Which component of the Security Content Automation Protocol (SCAP) specification contains the data required to estimate the severity of vulnerabilities identified automated vulnerability assessments?
Common Vulnerabilities and Exposures (CVE)
Common Vulnerability Scoring System (CVSS)
Asset Reporting Format (ARF)
Open Vulnerability and Assessment Language (OVAL)
The component of the Security Content Automation Protocol (SCAP) specification that contains the data required to estimate the severity of vulnerabilities identified by automated vulnerability assessments is the Common Vulnerability Scoring System (CVSS). CVSS is a framework that provides a standardized and objective way to measure and communicate the characteristics and impacts of vulnerabilities. CVSS consists of three metric groups: base, temporal, and environmental. The base metric group captures the intrinsic and fundamental properties of a vulnerability that are constant over time and across user environments. The temporal metric group captures the characteristics of a vulnerability that change over time, such as the availability and effectiveness of exploits, patches, and workarounds. The environmental metric group captures the characteristics of a vulnerability that are relevant and unique to a user’s environment, such as the configuration and importance of the affected system. Each metric group has a set of metrics that are assigned values based on the vulnerability’s attributes. The values are then combined using a formula to produce a numerical score that ranges from 0 to 10, where 0 means no impact and 10 means critical impact. The score can also be translated into a qualitative rating that ranges from none to low, medium, high, and critical. CVSS provides a consistent and comprehensive way to estimate the severity of vulnerabilities and prioritize their remediation.
The other options are not components of the SCAP specification that contain the data required to estimate the severity of vulnerabilities identified by automated vulnerability assessments, but rather components that serve other purposes. Common Vulnerabilities and Exposures (CVE) is a component that provides a standardized and unique identifier and description for each publicly known vulnerability. CVE facilitates the sharing and comparison of vulnerability information across different sources and tools. Asset Reporting Format (ARF) is a component that provides a standardized and extensible format for expressing the information about the assets and their characteristics, such as configuration, vulnerabilities, and compliance. ARF enables the aggregation and correlation of asset information from different sources and tools. Open Vulnerability and Assessment Language (OVAL) is a component that provides a standardized and expressive language for defining and testing the state of a system for the presence of vulnerabilities, configuration issues, patches, and other aspects. OVAL enables the automation and interoperability of vulnerability assessment and management.
The use of private and public encryption keys is fundamental in the implementation of which of the following?
Diffie-Hellman algorithm
Secure Sockets Layer (SSL)
Advanced Encryption Standard (AES)
Message Digest 5 (MD5)
The use of private and public encryption keys is fundamental in the implementation of Secure Sockets Layer (SSL). SSL is a protocol that provides secure communication over the Internet by using public key cryptography and digital certificates. SSL works as follows:
The use of private and public encryption keys is fundamental in the implementation of SSL because it enables the authentication of the parties, the establishment of the shared secret key, and the protection of the data from eavesdropping, tampering, and replay attacks.
The other options are not protocols or algorithms that use private and public encryption keys in their implementation. Diffie-Hellman algorithm is a method for generating a shared secret key between two parties, but it does not use private and public encryption keys, but rather public and private parameters. Advanced Encryption Standard (AES) is a symmetric encryption algorithm that uses the same key for encryption and decryption, but it does not use private and public encryption keys, but rather a single secret key. Message Digest 5 (MD5) is a hash function that produces a fixed-length output from a variable-length input, but it does not use private and public encryption keys, but rather a one-way mathematical function.
Which technique can be used to make an encryption scheme more resistant to a known plaintext attack?
Hashing the data before encryption
Hashing the data after encryption
Compressing the data after encryption
Compressing the data before encryption
Compressing the data before encryption is a technique that can be used to make an encryption scheme more resistant to a known plaintext attack. A known plaintext attack is a type of cryptanalysis where the attacker has access to some pairs of plaintext and ciphertext encrypted with the same key, and tries to recover the key or decrypt other ciphertexts. A known plaintext attack can exploit the statistical properties or patterns of the plaintext or the ciphertext to reduce the search space or guess the key. Compressing the data before encryption can reduce the redundancy and increase the entropy of the plaintext, making it harder for the attacker to find any correlations or similarities between the plaintext and the ciphertext. Compressing the data before encryption can also reduce the size of the plaintext, making it more difficult for the attacker to obtain enough plaintext-ciphertext pairs for a successful attack.
The other options are not techniques that can be used to make an encryption scheme more resistant to a known plaintext attack, but rather techniques that can introduce other security issues or inefficiencies. Hashing the data before encryption is not a useful technique, as hashing is a one-way function that cannot be reversed, and the encrypted hash cannot be decrypted to recover the original data. Hashing the data after encryption is also not a useful technique, as hashing does not add any security to the encryption, and the hash can be easily computed by anyone who has access to the ciphertext. Compressing the data after encryption is not a recommended technique, as compression algorithms usually work better on uncompressed data, and compressing the ciphertext can introduce errors or vulnerabilities that can compromise the encryption.
Who in the organization is accountable for classification of data information assets?
Data owner
Data architect
Chief Information Security Officer (CISO)
Chief Information Officer (CIO)
The person in the organization who is accountable for the classification of data information assets is the data owner. The data owner is the person or entity that has the authority and responsibility for the creation, collection, processing, and disposal of a set of data. The data owner is also responsible for defining the purpose, value, and classification of the data, as well as the security requirements and controls for the data. The data owner should be able to determine the impact of the data on the mission of the organization, which means assessing the potential consequences of losing, compromising, or disclosing the data. The impact of the data on the mission of the organization is one of the main criteria for data classification, which helps to establish the appropriate level of protection and handling for the data. The data owner should also ensure that the data is properly labeled, stored, accessed, shared, and destroyed according to the data classification policy and procedures.
The other options are not the persons in the organization who are accountable for the classification of data information assets, but rather persons who have other roles or functions related to data management. The data architect is the person or entity that designs and models the structure, format, and relationships of the data, as well as the data standards, specifications, and lifecycle. The data architect supports the data owner by providing technical guidance and expertise on the data architecture and quality. The Chief Information Security Officer (CISO) is the person or entity that oversees the security strategy, policies, and programs of the organization, as well as the security performance and incidents. The CISO supports the data owner by providing security leadership and governance, as well as ensuring the compliance and alignment of the data security with the organizational objectives and regulations. The Chief Information Officer (CIO) is the person or entity that manages the information technology (IT) resources and services of the organization, as well as the IT strategy and innovation. The CIO supports the data owner by providing IT management and direction, as well as ensuring the availability, reliability, and scalability of the IT infrastructure and applications.
Which security service is served by the process of encryption plaintext with the sender’s private key and decrypting cipher text with the sender’s public key?
Confidentiality
Integrity
Identification
Availability
The security service that is served by the process of encrypting plaintext with the sender’s private key and decrypting ciphertext with the sender’s public key is identification. Identification is the process of verifying the identity of a person or entity that claims to be who or what it is. Identification can be achieved by using public key cryptography and digital signatures, which are based on the process of encrypting plaintext with the sender’s private key and decrypting ciphertext with the sender’s public key. This process works as follows:
The process of encrypting plaintext with the sender’s private key and decrypting ciphertext with the sender’s public key serves identification because it ensures that only the sender can produce a valid ciphertext that can be decrypted by the receiver, and that the receiver can verify the sender’s identity by using the sender’s public key. This process also provides non-repudiation, which means that the sender cannot deny sending the message or the receiver cannot deny receiving the message, as the ciphertext serves as a proof of origin and delivery.
