The following data are available for a company that produces and sells a single product.
The company’s opening finished goods inventory was 2,500 units.
The fixed overhead absorption rate is $8.00 per unit.
The profit calculated using marginal costing is $16,000.
The profit calculated using absorption costing and valuing its inventory at standard cost is $22,400.
The company’s closing finished goods inventory is:
Which of the following is NOT a valid purpose of budgeting?
Which THREE of the following are included in the Global Management Accounting Principles? (Choose three.)
A company produces a single product for which the following cost data are available.
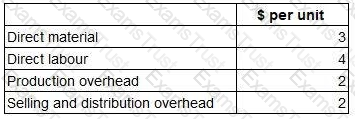
Analysis by the management accountant has shown that 100% of direct material cost and 50% of direct labour cost are variable costs. 50% of production overhead and 100% of selling and distribution overhead are variable costs.
What is the marginal cost per unit?
A company’s policy is to hold closing inventory each month equal to 10% of the next month’s budgeted sales volume. The budgeted sales volumes of product Q for months 1 and 2 are 1,660 units and 2,300 units respectively.
The production budget for product Q for month 1 is:
The possible returns and associated probabilities of two independent projects are as follows:
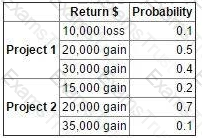
It has been decided that both projects are to be launched.
Which TWO of the following statements are correct? (Choose two.)
A company has three production departments X, Y and Z, and one service department.
The service department’s overhead has been apportioned to the production departments in the ratio 3:2:5. As a result of this apportionment, $2,070 was given to Department Y.
What is the amount of service department overhead that would have been apportioned to Department Z? Give your answer to the nearest dollar.
Every month for the last three years, a company has recorded the number of new customers for that month. The data have been summarised and grouped as follows:
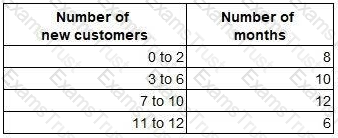
What is the arithmetic mean of the number of new customers per month?
Based upon extensive historical evidence, a company’s daily sales volume is known to be normally distributed with a mean of 1,728 units and a standard deviation of 273 units.
What is the probability that, on any one day, the sales volume will be at least 1,300 units?
A company wishes to compare the variability of its monthly sales revenue in country A with that of country B. The two countries use different currencies.
The monthly sales revenue for the last 48 months in country A (which is measured in $) has been analysed as follows.
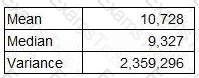
What is the coefficient of variation of this data?
Give your answer as a percentage to one decimal place.
The International Federation of Accountants (IFAC) stated that it was important that “accountants in business” should understand what the drivers of stakeholder value are. Which of the following statements is valid?
A company manufactures three products using the same direct labour which will be in short supply next month. No inventories are held. Data for the three products are as follows:
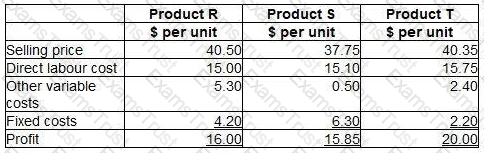
The fixed costs are all committed costs and cannot now be altered for the next month.
Place the labels against the correct product to indicate the order of priority for manufacture that will maximise the profit for the next month.
Which of the following would NOT be an appropriate performance measure for a profit centre manager?
A company absorbs production overhead using a direct labour hour rate. Data for the latest period are as follows:
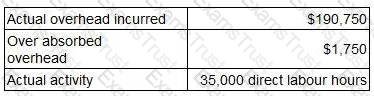
What is the overhead absorption rate per direct labour hour? Give your answer to one decimal place.
The following is an extract from a budgetary control report for the latest period:
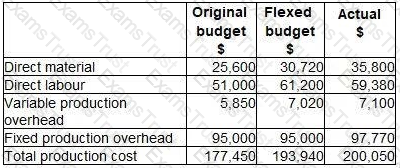
The budget variance for prime cost is:
A project is about to be launched. Two of the three possible outcomes and their associated probabilities are as follows:
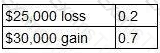
The remaining possible outcome is a $70,000 gain.
What is the correct calculation of the expected value of the project?
A confectionery manufacturer is considering adding a new product to the current range. Forecast data for the product are as follows.
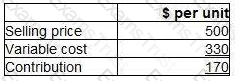
Incremental fixed costs attributable to the new product are forecast to be $24,000 each period.
The forecast sales volume of 180 units is insufficient to achieve the target profit of $10,000 each period.
Which of the following statements is correct?
According to CIMA’s Code of Ethics, CIMA members should not allow bias, conflict of interest of the influence of other people to override their professional judgement.
This is an example of:
A company operates an integrated standard cost accounting system. The standard price of raw material A is $20 per litre. At the start of period 1, the inventory of 500 litres of raw material A was valued at $20 per litre. During period 1, 100 litres of raw material A were purchased at an actual price of $21 per litre. During period 2, 550 litres of raw material A were issued to Job 789.
In respect of the above events, which TWO of the following statements are correct? (Choose two.)
A sales manager has analysed a sample of 350 sales transactions from the latest period. The manager wishes to investigate:
how many customers made their purchase online using the internet and how many purchased by telephone.
how many were new customers and how many were placing repeat orders.
The following table shows the results of the analysis.
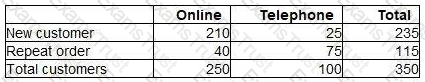
If the pattern of sales occurs next period, the probability of a particular sale being a repeat order placed online is closest to:
If the fixed costs are increased, the point at which the line plotted on a profit/volume (PV) graph cuts the horizontal axis will:
Each unit of product GM requires 4 labour hours to be produced. 25% of the units will be completed during overtime hours.
Sales of 24,000 units are planned and finished goods inventory is budgeted to rise by 2,000 units.
If the wage rate is £6 per hour and the overtime premium is 50%, what is the budgeted labour cost?
Refer to the exhibit.

