approximately three standard deviations (62 ± 15 years, or 47 to 77 years), which is even broader. Since the question specifies a range of one standard deviation on either side of the mean, the correct answer is 68%, corresponding to Option B.
In infection control, understanding the distribution of disease onset ages can help infection preventionists identify at-risk populations and allocate resources effectively, aligning with the CBIC’s focus on surveillance and data analysis (CBIC Practice Analysis, 2022). While the CBIC does not directly address statistical calculations in its core documents, the application of normal distribution principles is a standard epidemiological tool endorsed in public health guidelines, which inform CBIC practices.
References:
CBIC Practice Analysis, 2022.
Public Health Epidemiology Guidelines, Normal Distribution and Empirical Rule (commonly accepted statistical standards).
An infection control manager is training a new infection preventionist. In discussing surveillance strategies, which of the following types of hospital infection surveillance usually provides maximum benefit with minimum resources?
High-risk patient focus
Antibiotic monitoring
Prevalence surveys
Nursing care plan review
A high-risk patient focus maximizes benefits while minimizing resource use in infection surveillance.
Step-by-Step Justification:
Efficiency of High-Risk Surveillance:
Targeting ICU, immunocompromised patients, or surgical units helps detect infections where the risk is highest, leading to earlier interventions.
Resource Allocation:
Full hospital-wide surveillance is resource-intensive; focusing on high-risk groups is more efficient.
Why Other Options Are Incorrect:
B. Antibiotic monitoring:
Important for stewardship, but not the primary focus of infection surveillance.
C. Prevalence surveys:
Snapshot data only; does not provide ongoing monitoring.
D. Nursing care plan review:
Less direct in identifying infection trends.
CBIC Infection Control References:
APIC Text, "Surveillance Strategies for Infection Prevention".
A microbiology laboratory plays a pivotal role in both endemic and epidemic epidemiology. Which of the following should be investigated FIRST?
One blood isolate of Streptococcus agalactiae in the nursery.
Two isolates of Staphylococcus aureus in postoperative surgical sites.
Three respiratory isolates of multi-drug resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae in the medical ICU.
Two blood isolates of coagulase-negative staphylococci in the oncology unit.
Multi-drug resistant (MDR) Klebsiella pneumoniae in a high-risk area like the ICU requires urgent investigation because:
It spreads rapidly via contaminated hands or equipment.
It poses a serious risk to immunocompromised patients.
An outbreak could lead to severe hospital-acquired infections (HAIs).
Why the Other Options Are Incorrect?
A. One blood isolate of Streptococcus agalactiae in the nursery – Single cases are not indicative of an outbreak.
B. Two isolates of Staphylococcus aureus in postoperative surgical sites – Common post-surgical pathogen; requires monitoring but not immediate outbreak investigation.
D. Two blood isolates of coagulase-negative staphylococci in the oncology unit – Common contaminants in blood cultures and not immediately alarming.
CBIC Infection Control Reference
APIC guidelines prioritize investigating MDR pathogens in high-risk units, such as ICU, to prevent transmission.
Which of the following is an example of an outcome measure?
Hand hygiene compliance rate
Adherence to Environmental Cleaning
Rate of multi-drug resistant organisms acquisition
Timing of preoperative antibiotic administration
The correct answer is C, "Rate of multi-drug resistant organisms acquisition," as it represents an example of an outcome measure. According to the Certification Board of Infection Control and Epidemiology (CBIC) guidelines, outcome measures are indicators that reflect the impact or result of infection prevention and control interventions on patient health outcomes or the incidence of healthcare-associated infections (HAIs). The rate of multi-drug resistant organisms (MDRO) acquisition directly measures the incidence of new infections caused by resistant pathogens, which is a key outcome affected by the effectiveness of infection control practices (CBIC Practice Analysis, 2022, Domain II: Surveillance and Epidemiologic Investigation, Competency 2.4 - Evaluate the effectiveness of infection prevention and control interventions).