The other options are not the security services that are served by the process of encrypting plaintext with the sender’s private key and decrypting ciphertext with the sender’s public key. Confidentiality is the process of ensuring that the message is only readable by the intended parties, and it is achieved by encrypting plaintext with the receiver’s public key and decrypting ciphertext with the receiver’s private key. Integrity is the process of ensuring that the message is not modified or corrupted during transmission, and it is achieved by using hash functions and message authentication codes. Availability is the process of ensuring that the message is accessible and usable by the authorized parties, and it is achieved by using redundancy, backup, and recovery mechanisms.
Which of the following mobile code security models relies only on trust?
Code signing
Class authentication
Sandboxing
Type safety
Code signing is the mobile code security model that relies only on trust. Mobile code is a type of software that can be transferred from one system to another and executed without installation or compilation. Mobile code can be used for various purposes, such as web applications, applets, scripts, macros, etc. Mobile code can also pose various security risks, such as malicious code, unauthorized access, data leakage, etc. Mobile code security models are the techniques that are used to protect the systems and users from the threats of mobile code. Code signing is a mobile code security model that relies only on trust, which means that the security of the mobile code depends on the reputation and credibility of the code provider. Code signing works as follows:
Code signing relies only on trust because it does not enforce any security restrictions or controls on the mobile code, but rather leaves the decision to the code consumer. Code signing also does not guarantee the quality or functionality of the mobile code, but rather the authenticity and integrity of the code provider. Code signing can be effective if the code consumer knows and trusts the code provider, and if the code provider follows the security standards and best practices. However, code signing can also be ineffective if the code consumer is unaware or careless of the code provider, or if the code provider is compromised or malicious.
The other options are not mobile code security models that rely only on trust, but rather on other techniques that limit or isolate the mobile code. Class authentication is a mobile code security model that verifies the permissions and capabilities of the mobile code based on its class or type, and allows or denies the execution of the mobile code accordingly. Sandboxing is a mobile code security model that executes the mobile code in a separate and restricted environment, and prevents the mobile code from accessing or affecting the system resources or data. Type safety is a mobile code security model that checks the validity and consistency of the mobile code, and prevents the mobile code from performing illegal or unsafe operations.
What is the second phase of Public Key Infrastructure (PKI) key/certificate life-cycle management?
Implementation Phase
Initialization Phase
Cancellation Phase
Issued Phase
The second phase of Public Key Infrastructure (PKI) key/certificate life-cycle management is the initialization phase. PKI is a system that uses public key cryptography and digital certificates to provide authentication, confidentiality, integrity, and non-repudiation for electronic transactions. PKI key/certificate life-cycle management is the process of managing the creation, distribution, usage, storage, revocation, and expiration of keys and certificates in a PKI system. The key/certificate life-cycle management consists of six phases: pre-certification, initialization, certification, operational, suspension, and termination. The initialization phase is the second phase, where the key pair and the certificate request are generated by the end entity or the registration authority (RA). The initialization phase involves the following steps:
The other options are not the second phase of PKI key/certificate life-cycle management, but rather other phases. The implementation phase is not a phase of PKI key/certificate life-cycle management, but rather a phase of PKI system deployment, where the PKI components and policies are installed and configured. The cancellation phase is not a phase of PKI key/certificate life-cycle management, but rather a possible outcome of the termination phase, where the key pair and the certificate are permanently revoked and deleted. The issued phase is not a phase of PKI key/certificate life-cycle management, but rather a possible outcome of the certification phase, where the CA verifies and approves the certificate request and issues the certificate to the end entity or the RA.
Reciprocal backup site agreements are considered to be
a better alternative than the use of warm sites.
difficult to test for complex systems.
easy to implement for similar types of organizations.
easy to test and implement for complex systems.
According to the CISSP Official (ISC)2 Practice Tests3, reciprocal backup site agreements are considered to be easy to implement for similar types of organizations. A backup site is a location or a facility that is used to restore the business operations and functions, as well as the supporting resources, such as data, systems, personnel, and facilities, in the event of a disaster that disrupts the normal operations of an organization. A backup site can be classified into different types or levels, based on the availability, functionality, and compatibility of the backup site, such as the hot site, the warm site, or the cold site. A reciprocal backup site agreement is a type of backup site agreement that is established between two or more organizations that have similar types or levels of backup sites, and that agree to provide or share their backup sites with each other in the event of a disaster that affects one or more of the organizations. A reciprocal backup site agreement is considered to be easy to implement for similar types of organizations, as it does not require a lot of resources, costs, or efforts to set up or maintain the backup site agreement, and as it provides a high level of compatibility and flexibility for the backup site agreement.
What is the PRIMARY difference between security policies and security procedures?
Policies are used to enforce violations, and procedures create penalties
Policies point to guidelines, and procedures are more contractual in nature
Policies are included in awareness training, and procedures give guidance
Policies are generic in nature, and procedures contain operational details
The primary difference between security policies and security procedures is that policies are generic in nature, and procedures contain operational details. Security policies are the high-level statements or rules that define the goals, objectives, and requirements of security for an organization. Security procedures are the low-level steps or actions that specify how to implement, enforce, and comply with the security policies.
References: CISSP All-in-One Exam Guide, Eighth Edition, Chapter 1, page 17; Official (ISC)2 CISSP CBK Reference, Fifth Edition, Chapter 1, page 13
When using Generic Routing Encapsulation (GRE) tunneling over Internet Protocol version 4 (IPv4), where is the GRE header inserted?
Into the options field
Between the delivery header and payload
Between the source and destination addresses
Into the destination address
Generic Routing Encapsulation (GRE) is a protocol that encapsulates a packet of one protocol type within another protocol type4. When using GRE tunneling over IPv4, the GRE header is inserted between the delivery header and the payload5. The delivery header contains the new source and destination IP addresses of the tunnel endpoints, while the payload contains the original IP packet4. The GRE header contains information such as protocol type, checksum, and key6.
Drag the following Security Engineering terms on the left to the BEST definition on the right.
