AA manufactures computers. These are sold to BB at $100 a computer plus a 5% sales tax. BB subsequently sells the computers to CC for $200 a computer plus a 5% sales tax. C sells the computers to customers at $300 a computer plus a 5% sales tax.
The total tax received by the tax authority is $30.
Which type of tax is described above?
The following information relates to a single asset:
*Original cost of $186,000
*Estimated residual value of $6,000
*Expected useful life of 10 years
*Accumulated depreciation at 31 December 20X5 of $66,960
*Annual depreciation rate of 20% on a reducing balance basis
Calculate the amount of depreciation that should be charged to profit or loss for the year ended 31 December 20X6.
Give your answer to the nearest whole number.
DEF is considering introducing a Pay-As-You-Earn (PAYE) system but unsure of the advantages of using it.
Which of the following statements are advantages from the employees perspective of an entity using a PAYE system for collecting taxes from employees.
Select ALL that apply.
An entity has an inventory holding period of 52 days.
This means that the inventory:
In Country X corporate income tax is levied on profits as follows:
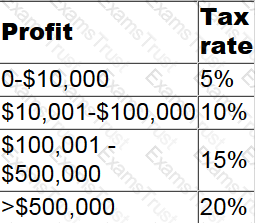
Which of the following describes the tax rate structure in Country X?
ST has an asset that was classified as held for sale at 30 June 20X4. The asset's carrying value was $230,000 and its fair value $210,000.
The cost of disposal was estimated to be $15,000.
In accordance with IFRS 5 Non-current Assets Held for Sale and Discontinued Operations, which of the following values should be used for the asset in the statement of financial position as at 30 June 20X4?
Which of the following would be capitalized as an intangible asset in accordance with IAS 38 Intangible Assets?
Refer to the exhibit.
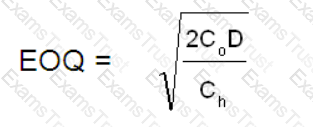
An entity sells 2,000 bags of product X each year. It has been estimated that the cost of holding one bag of product X is £4.
The cost of placing an order is £250.
where:
Co = cost of placing an order
Ch = cost of holding one unit in inventory for one year
D = annual demand
Calculate the Economic Order Quantity (EOQ) for bags of product X.
Give your answer to the nearest whole number of bags.
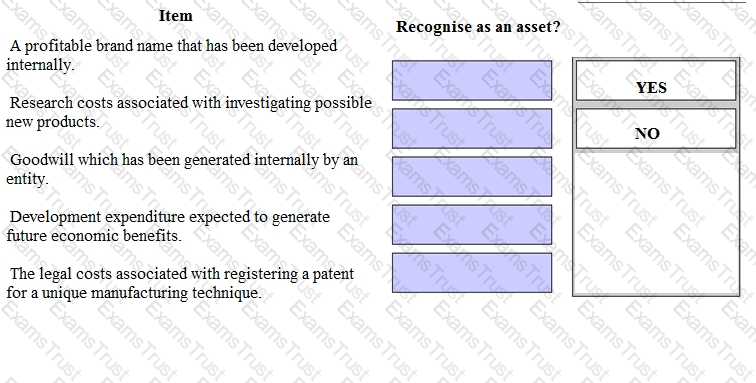
Identify from the list below which items can be recognised as assets within the financial statements of an entity in accordance with IAS 38 Intangible Assets. Place either yes or no as appropriate against each item.
On 1 January 20X2 an entity began work on constructing a factory. It purchased the land for $14 million, built the factory buildings for $11 million and installed plant and equipment for $7 million. The project was completed on 31 December 20X3 when the factory was deemed ready to use, however, the factory did not start operations until 1 June 20X4.
To fund the project the entity borrowed $25 million on 1 January 20X2, with interest at 10% per year.
The loan was repaid in full on 31 December 20X4.
Calculate the total amount to be added to the cost of property, plant and equipment in respect of the above development.
Give your answer to the nearest $ million.
The International Accounting Standards Board's "The Conceptual Framework for Financial Reporting" (known as The Conceptual Framework) states that "faithful representation" is a fundamental qualitative characteristic.
In accordance with the Conceptual Framework which of the following is NOT part of faithful representation?
The accounting profit before tax of an entity was $243,200 for the year ended 31 July 20X4.
The accounting profit included disallowable income from government grants of $48,000 and disallowable expenditure of $25,600 on entertaining expenses.
The entity also paid a $40,000 dividend to shareholders. The tax rates for the country were as follows:
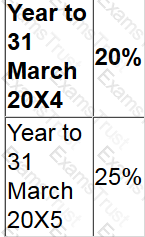
Calculate the tax the entity is due to pay for the year ending 31 July 20X4.
