Evaluate the role of strategic human management in creating competitive advantage for an organisation
XYZ is a high fashion clothing designer and wishes to complete a benchmarking exercise. Discuss priority dimensions to be measured in the benchmarking exercise and propose a strategy for completing the exercise
Evaluate the following approaches to supply chain management: the Business Excellence Model, Top-Down Management Approach and Six Sigma
Discuss how XYZ, a global beverage manufacturing organisation, could use the Boston Consultancy Group Framework to impact upon strategic decision making
Introduction
TheBoston Consulting Group (BCG) Matrixis a strategic tool used by organizations to analyze their product portfolio and allocate resources effectively. It classifies products intofour categories—Stars, Cash Cows, Question Marks, and Dogs—based onmarket growth rateandmarket share.
As aglobal beverage manufacturing organization, XYZ can use theBCG Matrixto evaluate its product range, identify growth opportunities, and make informed strategic decisions.
1. Explanation of the BCG Matrix
TheBCG Matrixis divided into four quadrants:
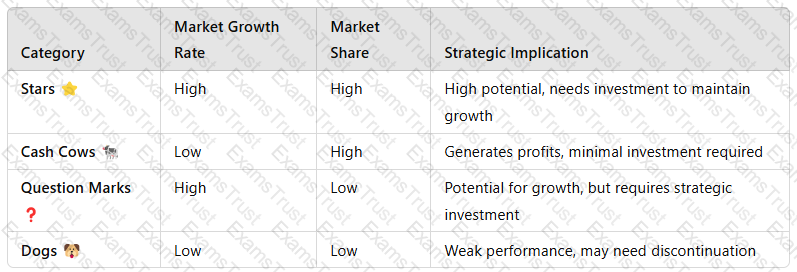
Example for XYZ:
Star:A fast-growingenergy drinkbrand in emerging markets.
Cash Cow:A flagshipcola productwith stable market demand.
Question Mark:A newfunctional health drinkwith uncertain market acceptance.
Dog:An underperformingdiet soda variantwith declining sales.
2. How XYZ Can Use the BCG Matrix for Strategic Decision-Making
XYZ can use the BCG Matrix to makeresource allocation and investment decisionsbased on product performance.

3. Advantages of Using the BCG Matrix for XYZ
✅Resource Allocation– Helps prioritize investment in high-growth products.
✅Strategic Focus– Identifies which products to grow, maintain, or phase out.
✅Market Adaptation– Helps XYZ adjust its beverage portfolio based on changing consumer trends.
????Example:IfXYZ’s energy drink(a Star) is experiencing high growth, more marketing and production investment may be justified.
4. Limitations of the BCG Matrix
❌Ignores Market Competition– A product may have a high market share, but competition could still impact profitability.
❌Simplistic Assumptions– Not all products neatly fit into one category; market dynamics are complex.
❌Focuses on Growth and Share Only– It does not consider external factors likeprofit margins, customer loyalty, or brand strength.
????Example:AQuestion Mark productmight have potential, but if consumer preferences shift, it may never become a Star.
5. Application of the BCG Matrix in the Beverage Industry
XYZ can apply theBCG Matrixby reviewing itsentire product portfolioacross different geographic markets.

Conclusion
TheBCG Matrixis a valuable strategic tool for XYZ to analyze itsproduct portfolio, prioritize investments, and make informedmarket-based decisions. However, it should be used alongside otherstrategic models(e.g.,PESTLE, VRIO) to ensure acomprehensive business strategy.
XYZ is a large manufacturing organisation which employs 200 skilled staff in its factory in Bolton. It has a large global supply chain with raw materials sourced from Asia and Africa. Discuss five areas of policy that can affect the people working in the supply chain
Explain 5 reasons why exchange rates can be volatile
Five Reasons Why Exchange Rates Can Be Volatile
Introduction
Exchange rates areconstantly fluctuatingdue to economic, political, and market forces. Volatility in exchange rates affectsglobal trade, procurement costs, and business profitability. Companies engaged ininternational supply chainsorglobal expansionmust understand the factors that drive currency fluctuations to manage risks effectively.
This answer exploresfive key reasonswhy exchange rates experience volatility.
1. Interest Rate Differentials????(Monetary Policy Impact)
Explanation
Central banks setinterest ratesto control inflation and economic growth. Countries withhigher interest ratesattract foreign investment, increasing demand for their currency.
✅How It Causes Volatility?
Rising interest rates→ Attracts foreign investors →Currency appreciates????