Option A (hand hygiene compliance rate) is an example of a process measure, which tracks adherence to specific protocols or practices intended to prevent infections, rather than the resulting health outcome. Option B (adherence to environmental cleaning) is also a process measure, focusing on the implementation of cleaning protocols rather than the end result, such as reduced infection rates. Option D (timing of preoperative antibiotic administration) is another process measure, assessing the timeliness of an intervention to prevent surgical site infections, but it does not directly indicate the outcome (e.g., infection rate) of that intervention.
Outcome measures, such as the rate of MDRO acquisition, are critical for evaluating the success of infection prevention programs and are often used to guide quality improvement initiatives. This aligns with CBIC’s emphasis on using surveillance data to assess the effectiveness of interventions and inform decision-making (CBIC Practice Analysis, 2022, Domain II: Surveillance and Epidemiologic Investigation, Competency 2.5 - Use data to guide infection prevention and control strategies). The focus on MDRO acquisition specifically highlights a significant healthcare challenge, making it a prioritized outcome measure in infection control.
References: CBIC Practice Analysis, 2022, Domain II: Surveillance and Epidemiologic Investigation, Competencies 2.4 - Evaluate the effectiveness of infection prevention and control interventions, 2.5 - Use data to guide infection prevention and control strategies.
Which performance improvement model should the infection preventionist use to aid in the evaluation of the infection control plan?
Six Sigma
Failure mode and effects analysis
Plan, Do, Study, Act
Root Cause Analysis
The Plan, Do, Study, Act (PDSA) model is a widely used performance improvement tool in infection prevention. It focuses on continuous quality improvement through planning, implementing, analyzing data, and making adjustments. This model aligns with infection control program evaluations and The Joint Commission’s infection prevention and control standards.
Why the Other Options Are Incorrect?
A. Six Sigma – A data-driven process improvement method but not as commonly used in infection control as PDSA.
B. Failure Mode and Effects Analysis (FMEA) – Used to identify risks before implementation, rather than ongoing evaluation.
D. Root Cause Analysis (RCA) – Used to analyze failures after they occur, rather than guiding continuous improvement.
CBIC Infection Control Reference
The PDSA cycle is a recognized model for evaluating and improving infection control plans.
Each item or package that is prepared for sterilization should be labeled with the
storage location.
type of sterilization process.
sterilizer identification number or code.
cleaning method (e.g., mechanical or manual).
The correct answer is C, "sterilizer identification number or code," as this is the essential information that each item or package prepared for sterilization should be labeled with. According to the Certification Board of Infection Control and Epidemiology (CBIC) guidelines, proper labeling of sterilized items is a critical component of infection prevention and control to ensure traceability and verify the sterilization process. The sterilizer identification number or code links the item to a specific sterilization cycle, allowing the infection preventionist (IP) and sterile processing staff to track the equipment used, confirm compliance with standards (e.g., AAMI ST79), and facilitate recall or investigation if issues arise (CBIC Practice Analysis, 2022, Domain III: Infection Prevention and Control, Competency 3.3 - Ensure safe reprocessing of medical equipment). This labeling ensures that the sterility of the item can be assured and documented, protecting patient safety by preventing the use of inadequately processed items.
Option A (storage location) is important for inventory management but is not directly related to the sterilization process itself and does not provide evidence of the sterilization event. Option B (type of sterilization process) indicates the method (e.g., steam, ethylene oxide), which is useful but less critical than the sterilizer identification, as the process type alone does not confirm the specific cycle or equipment used. Option D (cleaning method, e.g., mechanical or manual) is a preliminary step in reprocessing, but it is not required on the sterilization label, as the focus shifts to sterilization verification once the item is prepared.