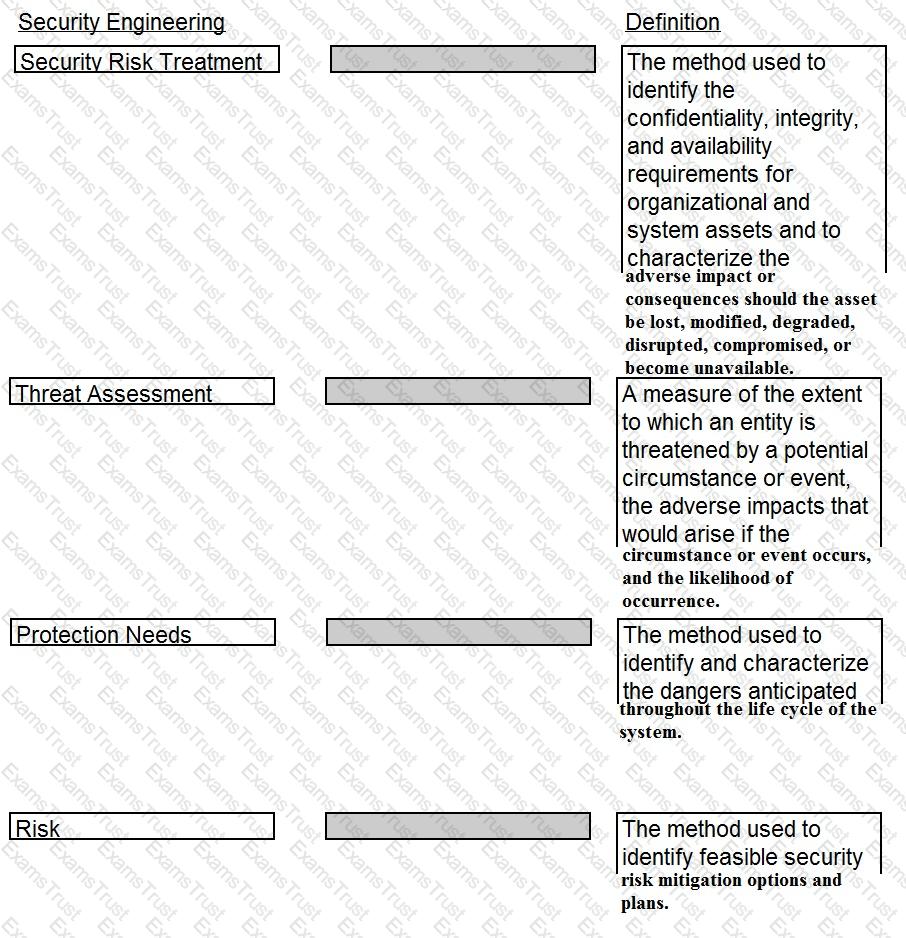
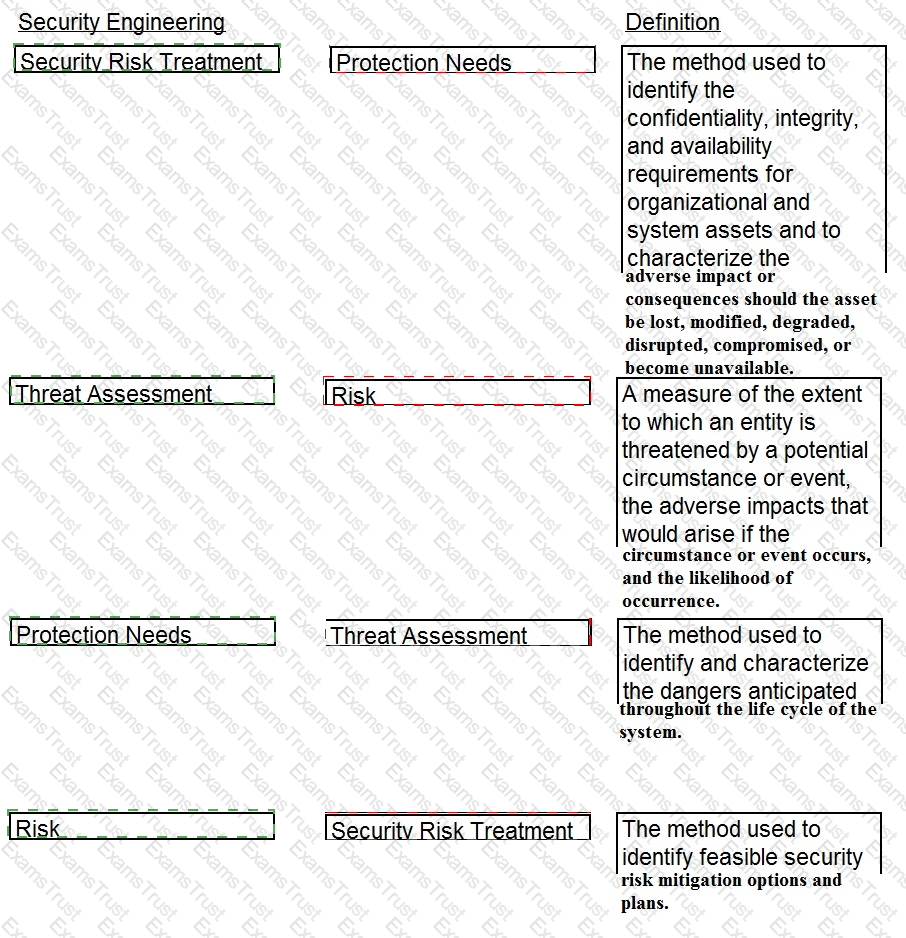
The correct matches are:
Comprehensive Explanation: These terms and definitions are based on the glossary of the Official (ISC)2 CISSP CBK Reference, Fifth Edition, Domain 3: Security Engineering, pp. 293-2941
References: Official (ISC)2 CISSP CBK Reference, Fifth Edition
Which of the following is the MOST important consideration when developing a Disaster Recovery Plan (DRP)?
The dynamic reconfiguration of systems
The cost of downtime
A recovery strategy for all business processes
A containment strategy
According to the CISSP All-in-One Exam Guide1, the most important consideration when developing a Disaster Recovery Plan (DRP) is to have a recovery strategy for all business processes. A DRP is a document that defines the procedures and actions to be taken in the event of a disaster that disrupts the normal operations of an organization. A recovery strategy is a plan that specifies how the organization will restore the critical business processes and functions, as well as the supporting resources, such as data, systems, personnel, and facilities, within the predefined recovery objectives and time frames. A recovery strategy should cover all business processes, not just the IT-related ones, as they may have interdependencies and impacts on each other. A recovery strategy should also be aligned with the business continuity plan (BCP), which is a document that defines the procedures and actions to be taken to ensure the continuity of the essential business operations during and after a disaster. The dynamic reconfiguration of systems is not the most important consideration when developing a DRP, although it may be a useful technique to enhance the resilience and availability of the systems. The dynamic reconfiguration of systems is the ability to change the configuration and functionality of the systems without interrupting their operations, such as adding, removing, or replacing components, modules, or services. The dynamic reconfiguration of systems may help to reduce the downtime and recovery time of the systems, but it does not address the recovery of the business processes and functions. The cost of downtime is not the most important consideration when developing a DRP, although it may be a factor that influences the recovery objectives and priorities. The cost of downtime is the amount of money that the organization loses or spends due to the disruption of its normal operations, such as loss of revenue, productivity, reputation, or customers, as well as the expenses for recovery, restoration, or compensation. The cost of downtime may help to justify the investment and budget for the DRP, but it does not address the recovery of the business processes and functions. A containment strategy is not the most important consideration when developing a DRP, although it may be a part of the incident response plan (IRP), which is a document that defines the procedures and actions to be taken to detect, analyze, contain, eradicate, and recover from a security incident. A containment strategy is a plan that specifies how the organization will isolate and control the incident, such as disconnecting the affected systems, blocking the malicious traffic, or changing the passwords. A containment strategy may help to prevent or limit the damage and spread of the incident, but it does not address the recovery of the business processes and functions. References: 1
Which of the following sets of controls should allow an investigation if an attack is not blocked by preventive controls or detected by monitoring?
