ABC produces fashion garments for sale m its chain of high street retail outlets.
Which THREE of the following activities would result m the organisation having to review its cyber security risks management program?
Division A of X plc produced the following results in the last financial year.
Net profit $200,000 Gross capital employed $1,000,000
For evaluation purposes all divisional assets are valued at original cost.
The division is considering a project that has a positive NPV, will increase annual net profit by $15,000, but will require average inventory levels to increase by $50,000 and non-current assets to increase by $50,000.
X plc imposes a 16% capital charge on its divisions. Given these circumstances, will the evaluation criteria of return on investment (ROI) and residual income (RI) motivate division A managers to accept the project?
S is a senior production manager for LK, which is about to set up a new production line requiring S4 million of new specialist equipment.
S's daughter goes to school and is friends with the daughter of R. the sales manager in GG. GG is a potential supplier of the specialist equipment that LK requires.
R owns a holiday home. S's daughter regularly accompanies R's daughter on family vacations at this holiday home, all at R's expense.
S is the only person working for LK who is qualified to select the specialist equipment. GG will definitely bid for the sale.
What should S do?
DRF is a manufacturing company
The internal auditor is conducting an investigation into the operation of the payroll system and has discovered a compliance error
The Head of Human Resources (HR) is required to add any new names to the payroll, using a specific computer password The Head of HR was absent for a month because of ill health During that period a senior member of the Wages Office, who is normally responsible only for organising wage payments, was issued a temporary password in order to add new names to the payroll The password was cancelled when the Head of HR returned to work
Which TWO of the following statements are correct?
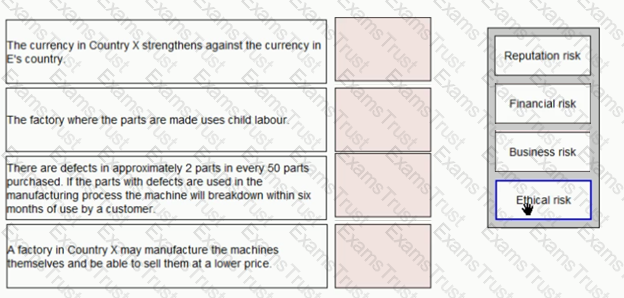
E purchases parts for one of the machines it manufactures from Country X Place the risk classification next to the risk it relates to:
A project has a net present value of $2 million.
Total cash outflows of this project have a present value of $14 million, which includes staff costs of $10 million.
What is the project's sensitivity to staff costs?
A hospital is part of a government provided health service which is free to patients. The management of the hospital is concerned with the need to minimise the risks to which the hospital is exposed from patient litigation.
In this context, which TWO of the following are appropriate steps to manage this risk?
QAW is a quoted building company QAW has detailed rules relating to the wording of its contracts and the need to seek Board approval for any changes to the standard wording
The Convener of the Audit Committee has just received a copy of an internal audit report relating to the QAW Land Reclamation subsidiary The subsidiary has signed several construction contracts over the past two years that have made significant changes to the standard wording, with no attempt to seek approval from QAW's Board
The internal audit report quotes the manager in charge of QAW Land Reclamation as refusing to accept that there is a compliance error at the subsidiary The manager stated that the nature of the business done by QAW Land Reclamation would make it inappropriate to use the standard contract terms and that it would be impractical to seek permission for every one of the many changes that are necessary
Which of the following would be an appropriate response to this item by QAW's Board?
JKL makes large export sales to customers in country X, whose currency fluctuates significantly against JKL's home currency JKL also makes large purchases from suppliers in countrrOC All of these transactions are in country X's currency
JKL's treasurer does not actively hedge currency risks because there is a natural hedge in place due to the company making both sales and purchases in the same currency
JKL's board has instructed the treasurer to put active hedging measures in place because the risk report would otherwise have to disclose the fact that JKL has a currency risk which is not actively hedged
Which of the following statements are correct? Select ALL that apply.
H is a senior production manager for P Ltd which is about to make a strategic decision on setting up a new production line requiring $3 million of new specialist equipment.
H's daughter is friends with and goes to school with the daughter of T, the sales manager in KK Ltd. KK Ltd is a potential supplier of the specialist equipment that P Ltd requires.
T owns a holiday home. H's daughter regularly accompanies T's daughter on family vacations at this holiday home, all at T's expense.
H is the only person working for P Ltd who is qualified to select the specialist equipment. KK Ltd will definitely bid for the sale.
What should H do?
B is a company with a strong risk appetite. Which of the following are benefits of using the certainty equivalent method of capital investment appraisal in B's case?
B is a quoted construction company. Its Board consists of qualified and experienced engineers Which TWO of the following statements are correct?
Which THREE of the following are principles of good corporate governance according to the UK Corporate Governance Code?
AZX sells electrical components.
AZX's annual turnover is S24 million. Half of all sales are on 30 days' (1 month) credit
5% of credit sales have to be written off as unrecovered debt
25% of such write off is subsequently recovered through debt collection and legal action.
What is the expected loss each year due to credit risk?