In accordance with IAS 16 Property, Plant and Equipment, in which of the following situations would subsequent expenditure on a non-current asset be capitalised?
An entity purchased an asset for $375,000 on 1 November 20X0 incurring legal fees of $33,000. Improvements were made to the asset for $65,000 on 1 December 20X2 which qualified as capital expenditure under the local tax rules. The entity also incurred repair costs on the asset on 1 February 20X3 amounting to $10,000.
The asset was sold for $680,000 on 1 December 20X5 incurring allowable costs on disposal of $15,000.
Indexation on the purchase cost and the improvement are allowable.
The index increased by 20% between November 20X0 and December 20X5,15% between December 20X2 and December 20X5 and 10% between February 20X3 and December 20X5
Calculate the chargeable gain on the disposal of the asset on 1 December 20X5.
Which of the following is NOT a feature of a multi-stage sales tax?
A specialized product was commissioned by a customer and the agreed price was $38,000. The product was completed at a cost of $34,000.
It was then discovered that new regulations meant that the specialized product now failed health and safety requirements. The specialized product had to be modified to meet the new regulations at a cost of $9,000. The customer agreed to pay an extra $3,000 towards the modifications.
At 31 December 20X5 the specialized product was still in inventory and had not been modified.
Calculate the value of the specialized product that should be included in inventory as at 31 December 20X5.
Give your answer to the nearest whole $000.
Which of the following would NOT be assessed for tax under a Pay-As-You-Earn system?
Entity T operates within several countries, but its country of residence is Country F. In 20X5, Entity T made $8.4 million in Country M. Country M has a flat rate corporation tax of 5.9%.
Country F and Country M operate a double taxation treaty which uses a foreign tax credit system. In Country F, there is a tax of 10% tax on all foreign income.
Taking into account the credit, what is the total tax liability that Entity T owes on its Country M income, in Country F?
Which THREE of the following statements are NOT true of the IFRS Foundation trustees?
Which THREE of the following are included in the International Accounting Standards Board's "The Conceptual Framework for Financial Reporting"?
FG purchased 40% of the equity shares of QR and exerted significant influence over the board of the directors.
QR will be classified as____of FG.
Country X levies corporate income tax at a rate of 25% and charges income tax on all profits irrespective of whether they are distributed by way of dividend. Country Y levies corporate income tax at a rate of 20%.
A, who is resident in Country X, pays a divided to B, who is resident in Country Y. B is required to pay corporate income tax on the dividend received from A, but a deduction can be made for the tax suffered on this dividend restricted to a rate of 20%.
Which method of relief for foreign tax does this describe?
What does the tax credit method of giving double taxation relief mean?
XYZ operates in Country P where the tax rules state entertaining costs and accounting depreciation are disallowable for tax purposes.
In year ending 31 March 20X4, XYZ made an accounting profit of $240,000.
Profit included $14,500 of entertaining costs and $5,000 of income exempt from taxation.
XYZ has plant and machinery with accounting depreciation amounting to $26,300 and tax depreciation amounting to $35,200.
Calculate the taxable profit for the year ended 31 March 20X4.
In Country X, trading losses in any year can be carried back and set off against trading profits in the previous year, with any unrelieved losses carried forward to set against the first available trade profits in future years.
GH had the following taxable profits and losses in years 20X1 to 20X4:
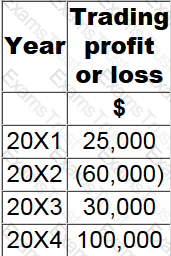
What are the taxable profits for 20X4, assuming the most efficient use of the loss is made?
A conservative policy for financing working capital is one where short-term finance is used to fund:
To apply the fundamental principles of the Code of Ethics, existing and potential threats to the entity first need to be identified and evaluated.
Which THREE of the following are identified in the Code as threats?
EF is a large manufacturing entity with several of its manufacturing sites in different locations. Currently all of the sites have a local procurement department. EF's board are looking to implement a centralized purchasing system.
Match the tokens according to whether you believe each statement is either an advantage or disadvantage of implementing a centralized purchasing system for EF.

BC manufactures product X and on 1 February 20X4 started a project to develop a new material for use in its production. The development project is due to be completed by 31 December 20X4 with the new material being used in production from 1 January 20X5. The development project costs have been reliably estimated at $200,000 and it is anticipated that the new material will increase the margin achieved on product X by 20%.
You are a CIMA accountant within BC and are considering how to treat the development costs of $200,000 in the financial statements for the year ended 31 December 20X4.
In accordance with the ethical principle of professional competence and due care, which of the following statements correctly explains how these costs should be accounted for?