Logging and audit trail controls to enable forensic analysis
Security incident response lessons learned procedures
Security event alert triage done by analysts using a Security Information and Event Management (SIEM) system
Transactional controls focused on fraud prevention
Logging and audit trail controls are designed to record and monitor the activities and events that occur on a system or network. They can provide valuable information for forensic analysis, such as the source, destination, time, and type of an event, the user or process involved, the data or resources accessed or modified, and the outcome or status of the event. Logging and audit trail controls can help identify the cause, scope, impact, and timeline of an attack, as well as the evidence and artifacts left by the attacker. They can also help determine the effectiveness and gaps of the preventive and detective controls, and support the incident response and recovery processes. Logging and audit trail controls should be configured, protected, and reviewed according to the organizational policies and standards, and comply with the legal and regulatory requirements.
A mobile device application that restricts the storage of user information to just that which is needed to accomplish lawful business goals adheres to what privacy principle?
Onward transfer
Collection Limitation
Collector Accountability
Individual Participation
Collection Limitation is the privacy principle that states that the collection of personal information should be limited, relevant, and lawful. It also implies that personal information should not be collected unless it is necessary for a specific purpose. This principle is aligned with the concept of data minimization, which means that only the minimum amount of data required to achieve a legitimate goal should be collected and processed. A mobile device application that restricts the storage of user information to just that which is needed to accomplish lawful business goals adheres to this principle by minimizing the amount of personal data it collects and stores. References: CISSP All-in-One Exam Guide, Eighth Edition, Chapter 1, page 35; Official (ISC)2 CISSP CBK Reference, Fifth Edition, Chapter 1, page 28
Order the below steps to create an effective vulnerability management process.
Changes to a Trusted Computing Base (TCB) system that could impact the security posture of that system and trigger a recertification activity are documented in the
security impact analysis.
structured code review.
routine self assessment.
cost benefit analysis.
Changes to a Trusted Computing Base (TCB) system that could impact the security posture of that system and trigger a recertification activity are documented in the security impact analysis. A TCB system is a system that consists of the hardware, software, and firmware components that enforce the security policy and protect the security-relevant information of the system. A TCB system is usually certified or accredited to meet certain security standards or criteria, such as the Common Criteria or the Trusted Computer System Evaluation Criteria (TCSEC). A security impact analysis is a document that describes the changes made to a TCB system, such as adding, modifying, or removing components or functions, and analyzes the potential effects of the changes on the security of the system, such as introducing new vulnerabilities, risks, or threats. A security impact analysis can help to determine whether the changes require a recertification or reaccreditation of the TCB system, or whether the changes can be accepted without affecting the security level or assurance of the system. The other options are not the documents that document the changes to a TCB system, but rather different types of documents. A structured code review is a document that records the results of a systematic and rigorous examination of the source code of a software component or system, such as a TCB system, to detect errors, bugs, or vulnerabilities. A structured code review can help to improve the quality, reliability, and security of the software, but it does not document the changes made to the software. A routine self assessment is a document that reports the findings and recommendations of a periodic and voluntary evaluation of the security controls and measures of a system or organization, such as a TCB system, to measure the effectiveness, efficiency, and compliance of the security. A routine self assessment can help to identify and address the security gaps, weaknesses, or issues, but it does not document the changes made to the system. A cost benefit analysis is a document that compares the costs and benefits of different security solutions or alternatives for a system or organization, such as a TCB system, to justify the investment in security. A cost benefit analysis can help to evaluate the trade-offs between the security costs and the security benefits, but it does not document the changes made to the system. References: CISSP All-in-One Exam Guide, Eighth Edition, Chapter 8, p. 416; Official (ISC)2 CISSP CBK Reference, Fifth Edition, Chapter 3, p. 149.
Which of the following is a strategy of grouping requirements in developing a Security Test and Evaluation (ST&E)?
Tactical, strategic, and financial
Management, operational, and technical
Documentation, observation, and manual
Standards, policies, and procedures
According to the CISSP Official (ISC)2 Practice Tests3, a strategy of grouping requirements in developing a Security Test and Evaluation (ST&E) is management, operational, and technical. ST&E is the process of verifying and validating the security posture and effectiveness of a system, network, or application, by conducting various tests and evaluations on the security controls and mechanisms that are implemented on them. The requirements for ST&E are the criteria and standards that define the scope, objectives, methods, and deliverables of the ST&E process, as well as the roles and responsibilities of the stakeholders involved. The requirements for ST&E can be grouped into three categories: management, operational, and technical. Management requirements are the requirements that relate to the planning, coordination, and oversight of the ST&E process, such as the budget, schedule, resources, policies, and procedures. Operational requirements are the requirements that relate to the functionality, performance, and usability of the system, network, or application, as well as the security services and processes that support them, such as availability, reliability, scalability, backup, recovery, and incident response. Technical requirements are the requirements that relate to the design, implementation, and configuration of the system, network, or application, as well as the security controls and mechanisms that protect them, such as encryption, authentication, authorization, auditing, and logging. Tactical, strategic, and financial is not a strategy of grouping requirements in developing a ST&E, although they may be factors that influence the requirements. Tactical, strategic, and financial are terms that describe the level, scope, and purpose of the decisions and actions that are taken by the organization, such as the goals, objectives, plans, and resources. Documentation, observation, and manual is not a strategy of grouping requirements in developing a ST&E, although they may be methods or techniques that are used in the ST&E process. Documentation is the process of creating and maintaining the records and reports of the ST&E process, such as the test plan, test cases, test results, and test analysis. Observation is the process of monitoring and inspecting the system, network, or application, as well as the security controls and mechanisms, during the ST&E process, such as using tools, sensors, or cameras. Manual is the process of performing the ST&E process manually, without using any automated tools or scripts, such as using human testers, checklists, or interviews. Standards, policies, and procedures is not a strategy of grouping requirements in developing a ST&E, although they may be sources or references that are used in the ST&E process. Standards, policies, and procedures are the documents that define the rules, principles, and guidelines for the security of the system, network, or application, as well as the ST&E process, such as the security requirements, best practices, and compliance criteria. References: 3
After a thorough analysis, it was discovered that a perpetrator compromised a network by gaining access to the network through a Secure Socket Layer (SSL) Virtual Private Network (VPN) gateway. The perpetrator guessed a username and brute forced the password to gain access. Which of the following BEST mitigates this issue?
Implement strong passwords authentication for VPN
Integrate the VPN with centralized credential stores
Implement an Internet Protocol Security (IPSec) client
Use two-factor authentication mechanisms
The best way to mitigate the issue of a perpetrator compromising a network by gaining access to the network through an SSL VPN gateway by guessing a username and brute forcing the password is to use two-factor authentication mechanisms. Two-factor authentication is a method of verifying the identity of a user or device by requiring two different types of factors, such as something the user knows (e.g., password, PIN, etc.), something the user has (e.g., token, smart card, etc.), or something the user is (e.g., biometric, fingerprint, etc.). Two-factor authentication can enhance the security of the network access by making it harder for attackers to impersonate or compromise the legitimate users or devices. If the perpetrator only knows the username and password, they will not be able to access the network without the second factor, such as a token or a biometric34 References: CISSP All-in-One Exam Guide, Eighth Edition, Chapter 6: Communication and Network Security, p. 321; Official (ISC)2 CISSP CBK Reference, Fifth Edition, Domain 4: Communication and Network Security, p. 449.