The requirement for a sterilizer identification number or code aligns with CBIC’s emphasis on maintaining rigorous tracking and quality assurance in the reprocessing of medical devices, ensuring accountability and adherence to best practices (CBIC Practice Analysis, 2022, Domain III: Infection Prevention and Control, Competency 3.5 - Evaluate the environment for infection risks). This practice is mandated by standards such as AAMI ST79 to support effective infection control in healthcare settings.
References: CBIC Practice Analysis, 2022, Domain III: Infection Prevention and Control, Competencies 3.3 - Ensure safe reprocessing of medical equipment, 3.5 - Evaluate the environment for infection risks. AAMI ST79:2017, Comprehensive guide to steam sterilization and sterility assurance in health care facilities.
The degree of infectiousness of a patient with tuberculosis correlates with
the hand-hygiene habits of the patient.
a presence of acid-fast bacilli in the blood.
a tuberculin skin test result that is greater than 20 mm
the number of organisms expelled into the air
The infectiousness of tuberculosis (TB) is directly related to the number of Mycobacterium tuberculosis organisms expelled into the air by an infected patient.
Step-by-Step Justification:
TB Transmission Mechanism:
TB spreads through airborne droplet nuclei, which remain suspended for long periods.
Factors Affecting Infectiousness:
High bacterial load in sputum: Smear-positive patients are much more infectious.
Coughing and sneezing frequency: More expelled droplets increase exposure risk.
Environmental factors: Poor ventilation increases transmission.
Why Other Options Are Incorrect:
A. Hand hygiene habits: TB is airborne, not transmitted via hands.
B. Presence of acid-fast bacilli (AFB) in blood: TB is not typically hematogenous, and blood AFB does not correlate with infectiousness.
C. Tuberculin skin test (TST) >20 mm: TST indicates prior exposure, not infectiousness.
CBIC Infection Control References:
APIC Text, "Tuberculosis Transmission and Control Measures".
An 84-year-old male with a gangrenous foot is admitted to the hospital from an extended-care facility (ECF). The ECF is notified that the wound grew Enterococcus faecium with the following antibiotic sensitivity results:
ampicillin – R
vancomycin – R
penicillin – R
linezolid – S
This is the fourth Enterococcus species cultured from residents within the same ECF wing in the past month. The other cultures were from two urine specimens and a draining wound. The Infection Preventionist (IP) should immediately:
Notify the medical director of the outbreak.
Compare the four culture reports and sensitivity patterns.
Conduct surveillance cultures for this organism in all residents.
Notify the nursing administrator to close the wing to new admissions.
The scenario describes a potential outbreak of multidrug-resistant Enterococcus faecium in an extended-care facility (ECF) wing, indicated by four positive cultures (including the current case and three prior cases from urine and a draining wound) within a month. The organism exhibits resistance to ampicillin, vancomycin, and penicillin, but sensitivity to linezolid, suggesting a possible vancomycin-resistant Enterococcus (VRE) strain, which is a significant concern in healthcare settings. The Certification Board of Infection Control and Epidemiology (CBIC) emphasizes the importance of rapid outbreak detection and response in the "Surveillance and Epidemiologic Investigation" domain, aligning with Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) guidelines for managing multidrug-resistant organisms (MDROs).
Option A, "Notify the medical director of the outbreak," is the most immediate and critical action. Identifying an outbreak—defined by the CDC as two or more cases of a similar illness linked by time and place—requires prompt notification to the facility’s leadership (e.g., medical director) to initiate a coordinated response. The presence of four Enterococcus cases, including a multidrug-resistant strain, within a single ECF wing over a month suggests a potential cluster, necessitating urgent action to assess the scope, implement control measures, and allocate resources. The CDC’s "Management of Multidrug-Resistant Organisms in Healthcare Settings" (2006) recommends immediate reporting to facility leadership as the first step to activate an outbreak investigation team, making this the priority.
