For IP destinations not found in the IS-IS Level 1 database, the Level 1 router must forward packets to the nearest Level 1-Level 2 router with which set?
What is the CLI command to obtain the software version in Ericsson Router 6000 products?
Within an IGP area, which two statements are correct? (Choose two.)
Which statement is true about LDP?
Review the exhibit.
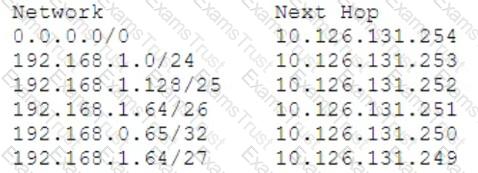
Given the routing table shown in the exhibit, what is the next-hop to reach the host 192.168.1.129?
Which two statements are true regarding the LSP? (Choose two.)
Which mismatched field would cause an IS-IS adjacency between two routers to fail?
Which two label actions are performed by a P router? (Choose two.)
What is the function of LSR from an LDP perspective?
What are two roles of the DHCP protocol in a network? (Choose two.)
Which router function advertises external routes in OSPF?
Which two protocols apply to both IPv4 and IPv6? (Choose two.)
In a company network, a host sends an Ethernet frame destined to the address FF:FF:FF:FF:FF:FF.
What will an Ethernet switch do with this frame?
Which two statements are true about link-state routing protocols? (Choose two.)
What is the correct abbreviation for the IP address: BFEA:DACA:0000:0000:9390:0000:0000:D91?
A network operator wants to make sure voice data is prioritized.
In this scenario, to which Ethernet traffic class should it be assigned.
What network information is, without additional configuration, shared between two iBGP neighbors by default?
Which two statements are true about priority queuing (PQ)? (Choose two.)