Which of the following standards/guidelines requires an Information Security Management System (ISMS) to be defined?
International Organization for Standardization (ISO) 27000 family
Information Technology Infrastructure Library (ITIL)
Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard (PCIDSS)
ISO/IEC 20000
The International Organization for Standardization (ISO) 27000 family of standards/guidelines requires an Information Security Management System (ISMS) to be defined. An ISMS is a systematic approach to managing the security of information assets, such as data, systems, processes, and people. An ISMS includes policies, procedures, controls, and activities that aim to protect the confidentiality, integrity, and availability of information, as well as to comply with the legal and regulatory requirements. The ISO 27000 family provides best practices and guidance for establishing, implementing, maintaining, and improving an ISMS. The ISO 27001 standard specifies the requirements for an ISMS, while the other standards in the family provide more detailed or specific guidance on different aspects of information security34 References: CISSP All-in-One Exam Guide, Eighth Edition, Chapter 1: Security and Risk Management, p. 23; Official (ISC)2 CISSP CBK Reference, Fifth Edition, Domain 1: Security and Risk Management, p. 25.
Which of the following roles has the obligation to ensure that a third party provider is capable of processing and handling data in a secure manner and meeting the standards set by the organization?
Data Custodian
Data Owner
Data Creator
Data User
The role that has the obligation to ensure that a third party provider is capable of processing and handling data in a secure manner and meeting the standards set by the organization is the data owner. A data owner is a person or an entity that has the authority or the responsibility for the data or the information within an organization, and that determines or defines the classification, the usage, the protection, or the retention of the data or the information. A data owner has the obligation to ensure that a third party provider is capable of processing and handling data in a secure manner and meeting the standards set by the organization, as the data owner is ultimately accountable or liable for the security or the quality of the data or the information, regardless of who processes or handles the data or the information. A data owner can ensure that a third party provider is capable of processing and handling data in a secure manner and meeting the standards set by the organization, by performing the tasks or the functions such as conducting due diligence, establishing service level agreements, defining security requirements, monitoring performance, or auditing compliance. References: CISSP All-in-One Exam Guide, Eighth Edition, Chapter 2, page 61; Official (ISC)2 CISSP CBK Reference, Fifth Edition, Chapter 2, page 67
Which of the following would BEST describe the role directly responsible for data within an organization?
Data custodian
Information owner
Database administrator
Quality control
According to the CISSP For Dummies, the role that is directly responsible for data within an organization is the information owner. The information owner is the person or role that has the authority and accountability for the data or information that the organization owns, creates, uses, or maintains, such as data, documents, records, or intellectual property. The information owner is responsible for defining the classification, value, and sensitivity of the data or information, as well as the security requirements, policies, and standards for the data or information. The information owner is also responsible for granting or revoking the access rights and permissions to the data or information, as well as for monitoring and auditing the compliance and effectiveness of the security controls and mechanisms for the data or information. The data custodian is not the role that is directly responsible for data within an organization, although it may be a role that supports or assists the information owner. The data custodian is the person or role that has the responsibility for implementing and maintaining the security controls and mechanisms for the data or information, as defined by the information owner. The data custodian is responsible for performing the technical and operational tasks and activities for the data or information, such as backup, recovery, encryption, or disposal. The database administrator is not the role that is directly responsible for data within an organization, although it may be a role that supports or assists the information owner or the data custodian. The database administrator is the person or role that has the responsibility for managing and administering the database system that stores and processes the data or information. The database administrator is responsible for performing the technical and operational tasks and activities for the database system, such as installation, configuration, optimization, or troubleshooting.
What is the difference between media marking and media labeling?
Media marking refers to the use of human-readable security attributes, while media labeling refers to the use of security attributes in internal data structures.
Media labeling refers to the use of human-readable security attributes, while media marking refers to the use of security attributes in internal data structures.
Media labeling refers to security attributes required by public policy/law, while media marking refers to security required by internal organizational policy.
Media marking refers to security attributes required by public policy/law, while media labeling refers to security attributes required by internal organizational policy.
According to the CISSP CBK Official Study Guide1, the difference between media marking and media labeling is that media labeling refers to the use of human-readable security attributes, while media marking refers to the use of security attributes in internal data structures. Media marking and media labeling are two methods or techniques of applying security attributes to the media, which are the physical or tangible devices or materials that store or contain the data or information, such as the disks, tapes, or papers. Security attributes are the tags or markers that indicate the classification, sensitivity, or clearance of the media, data, or information, such as top secret, secret, or confidential. Security attributes help to protect the media, data, or information from unauthorized or unintended access, disclosure, modification, corruption, loss, or theft, as well as to support the access control and audit mechanisms. Media labeling is the method or technique of applying security attributes to the media in a human-readable form, such as the words, symbols, or colors that are printed, stamped, or affixed on the media. Media labeling helps to identify and distinguish the media, data, or information based on their security attributes, as well as to inform and instruct the users or handlers of the media, data, or information about the proper and secure handling and disposal of them. Media marking is the method or technique of applying security attributes to the media in an internal data structure form, such as the bits, bytes, or fields that are embedded, encoded, or encrypted in the media. Media marking helps to verify and validate the media, data, or information based on their security attributes, as well as to enforce and monitor the access control and audit mechanisms for them. Media marking refers to security attributes required by public policy/law, while media labeling refers to security required by internal organizational policy is not the difference between media marking and media labeling, as it is not related to the form or format of the security attributes, but to the source or authority of the security attributes. Media marking and media labeling may both refer to security attributes required by public policy/law, such as the Controlled Unclassified Information (CUI) or the Personal Identifiable Information (PII), or to security attributes required by internal organizational policy, such as the proprietary or confidential information. The difference between media marking and media labeling is not based on who or what requires the security attributes, but on how the security attributes are applied or represented on the media.
During the risk assessment phase of the project the CISO discovered that a college within the University is collecting Protected Health Information (PHI) data via an application that was developed in-house. The college collecting this data is fully aware of the regulations for Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA) and is fully compliant.
What is the best approach for the CISO?
Below are the common phases to creating a Business Continuity/Disaster Recovery (BC/DR) plan. Drag the remaining BC\DR phases to the appropriate corresponding location.
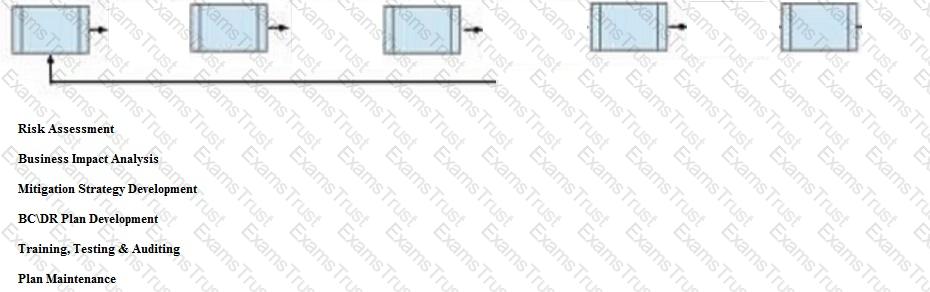


The common phases to creating a Business Continuity/Disaster Recovery (BC/DR) plan are as follows:
The image that you sent shows a flowchart or process diagram with five empty boxes connected by arrows, indicating a sequence of steps. The boxes are placeholders for the phases of the BC/DR plan. Below the image, there is a list of the phases of the BC/DR plan. To complete the image, you need to drag the phases from the list to the appropriate boxes in the diagram. The correct order of the phases is as follows:
The phase of Plan Maintenance is not shown in the image, but it is an ongoing and continuous phase that should be performed after the completion of the other phases.