Option B, "Compare the four culture reports and sensitivity patterns," is an important subsequent step in outbreak investigation. Analyzing the antibiotic susceptibility profiles and culture sources can confirm whether the cases are epidemiologically linked (e.g., clonal spread of VRE) and guide treatment and control strategies. However, this is a detailed analysis that follows initial notification and should not delay alerting the medical director. Option C, "Conduct surveillance cultures for this organism in all residents," is a proactive measure to determine the prevalence of Enterococcus faecium, especially VRE, within the wing. The CDC recommends targeted surveillance during outbreaks, but this requires prior authorization and planning by the outbreak team, making it a secondary action after notification. Option D, "Notify the nursing administrator to close the wing to new admissions," may be a control measure to prevent further spread, as suggested by the CDC for MDRO outbreaks. However, closing a unit is a significant decision that should be guided by the medical director and infection control team after assessing the situation, not an immediate independent action by the IP.
The CBIC Practice Analysis (2022) and CDC guidelines prioritize rapid communication with leadership to initiate a structured outbreak response, including resource allocation and policy adjustments. Given the multidrug-resistant nature and cluster pattern, notifying the medical director (Option A) is the most immediate and appropriate action to ensure a comprehensive response.
References:
CBIC Practice Analysis, 2022.
CDC Management of Multidrug-Resistant Organisms in Healthcare Settings, 2006.
The primary source of organisms that cause surgical silo infections is the
operating room environment.
operating room personnel.
patient's endogenous flora
healthcare personnel's hands.
The primary source of organisms causing surgical site infections (SSIs) is the patient’s own endogenous flora. Bacteria from the skin, mucous membranes, or gastrointestinal tract contaminate the surgical site, leading to infection. Common pathogens include Staphylococcus aureus, coagulase-negative staphylococci, and Enterobacteriaceae.
Why the Other Options Are Incorrect?
A. Operating room environment – While environmental contamination can contribute, it is not the primary source.
B. Operating room personnel – Infection control measures (hand hygiene, gloves, masks) reduce transmission from personnel.
D. Healthcare personnel’s hands – Although hand contamination is a risk, it is secondary to the patient’s endogenous flora.
CBIC Infection Control Reference
According to APIC guidelines, the patient’s own flora is the primary source of SSIs.
There are four cases of ventilator-associated pneumonia in a surgical intensive care unit with a total of 200 ventilator days and a census of 12 patients. Which of the following BEST expresses how this should be reported?
Ventilator-associated pneumonia rate of 2%
20 ventilator-associated pneumonia cases/1000 ventilator days
Postoperative pneumonia rate of 6% in SICU patients
More information is needed regarding ventilator days per patient
The standard way to report ventilator-associated pneumonia (VAP) rates is:
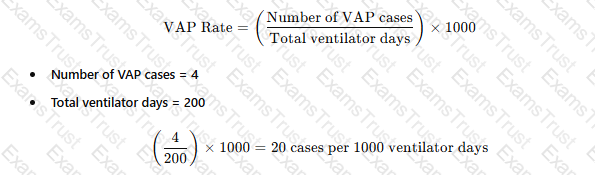 A white paper with black text
AI-generated content may be incorrect.
A white paper with black text
AI-generated content may be incorrect.
Why the Other Options Are Incorrect?
A. Ventilator-associated pneumonia rate of 2% – This does not use the correct denominator (ventilator days).
C. Postoperative pneumonia rate of 6% in SICU patients – Not relevant, as the data focuses on VAP, not postoperative pneumonia.
D. More information is needed regarding ventilator days per patient – The total ventilator days are already provided, so no additional data is required.
CBIC Infection Control Reference
APIC and NHSN recommend reporting VAP rates as cases per 1,000 ventilator days.
An infection preventionist (IP) is informed of a measles outbreak in a nearby community. What is the IP’s FIRST priority when working with Occupational Health?
Isolate employees who have recently traveled to areas with measles outbreaks.
Reassign employees who are pregnant from caring for patients with suspected measles.
Verify that employees in high-risk exposure areas of the facility have adequate immunity to measles.