The shares of a company have a beta factor of 1.15. Therefore, which of the following must be true?
Which of the following are threats to the control environment?
DBB is a mining company. The company's business requires manners to work underground in hazardous conditions DBB takes every possible precaution to protect the safety and wellbeing of its miners, but that does not prevent the occurrence of four or five serious injuries every year. That number is small in relation to the many thousands of owners employed by DBB.
DBB's Board is preparing a risk map Most directors believe that injuries to miners should be classified as high Likelihood and high impact, which Is a category of risk that should be avoided according to the TARA framework One of the directors has suggested that the risk should be classified as low likelihood and high impact because that would move the risk into the quadrant associated with transference or sharing and so could be draft with by, say, insurance
Which TWO of the following are correct?
Which of the following is NOT a financial risk.
R plc is considering an investment of $1,100,000 in a new machine which is expected to have substantial cash inflows over the next five years.
The annual cash flows from this investment and their probability are shown below:
Annual cash flow ($) Probability
200,000 0.4
280,000 0.5
350,000 0.1
At the end of its five-year life, the asset is expected to sell for $100,000. The cost of capital is 5%.
What is the Expected Net Present Value?
Give your answer to the nearest whole $.
They key objective of maximizing shareholders wealth would indicates that a capital investment project with a large positive BPV should be accepted.
Which THREE of the following statements are correct?
A US company has to pay £500,000 for a new machine.
You have the following information on currencies.
EUR 1 = £1.2300
EUR 1 = USD 1.6200
What is the cost of the machine in USD?
Give your answer to the nearest $.
Company H operates a fleet of lorries. The Internal Auditor recently conducted an investigation into the transport needs of the company. Their report recommended that the lorries be disposed of, the drivers made redundant, and the distribution of the company's products be outsourced.
The type of investigation carried out by the Internal Auditor is best described as a:
Company W produces mobile phone components and has recently tendered for a substantial contract. The results of the tendering process will not become available until three months from now. If the company is successful it will require 2,000 units of a commodity which is currently traded in an open commodity market for $740 per unit. However, there has been speculation that this commodity could increase substantially in price over the next three months and so the company is considering purchasing the commodity now and storing it for three months.
The funds to buy the commodity would be borrowed at an annual interest rate of 7% and the storage cost of the product would be $5.40 per unit per month. The storage costs would be paid at the end of the three month storage period.
Which of the following represents the gain or loss (to the nearest thousand dollars) that will accrue to Company W assuming that the price of the commodity rises to $800 in three months' time?
Multinational companies have a variety of methods by which to manage currency risk.
Select ALL internal hedging methods from the following list.
Which TWO of the following are reasons for a company to comply with the Committee of Sponsoring Organisations of the Treadway Commission 2017 Enterprise Risk Management Framework (COSO Framework)?
A project has been evaluated on the basis that it will cost $22 million and will have a net present value of $4.3 million The project has commenced and $5 million of the $22 million has been invested. A problem has been discovered that will cost an additional $4.5 million to rectify. The $4.5 million will be payable immediately. What is the NPV of continuing with this project?
James owns a small company which sometimes suffers from credit risk.
Which of the following measures should he put in place to help reduce this risk?
Risk management involves all parties in an organisation.
Which of the following describe the Board's responsibilities for risk management?
VBN's home currency is the V$. On 1 January, VBN must make a payment of C$2 million on 31 March of that same year.
On 1 January the spot exchange rate was V$1 = C$0.4.
On 1 January VBN paid $180,000 for a call option to buy C$2 million for V$5.5 million on 31 March. VBN's cost of borrowing was 8% per year.
On 31 March the spot rate was V$1 = C$0.45.
What was the total cost, including the cost of the option, of settling the payable?
NLC, a retail chain, is considering moving its information systems which support its point of sale infrastructure into the cloud.
Which TWO factors should it consider in choosing its supplier?
You are the Management Accountant for P, a food manufacturing company with an annual sales revenue of $5 million.
You discover that the Production Manager's records are inconsistent. Raw materials purchased do not agree to the total recorded for transfers to production plus wastage. There is an average shortfall of 2% of purchases.
You investigated and discovered that there are often mistakes made during manufacturing that results in food that is safe to eat, but cannot be sold because of visual flaws. The Production Manager is supposed to scrap all such damaged product and write all such losses off as waste, but you discovered that he has been giving the damaged food to a charity that assists homeless people. No records are made of such gifts in order to conceal the losses due to manufacturing errors.
What should you do?
IOP manufactures aircraft engines. The company is presently engaged in a scenario planning exercise to consider the implications of a possible ban on the use of fossil fuels by the year 2040.
Which TWO of the following would be realistic responses to the scenario?
Under the COSO Enterprise Risk Management Framework, who is responsible for risk management?
Which of the following is an ethical dilemma?
An internal audit investigation involved conducting compliance tests on the processing of purchase invoices.
The purchase ledger clerk compares invoices against purchase orders and passes them for payment The invoices are then input into a computerised purchase ledger system The system checks that the supplier has a valid purchase ledger account, as authorised by the chief buyer, before crediting the supplier's account with the value of the invoice.