Which of the following BEST describes a rogue Access Point (AP)?
An AP that is not protected by a firewall
An AP not configured to use Wired Equivalent Privacy (WEP) with Triple Data Encryption Algorithm (3DES)
An AP connected to the wired infrastructure but not under the management of authorized network administrators
An AP infected by any kind of Trojan or Malware
A rogue Access Point (AP) is an AP connected to the wired infrastructure but not under the management of authorized network administrators. A rogue AP can pose a serious security threat, as it can allow unauthorized access to the network, bypass security controls, and expose sensitive data. The other options are not correct descriptions of a rogue AP. Option A is a description of an unsecured AP, which is an AP that is not protected by a firewall or other security measures. Option B is a description of an outdated AP, which is an AP not configured to use Wired Equivalent Privacy (WEP) with Triple Data Encryption Algorithm (3DES), which are weak encryption methods that can be easily cracked. Option D is a description of a compromised AP, which is an AP infected by any kind of Trojan or Malware, which can cause malicious behavior or damage to the network. References: CISSP All-in-One Exam Guide, Eighth Edition, Chapter 6, p. 325; Official (ISC)2 CISSP CBK Reference, Fifth Edition, Chapter 4, p. 241.
Which of the following is a function of Security Assertion Markup Language (SAML)?
File allocation
Redundancy check
Extended validation
Policy enforcement
A function of Security Assertion Markup Language (SAML) is policy enforcement. SAML is an XML-based standard for exchanging authentication and authorization information between different entities, such as service providers and identity providers. SAML enables policy enforcement by allowing the service provider to specify the security requirements and conditions for accessing its resources, and allowing the identity provider to assert the identity and attributes of the user who requests access. The other options are not functions of SAML, but rather different concepts or technologies. File allocation is the process of assigning disk space to files. Redundancy check is a method of detecting errors in data transmission or storage. Extended validation is a type of certificate that provides a higher level of assurance for the identity of the website owner. References: CISSP All-in-One Exam Guide, Eighth Edition, Chapter 5, p. 283; Official (ISC)2 CISSP CBK Reference, Fifth Edition, Chapter 6, p. 361.
Which of the following approaches is the MOST effective way to dispose of data on multiple hard drives?
Delete every file on each drive.
Destroy the partition table for each drive using the command line.
Degauss each drive individually.
Perform multiple passes on each drive using approved formatting methods.
According to the CISSP Official (ISC)2 Practice Tests3, the most effective way to dispose of data on multiple hard drives is to perform multiple passes on each drive using approved formatting methods. This means that the data on the hard drives should be overwritten with random or meaningless patterns several times, using software tools or commands that follow the standards and guidelines for secure data erasure. This can ensure that the data on the hard drives is irrecoverable and unreadable, even by using advanced forensic techniques or tools. Deleting every file on each drive is not an effective way to dispose of data on multiple hard drives, as it does not actually erase the data, but only removes the pointers or references to the data. The data can still be recovered and read by using undelete or recovery tools, or by accessing the slack or unallocated space on the drive. Destroying the partition table for each drive using the command line is not an effective way to dispose of data on multiple hard drives, as it does not actually erase the data, but only removes the information about how the drive is divided into logical sections. The data can still be recovered and read by using partition recovery tools, or by accessing the raw data on the drive. Degaussing each drive individually is not an effective way to dispose of data on multiple hard drives, as it may not work on modern hard drives that use perpendicular recording technology. Degaussing is a process that uses a strong magnetic field to erase the data on magnetic media, such as tapes or disks. However, modern hard drives have higher coercivity, which means they require a stronger magnetic field to be erased, and degaussing may not be able to generate such a field. Degaussing may also damage the hard drive components and render them unusable. References: 3
A global organization wants to implement hardware tokens as part of a multifactor authentication solution for remote access. The PRIMARY advantage of this implementation is
the scalability of token enrollment.
increased accountability of end users.
it protects against unauthorized access.
it simplifies user access administration.
The primary advantage of implementing hardware tokens as part of a multifactor authentication solution for remote access is that it protects against unauthorized access by requiring the user to possess something (the token) and to know something (the PIN or password) to authenticate. Hardware tokens are physical devices that generate one-time passwords (OTP) or digital certificates that are used in conjunction with a personal identification number (PIN) or a password to verify the user’s identity.
References: CISSP All-in-One Exam Guide, Eighth Edition, Chapter 5, page 274; Official (ISC)2 CISSP CBK Reference, Fifth Edition, Chapter 5, page 223
In which order, from MOST to LEAST impacted, does user awareness training reduce the occurrence of the events below?
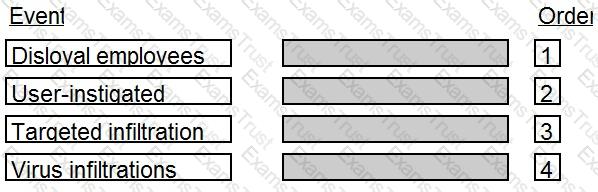

The correct order is:
Comprehensive Explanation: User awareness training is a process of educating and informing users about the security policies, procedures, and best practices of an organization. User awareness training can help reduce the occurrence of security events by increasing the users’ knowledge, skills, and attitude towards security. User awareness training can have different impacts on different types of security events, depending on the nature and source of the events. The order of impact from most to least is as follows:
References: CISSP All-in-One Exam Guide, Eighth Edition, Chapter 7: Security Operations, p. 440; Official (ISC)2 CISSP CBK Reference, Fifth Edition, Domain 7: Security Operations, p. 852.
Which of the following is a recommended alternative to an integrated email encryption system?
Sign emails containing sensitive data
Send sensitive data in separate emails
Encrypt sensitive data separately in attachments
Store sensitive information to be sent in encrypted drives
The recommended alternative to an integrated email encryption system is to encrypt sensitive data separately in attachments. An integrated email encryption system is a system or a service that provides or offers the encryption or the protection for the email messages or the email communications, by using or applying the cryptographic techniques or the mechanisms, such as the public key encryption, the symmetric key encryption, or the digital signatures. An integrated email encryption system can protect the confidentiality, the integrity, or the authenticity of the email messages or the email communications, as it can prevent or reduce the risk of unauthorized or inappropriate access, disclosure, modification, or spoofing of the email messages or the email communications by the third parties or the attackers who intercept or capture the email messages or the email communications over the network. However, an integrated email encryption system can also have some limitations or challenges, such as the compatibility, the usability, or the cost. Therefore, the recommended alternative to an integrated email encryption system is to encrypt sensitive data separately in attachments, which means that instead of encrypting the entire email message or the email communication, only the sensitive data or the information that is attached or appended to the email message or the email communication, such as the documents, the files, or the images, are encrypted or protected, using the cryptographic techniques or the mechanisms, such as the password, the passphrase, or the key. Encrypting sensitive data separately in attachments can provide a similar level of security or protection for the email messages or the email communications, as it can prevent or reduce the risk of unauthorized or inappropriate access, disclosure, modification, or spoofing of the sensitive data or the information by the third parties or the attackers who intercept or capture the email messages or the email communications over the network, and it can also overcome or address some of the limitations or challenges of the integrated email encryption system, such as the compatibility, the usability, or the cost. References: CISSP All-in-One Exam Guide, Eighth Edition, Chapter 4, page 116; Official (ISC)2 CISSP CBK Reference, Fifth Edition, Chapter 4, page 173
Which of the following information MUST be provided for user account provisioning?