T operates a process costing system. Data is available for Process A for the month of July.
Inputs for the month:
Normal losses are 15% of input and can be sold for $6 per kg. Actual output was 2,600 kg. There is no opening or closing work in progress for the period.
What is the value of the output from the process in the month?
Refer to the exhibit.

DS is manufacturing company that uses an integrated accounting system. The following payroll data is available for the month of August:
The Employers' National Insurance for the period was $13,790. An analysis of the wages is as follows:
Which of the following factors affect the budgeted cash flow:
(a) Funds from the issue of share capital
(b) Bank Interest on a long term loan
(c) Depreciation on fixed assets
(d) Bad debt write off
A company currently allows a discount of 20% to customers who pay at the time of purchase. If 30% of customers pay immediately, the extra sales needed in July to increase the cash receipts in that month by £6,000 are:
The accounting treatment for overheads over absorbed is to:
Refer to the exhibit.
The following information relates to Job 123:
The selling price to the customer for Job 123 is:
Which ONE of the following would be the LEAST effective performance indicator for a distribution manager who is responsible for controlling the cost of the transport fleet?
Refer to the exhibit.

Each unit of product ‘Smitten’ uses 5 kgs of material 'Z'.
The budgeted details for March are as follows:
It is anticipated that sales of product ‘Smitten’ in March will be 20000 units.
The amount of material 'Z' that needs to be purchased in March is:
The following costs are incurred by a company which owns a five star hotel. Which THREE of the items would normally be classified as variable costs?
Apex Plc has budgeted to sell 8,000 units of A in the year. Opening inventory of A is estimated at 1,000 units and the company plans to reduce inventory levels of all products by 15%.
What will be the production budget (in units) for the year?
A company can increase its margin of safety by which of the following independent actions?
(a) Increasing sales and production
(b) Raising the selling price per unit
(c) Raising the variable cost per unit
(d) Lowering fixed costs
The production manager of your company has asked you to explain the methods of overhead analysis used, in particular the meaning of reciprocal servicing.
Reciprocal servicing is:
Refer to the exhibit.
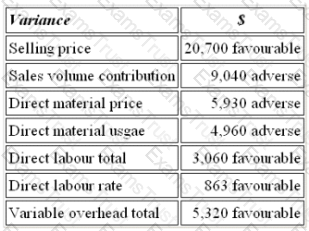
The budgeted contribution for last month was $53,600. The variances reported were as follows:
The actual contribution for last month was:
Refer to the exhibit.

A company is considering purchasing a machine that will have a useful life of three years after which time it will be sold. Relevant cash flows relating to the purchase and operation of the machine are as follows.
The annual cost of capital is 14%.
The net present value of the investment in the machine is, to the nearest whole $:
Which of the following is the LEAST appropriate basis on which to apportion the insurance costs of plant and machinery:
Each finished carton of product P contains 15 litres of liquid L. During the production process there is an unavoidable loss of 20% of the liquid input. The standard price of liquid L is $2 per litre.
The standard ingredient cost for liquid L shown on the standard cost card for one carton of product P will be
Refer to the exhibit.
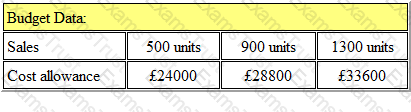
Budget information for 'Crome Ltd' is as follows:
The budgeted cost allowance for the sale of 1000 units would be:
Fixed costs can best be described as:
A product sells for £10 per unit and has an annual break-even volume of 50,000 units. The annual fixed costs are £100,000.
The variable cost per unit is:
Give your answer to 2 decimal places.
Refer to the exhibit.