The internal auditor checked a sample of recorded purchase invoices against their corresponding purchase orders The internal auditor found four cases where invoices could not be agreed to corresponding purchase orders.
What is the potential significance of this compliance error?
C Ltd is a private, family-owned company which is hoping to become listed on a recognised Stock Exchange within the next two years. At the moment, the Board of Directors comprises five directors; four of whom are from the founding family and all of whom are involved in the day-to-day running of the business. The remaining director obtained a seat on the Board three years ago as a condition of an investment by a venture capital fund.
The Board meets in half-day sessions once a fortnight and the Board meetings are reasonably well run. All decisions are taken by the Board as a whole. There are no sub-committees.
Which of the following steps would it be appropriate for C Ltd to take in the light of the proposed listing?
P has decided to invest in a new warehouse at a cost of $2,000,000. The discount rate of the project is 18% and the present value of the tax shield is £26,000.
What is the minimum acceptable Internal Rate of Return of the project?
With regard to the rote of the audit committee which of the following statements are correct? Select ALL that apply
C Ltd is a private, family-owned company which is hoping to become listed on a recognised Stock Exchange within the next two years. At the moment, the Board of Directors comprises five directors; four of whom are from the founding family and all of whom are involved in the day-to-day running of the business. The remaining director obtained a seat on the Board three years ago as a condition of an investment by a venture capital fund.
The Board meets in half-day sessions once a fortnight and the Board meetings are reasonably well run. All decisions are taken by the Board as a whole. There are no sub-committees.
Which of the following steps would it be appropriate for C Ltd to take in the light of the proposed listing?
Which TWO of the following might create a good control environment?
Will owns $400,000 of shares in Company X.
Company X has a daily volatility of 1% of its share price.
Calculate the 28 day value at risk that shows the most Will can expect to lose during a 28 day period.
(Will wishes to be 90% certain that the actual loss in any month will be less than your predicted figure).
Give your answer to the nearest $000.
Which risks should be given the highest priority?
Which of the following statements concerning the use of balanced scorecards to measure divisional performance is correct?
Company A's gross profit percentage has fallen from 70% to 61 % Which of the following possible explanations would most concern the internal auditors?
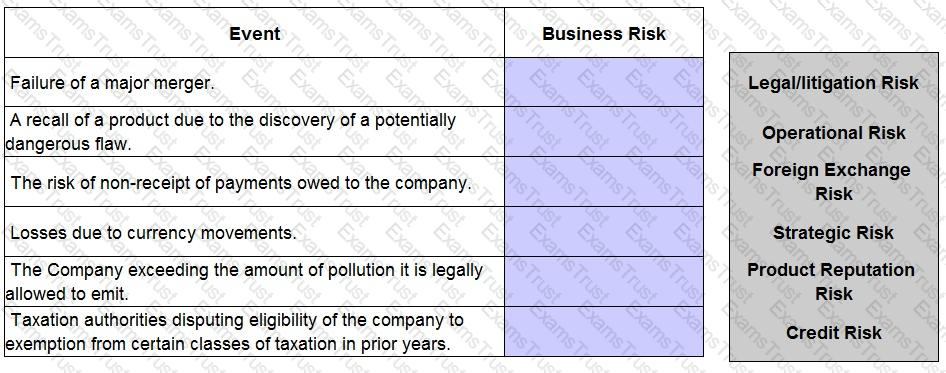
Identify, from the list provided, which category of business risk most accurately describes the events detailed below.
A project requires a capital investment of £2.7million. The project will save £450,000 each year after taxation. Assume the savings are in perpetuity. The business risk of the venture requires a 15% discount rate. The company has to borrow £1million to finance the project at a rate of 9% and the net tax shield is 30%, the project supports debt which generates an interest tax shield of 0.30 x 0.09 x £1million, which is £27,000 per year in perpetuity.
Calculate the project's adjusted present value.
You have just been employed as a management accountant in a small business with an annual turnover of $0.5 million.
You have a wide range of duties because the business is small.
Which of the following is an ethical risk?
There are many method for appraising capital projects.
Select ALL correct statements.
RFD, a listed company, is considering making an investment in a risky new venture. RFD has a substantial cash surplus that will be used to acquire the necessary resources. It is unlikely that RFD would have been able to raise finance for this investment because the company is already highly geared.
Which of the following statements about stakeholders' conflicting interests are true?
S Doc is an out-of-hours service provided by a country's government. The service allows members of the public to call and speak to a nurse who can advise on medical situations which are not obviously emergencies. Depending on the situation the caller can be referred to the full emergency services, or be advised to go to Accident and Emergency at the nearest hospital. Alternatively, a callout from a general practitioner (GP) can be organised; the caller can be advised of where GP services are available; advice can be given over the phone; or a decision can be taken that no further action is required at least until normal services resume on the next working day.
There has been a suggestion that the nurses who take these calls could be replaced by suitably trained operatives who have available to them a specially designed expert system.
Which of the following are advantages of using an expert system instead of nurses?