Full name
Unique identifier
Security question
Date of birth
According to the CISSP CBK Official Study Guide1, the information that must be provided for user account provisioning is the unique identifier. User account provisioning is the process of creating, managing, and deleting user accounts or identities in the system or the network, by using or applying the appropriate methods or mechanisms, such as the policies, procedures, or tools of the system or the network. User account provisioning helps to ensure the security or the integrity of the system or the network, as well as the resources, data, or information that are accessed or used by the user accounts or identities, by enforcing or implementing the principles or the concepts of the identification, authentication, authorization, or accountability of the user accounts or identities. The information that must be provided for user account provisioning is the unique identifier, as it is the essential or the fundamental component or element of the user account or identity, which is used or applied to identify or distinguish the user account or identity from other user accounts or identities in the system or the network, such as the username, the email address, or the employee number of the user account or identity. The unique identifier helps to ensure the security or the integrity of the system or the network, as well as the resources, data, or information that are accessed or used by the user account or identity, by preventing or avoiding the duplication, confusion, or collision of the user account or identity with other user accounts or identities in the system or the network, which may lead to the attacks or threats that may compromise or harm the system or the network, such as the impersonation, spoofing, or masquerading of the user account or identity. Full name is not the information that must be provided for user account provisioning, although it may be a benefit or a consequence of providing the unique identifier. Full name is the information that consists of the first name, middle name, and last name of the user account or identity, which is used or applied to represent or display the user account or identity in the system or the network, such as the John Smith, Jane Doe, or Alice Cooper of the user account or identity. Full name helps to provide a more human or personal touch or factor to the user account or identity, as well as to facilitate or enhance the communication or the interaction of the user account or identity with other user accounts or identities in the system or the network. Full name may be a benefit or a consequence of providing the unique identifier, as the unique identifier may be derived or generated from the full name, or the full name may be associated or linked with the unique identifier, of the user account or identity. However, full name is not the information that must be provided for user account provisioning, as it is not the essential or the fundamental component or element of the user account or identity, which is used or applied to identify or distinguish the user account or identity from other user accounts or identities in the system or the network. Security question is not the information that must be provided for user account provisioning, although it may be a benefit or a consequence of providing the unique identifier. Security question is the information that consists of a question and an answer that are related or relevant to the user account or identity, which are used or applied to verify or confirm the user account or identity in the system or the network, such as the What is your mother’s maiden name?, What is your favorite color?, or What is the name of your first pet? of the user account or identity. Security question helps to provide an additional layer or level of security or protection to the user account or identity, as well as to facilitate or enhance the recovery or the reset of the user account or identity in the system or the network, in the event of the loss, forgetfulness, or compromise of the user account or identity, such as the password, username, or email address of the user account or identity. Security question may be a benefit or a consequence of providing the unique identifier, as the security question may be derived or generated from the unique identifier, or the security question may be associated or linked with the unique identifier, of the user account or identity. However, security question is not the information that must be provided for user account provisioning, as it is not the essential or the fundamental component or element of the user account or identity, which is used or applied to identify or distinguish the user account or identity from other user accounts or identities in the system or the network. Date of birth is not the information that must be provided for user account provisioning, although it may be a benefit or a consequence of providing the unique identifier. Date of birth is the information that consists of the day, month, and year of the birth of the user account or identity, which is used or applied to represent or display the age or the birthday of the user account or identity in the system or the network, such as the 01/01/2000, 31/12/1999, or 29/02/2000 of the user account or identity. Date of birth helps to provide a more human or personal touch or factor to the user account or identity, as well as to facilitate or enhance the communication or the interaction of the user account or identity with other user accounts or identities in the system or the network. Date of birth may be a benefit or a consequence of providing the unique identifier, as the date of birth may be derived or generated from the unique identifier, or the date of birth may be associated or linked with the unique identifier, of the user account or identity. However, date of birth is not the information that must be provided for user account provisioning, as it is not the essential or the fundamental component or element of the user account or identity, which is used or applied to identify or distinguish the user account or identity from other user accounts or identities in the system or the network. References: 1
Which of the following BEST describes a chosen plaintext attack?
The cryptanalyst can generate ciphertext from arbitrary text.
The cryptanalyst examines the communication being sent back and forth.
The cryptanalyst can choose the key and algorithm to mount the attack.
The cryptanalyst is presented with the ciphertext from which the original message is determined.
According to the CISSP CBK Official Study Guide, a chosen plaintext attack is a type of cryptanalysis that allows the cryptanalyst to generate ciphertext from arbitrary text. A cryptanalysis is the process of breaking or analyzing a cryptographic system or algorithm, by finding the plaintext, the key, or the algorithm from the ciphertext, or by exploiting the weaknesses or vulnerabilities of the system or algorithm. A chosen plaintext attack is a scenario where the cryptanalyst has access to the encryption function or device, and can choose any plaintext and obtain the corresponding ciphertext. A chosen plaintext attack can help the cryptanalyst to deduce the key or the algorithm, or to create a codebook or a dictionary that maps the plaintext to the ciphertext. The cryptanalyst does not examine the communication being sent back and forth, as this would be a ciphertext-only attack, where the cryptanalyst only has access to the ciphertext, and tries to infer the plaintext, the key, or the algorithm from the statistical or linguistic analysis of the ciphertext. The cryptanalyst does not choose the key and algorithm to mount the attack, as this would be a known plaintext attack, where the cryptanalyst has access to some pairs of plaintext and ciphertext that are encrypted with the same key and algorithm, and tries to find the key or the algorithm from the correlation or pattern between the plaintext and the ciphertext. The cryptanalyst is not presented with the ciphertext from which the original message is determined, as this would be a decryption problem, where the cryptanalyst has access to the ciphertext and the key or the algorithm, and tries to recover the plaintext from the ciphertext.
If compromised, which of the following would lead to the exploitation of multiple virtual machines?
Virtual device drivers
Virtual machine monitor
Virtual machine instance
Virtual machine file system
If compromised, the virtual machine monitor would lead to the exploitation of multiple virtual machines. The virtual machine monitor, also known as the hypervisor, is the software layer that creates and manages the virtual machines on a physical host. The virtual machine monitor controls the allocation and distribution of the hardware resources, such as CPU, memory, disk, and network, among the virtual machines. The virtual machine monitor also provides the isolation and separation of the virtual machines from each other and from the physical host. If the virtual machine monitor is compromised, the attacker can gain access to all the virtual machines and their data, as well as the physical host and its resources.