The standard variable cost per unit of Product W is $26. The budgeted sales of Product W in April was 3,300 units. The company recorded the following variances for the month of April:
During April 3,600 units of Product W were actually sold.
The budgeted contribution for Product W in April was to the nearest $000:
Refer to the exhibit.
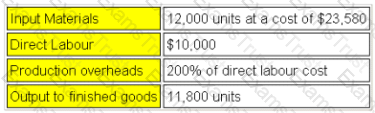
PD manufactures a product in a process operation. Normal loss is 5% of input and occurs at the end of the process. The following data is available for the month of August:
What was full cost of output to finished goods in August?
Refer to the exhibit.
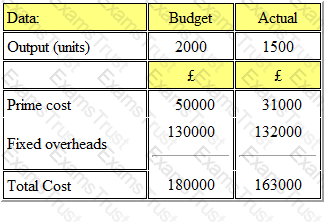
A company issued its production budget based on an anticipated output of 2000 units. The actual output for the period was 1500 units. The details of the costs are shown below:
The budget volume variance was:
When making a decision, for a cost or revenue to be classified as "relevant" it must be:
(a) Incremental
(b) Notional
(c) Cash
(d) Future
A profit margin of 20% of sales is the same as a profit on total cost of:
Give your answer to 2 decimal places.
A new range of clothing is very unique and will not appeal everyone. You are aware that if you were to equally distribute all the units there is a chance that they would not all sell.
You decide that the best option would be to select specific stores in which to sell the items, making them rare and desirable. This way they will become highly sought after.
However, whilst this has the potential to be very profitable it also has the lowest probability.
By making this decision you are considered to be_______.
Which of the following are NOT behavioural aspects of budgetary controls? (Select ALL that apply.)
Refer to the exhibit.
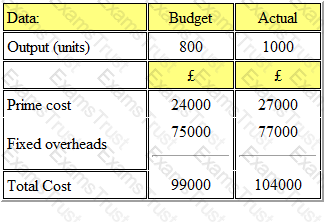
A company issued its production budget based on an anticipated output of 800 units. Actual output was 1000 units. The details of the costs are shown below:
The budget volume variance was:
A chemical process has a normal wastage of 8% of input. For the month of June, 5,000 liters of materials were input and there was an abnormal gain of 200 liters.
The quantity of good production achieved was
Refer to the exhibit.
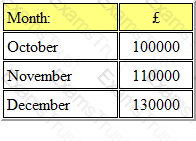
The budgeted sales revenues for a retailer are as follows:
The payment patterns of customers are expected to be as follows:
*The remaining 10% of sales are bad debts.
*A discount of 20% is given on cash sales.
The budgeted receipts from customers in December are:
Refer to the exhibit.
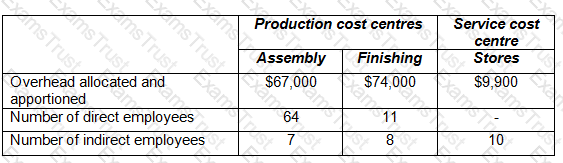
A management accountant had prepared the following initial overhead analysis, showing the overhead allocated and apportioned to the three cost centres. The number of employees in each cost centre is also shown.
The service cost centre costs are now to be reapportioned to the production cost centres on the basis of the number of employees in each production cost centre. After the reapportionment has been completed, the total overhead cost of the Assembly department will be:
Which of the following is the correct definition is an annuity:
A company achieves a profit/volume ratio of 25%. Sales for the month of July were £127,280 and fixed costs were £24,872.
What was the profit for the month?
VL manufactures a single product. The management accountant has estimated that the margin of safety as a percentage of budgeted sales is 25%. The company's profit/volume ratio is 20%, variable costs are $8 per unit and budgeted sales for the year are 80,000 units.
The budgeted fixed costs for the year, to the nearest $000, are.
In a manufacturing company which produces a range of products, the cost of factory rent and rates would be classified as A.
A product has a break-even point of 40,000 units and a margin of safety of 20%. The contribution per unit is £3.
What is the budgeted profit?
Refer to the exhibit.
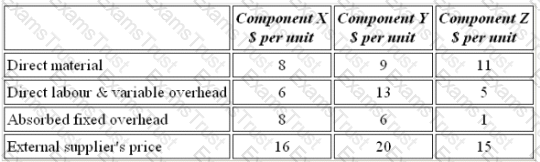
A company manufactures three components on the same machine, on which there is spare capacity. An external supplier has offered to supply all of the company's requirements of the components. Data for the components are as follows:
Which components should be purchased from the external supplier?
In investment appraisal, the net present value (NPV) is