Falling interest rates→ Reduces investment appeal →Currency depreciates????
????Example:When theUS Federal Reserve raises interest rates, theUS dollar strengthensasinvestors move capital to USD-based assets.
????Key Takeaway:Exchange rates fluctuate as investorsadjust capital flowsbased oninterest rate expectations.
2. Inflation Rates????(Purchasing Power Impact)
Explanation
Inflation reduces thevalue of money, leading to lower purchasing power. Countries withhigh inflationtend to see their currencyweaken, while those withlow inflationmaintain a stronger currency.
✅How It Causes Volatility?
High inflation→ Reduces confidence in currency →Depreciation????
Low inflation→ Increases currency stability →Appreciation????
????Example:TheTurkish Lirahas depreciated significantly due tohigh inflation rates, making imports expensive.
????Key Takeaway:Inflation affects thereal value of money, influencingexchange rate stability.
3. Speculation and Market Sentiment????(Investor Behavior Impact)
Explanation
Foreign exchange markets (Forex) are driven byinvestor speculation. Traders buy and sell currencies based onmarket trends, geopolitical risks, and economic forecasts.
✅How It Causes Volatility?
If investorsexpect a currency to strengthen, they buy more →Increases demand and value????
If investorslose confidence, they sell off holdings →Causes depreciation????
????Example:In 2016, after theBrexit referendum, speculation about the UK economy caused theBritish pound (GBP) to drop sharply.
????Key Takeaway:Investor behavior and speculationcreate short-term exchange rate volatility.
4. Political Instability & Economic Uncertainty????️(Government Policies & Geopolitics)
Explanation
Political uncertainty and economic instabilityweaken investor confidence, leading tocapital flightfrom riskier currencies. Countries withstable governments and strong economiesmaintain more stable exchange rates.
✅How It Causes Volatility?
Political crises, elections, or policy changes→ Uncertainty →Currency depreciation????
Stable governance and economic reforms→ Confidence →Currency appreciation????
????Example:
Argentina’s peso lost valuedue to economic instability and high debt.
Switzerland’s Swiss Franc (CHF)remains strong due topolitical stabilityand its reputation as a "safe-haven" currency.
????Key Takeaway:Political and economic uncertainty increase exchange rate volatilityby influencing investor confidence.
5. Trade Balances & Current Account Deficits????(Export-Import Impact)
Explanation
Thebalance of trade(exports vs. imports) impacts currency demand. Countries thatexport more than they importexperiencehigher demand for their currency, leading to appreciation. Conversely, nations withlarge trade deficitssee their currencies depreciate.
✅How It Causes Volatility?
Trade surplus(more exports) → Demand for local currency rises →Appreciation????
Trade deficit(more imports) → Increased need for foreign currency →Depreciation????
????Example:
China’s trade surplusstrengthens theChinese Yuan (CNY).
The US dollar fluctuatesbased on itsimport-export trade balance.
????Key Takeaway:Exchange rates shift asglobal trade patterns change, affecting currency demand.
Conclusion
Exchange rate volatility is driven byeconomic, financial, and political factors:
1️⃣Interest Rates– Higher rates attract investment, strengthening currency.
2️⃣Inflation Rates– High inflation erodes value, weakening currency.
3️⃣Speculation & Market Sentiment– Investor behavior influences short-term fluctuations.
4️⃣Political & Economic Uncertainty– Instability causes capital flight and depreciation.
5️⃣Trade Balances & Deficits– Export-driven economies see appreciation, while import-heavy nations experience depreciation.
Understanding these drivers helps businessesmanage currency riskswhen engaging inglobal procurement, contracts, and financial planning.
XYX is an airline whose profits have been severely affected due to not being able to operate during a two-year pandemic. Cash reserves at the organisation are at an all time low and XYZ are looking into sources of short-term funding for working capital. Discuss four sources and suggest which one XYZ should use.
Why is it important for an organisation to measure performance? Describe one tool that can be used to measure performance
Describe 5 strategic decisions a company can make and how these decisions could impact upon competitive advantage.
Using Porter’s 5 Forces, describe the business environment of a company of your choice
Currency Options and Currency Swaps are instruments used in foreign exchange. Explain the advantages of using these derivatives compared to the use of spot transactions
XYZ is a large and successful airline which is looking to expand into a new geographical market. It currently offers short haul flights in Europe and wishes to expand into the Asian market. In order to do this, the CFO is considering medium/ long term financing options.Describe 4 options that could be used.