Set up a mandatory vaccination clinic in collaboration with Occupational Health and local public health partners.
When an infection preventionist (IP) is informed of a measles outbreak in a nearby community, the immediate priority is to protect healthcare workers and patients from potential exposure, particularly in a healthcare setting where vulnerable populations are present. Working with Occupational Health, the IP must follow a structured approach to mitigate the risk of transmission, guided by principles from the Certification Board of Infection Control and Epidemiology (CBIC) and public health guidelines. Let’s evaluate each option to determine the first priority:
A. Isolate employees who have recently traveled to areas with measles outbreaks: Isolating employees who may have been exposed to measles during travel is an important infection control measure to prevent transmission within the facility. However, this action assumes that exposure has already occurred and requires identification of affected employees first. Without knowing the immunity status of the workforce, this step is reactive rather than preventive and cannot be the first priority.
B. Reassign employees who are pregnant from caring for patients with suspected measles: Reassigning pregnant employees is a protective measure due to the severe risks measles poses to fetuses (e.g., congenital rubella syndrome risks, though measles itself is more about maternal complications). This action is specific to a subset of employees and depends on identifying patients with suspected measles, which may not yet be confirmed. It is a secondary step that follows assessing overall immunity and exposure risks, making it inappropriate as the first priority.
C. Verify that employees in high-risk exposure areas of the facility have adequate immunity to measles: Verifying immunity is the foundational step in preventing measles transmission in a healthcare setting. Measles is highly contagious, and healthcare workers in high-risk areas (e.g., emergency departments, pediatric wards) are at increased risk of exposure. The CBIC and CDC recommend ensuring that all healthcare personnel have documented evidence of measles immunity (e.g., two doses of MMR vaccine, laboratory evidence of immunity, or prior infection) as a primary infection control strategy during outbreaks. This step allows the IP to identify vulnerable employees, implement targeted interventions, and comply with occupational health regulations. It is the most proactive and immediate priority when an outbreak is reported in the community.
D. Set up a mandatory vaccination clinic in collaboration with Occupational Health and local public health partners: Establishing a vaccination clinic is a critical long-term strategy to increase immunity and control the outbreak. However, this requires planning, resource allocation, and coordination, which take time. It is a subsequent step that follows verifying immunity status to identify those who need vaccination. While important, it cannot be the first priority due to its logistical demands.
The first priority is C, as verifying immunity among employees in high-risk areas establishes a baseline to prevent transmission before reactive measures (e.g., isolation, reassignment) or broader interventions (e.g., vaccination clinics) are implemented. This aligns with CBIC’s focus on proactive risk assessment and occupational health safety during infectious disease outbreaks, ensuring a rapid response to protect the healthcare workforce and patients.
References:
CBIC Infection Prevention and Control (IPC) Core Competency Model (updated 2023), Domain III: Prevention and Control of Infectious Diseases, which prioritizes immunity verification during outbreaks.
CBIC Examination Content Outline, Domain IV: Environment of Care, which includes ensuring employee immunity as part of outbreak preparedness.
CDC Guidelines for Measles Prevention (2023), which recommend verifying healthcare worker immunity as the initial step during a measles outbreak.
Which of the following control measures is MOST effective in preventing transmission of Legionella in healthcare water systems?
Flushing all faucets with hot water for 5 minutes daily.
Maintaining hot water storage temperatures above 140°F (60°C).
Installing carbon filters on all hospital water outlets.
Routine testing for Legionella in hospital water.
Maintaining hot water at 140°F (60°C) prevents Legionella growth and is the most effective control strategy.
Flushing water (A) alone is not sufficient.
Carbon filters (C) do not remove Legionella.
Routine testing (D) is not always necessary unless an outbreak occurs.
CBIC Infection Control References:
APIC Text, "Waterborne Pathogens and Infection Control," Chapter 9.
Copyright © 2014-2025 Examstrust. All Rights Reserved