References: CISSP All-in-One Exam Guide, Eighth Edition, Chapter 5, page 269; Official (ISC)2 CISSP CBK Reference, Fifth Edition, Chapter 5, page 234
The World Trade Organization's (WTO) agreement on Trade-Related Aspects of Intellectual Property Rights (TRIPS) requires authors of computer software to be given the
right to refuse or permit commercial rentals.
right to disguise the software's geographic origin.
ability to tailor security parameters based on location.
ability to confirm license authenticity of their works.
The World Trade Organization’s (WTO) agreement on Trade-Related Aspects of Intellectual Property Rights (TRIPS) requires authors of computer software to be given the right to refuse or permit commercial rentals. TRIPS is an international treaty that sets the minimum standards and rules for the protection and enforcement of intellectual property rights, such as patents, trademarks, or copyrights. TRIPS requires authors of computer software to be given the right to refuse or permit commercial rentals, which means that they can control whether their software can be rented or leased to others for profit. This right is intended to prevent the unauthorized copying or distribution of the software, and to ensure that the authors receive fair compensation for their work. The other options are not the rights that TRIPS requires authors of computer software to be given, but rather different or irrelevant concepts. The right to disguise the software’s geographic origin is not a right, but rather a violation, of TRIPS, as it can mislead or deceive the consumers or authorities about the source or quality of the software. The ability to tailor security parameters based on location is not a right, but rather a feature, of some software, such as encryption or authentication software, that can adjust the security settings or functions according to the location or jurisdiction of the user or device. The ability to confirm license authenticity of their works is not a right, but rather a benefit, of some software, such as digital rights management or anti-piracy software, that can verify or validate the license or ownership of the software. References: CISSP All-in-One Exam Guide, Eighth Edition, Chapter 1, p. 40; Official (ISC)2 CISSP CBK Reference, Fifth Edition, Chapter 5, p. 302.
What type of wireless network attack BEST describes an Electromagnetic Pulse (EMP) attack?
Radio Frequency (RF) attack
Denial of Service (DoS) attack
Data modification attack
Application-layer attack
A Denial of Service (DoS) attack is a type of wireless network attack that aims to prevent legitimate users from accessing or using a wireless network or service. An Electromagnetic Pulse (EMP) attack is a specific form of DoS attack that involves generating a powerful burst of electromagnetic energy that can damage or disrupt electronic devices and systems, including wireless networks. An EMP attack can cause permanent or temporary loss of wireless network availability, functionality, or performance. A Radio Frequency (RF) attack is a type of wireless network attack that involves interfering with or jamming the radio signals used by wireless devices and networks, but it does not necessarily involve an EMP. A data modification attack is a type of wireless network attack that involves altering or tampering with the data transmitted or received over a wireless network, but it does not necessarily cause a DoS. An application-layer attack is a type of wireless network attack that targets the applications or services running on a wireless network, such as web servers or email servers, but it does not necessarily involve an EMP.
The application of a security patch to a product previously validate at Common Criteria (CC) Evaluation Assurance Level (EAL) 4 would
require an update of the Protection Profile (PP).
require recertification.
retain its current EAL rating.
reduce the product to EAL 3.
Common Criteria (CC) is an international standard for evaluating the security of IT products and systems. Evaluation Assurance Level (EAL) is a numerical grade that indicates the level of assurance and rigor of the evaluation process. EAL ranges from 1 (lowest) to 7 (highest). A product that has been validated at EAL 4 has been methodically designed, tested, and reviewed, and provides a moderate level of independently assured security. The application of a security patch to a product previously validated at EAL 4 would require recertification, as the patch may introduce new vulnerabilities or affect the security functionality of the product. The recertification process would ensure that the patched product still meets the EAL 4 requirements and does not compromise the security claims of the original evaluation. Updating the Protection Profile (PP), retaining the current EAL rating, or reducing the product to EAL 3 are not valid options, as they do not reflect the impact of the security patch on the product’s security assurance.
What maintenance activity is responsible for defining, implementing, and testing updates to application systems?
Program change control
Regression testing
Export exception control
User acceptance testing
Program change control is the maintenance activity that is responsible for defining, implementing, and testing updates to application systems. Program change control ensures that the changes are authorized, documented, reviewed, tested, and approved before being deployed to the production environment. Program change control also maintains a record of the changes and their impact on the system . References: : CISSP All-in-One Exam Guide, Eighth Edition, Chapter 8, page 823. : CISSP For Dummies, 7th Edition, Chapter 8, page 263.
The type of authorized interactions a subject can have with an object is
control.
permission.
procedure.
protocol.
Permission is the type of authorized interactions a subject can have with an object. Permission is a rule or a setting that defines the specific actions or operations that a subject can perform on an object, such as read, write, execute, or delete1. Permission is usually granted by the owner or the administrator of the object, and can be based on the identity, role, or group membership of the subject. Control, procedure, and protocol are not types of authorized interactions a subject can have with an object, as they are related to different aspects of access control or security. References: 1: CISSP All-in-One Exam Guide, Eighth Edition, Chapter 6, page 355.
Which of the following does Temporal Key Integrity Protocol (TKIP) support?
Multicast and broadcast messages
Coordination of IEEE 802.11 protocols
Wired Equivalent Privacy (WEP) systems
Synchronization of multiple devices
Temporal Key Integrity Protocol (TKIP) supports multicast and broadcast messages by using a group temporal key that is shared by all the devices in the same wireless network. This key is used to encrypt and decrypt the messages that are sent to multiple recipients at once. TKIP also supports unicast messages by using a pairwise temporal key that is unique for each device and session. TKIP does not support coordination of IEEE 802.11 protocols, as it is a protocol itself that was designed to replace WEP. TKIP is compatible with WEP systems, but it does not support them, as it provides more security features than WEP. TKIP does not support synchronization of multiple devices, as it does not provide any clock or time synchronization mechanism . References: 1: Temporal Key Integrity Protocol - Wikipedia 2: Wi-Fi Security: Should You Use WPA2-AES, WPA2-TKIP, or Both? - How-To Geek
In a basic SYN flood attack, what is the attacker attempting to achieve?
Exceed the threshold limit of the connection queue for a given service
Set the threshold to zero for a given service
Cause the buffer to overflow, allowing root access
Flush the register stack, allowing hijacking of the root account
A SYN flood attack is a type of denial-of-service attack that exploits the TCP three-way handshake process. The attacker sends a large number of SYN packets to the target server, often with spoofed IP addresses, and does not complete the handshake by sending the final ACK packet. This causes the server to allocate resources for half-open connections, which eventually consume all the available ports and prevent legitimate traffic from reaching the server
As one component of a physical security system, an Electronic Access Control (EAC) token is BEST known for its ability to
overcome the problems of key assignments.
monitor the opening of windows and doors.
trigger alarms when intruders are detected.
lock down a facility during an emergency.
An Electronic Access Control (EAC) token is best known for its ability to overcome the problems of key assignments in a physical security system. An EAC token is a device that can be used to authenticate a user or grant access to a physical area or resource, such as a door, a gate, or a locker2. An EAC token can be a smart card, a magnetic stripe card, a proximity card, a key fob, or a biometric device. An EAC token can overcome the problems of key assignments, which are the issues or challenges of managing and distributing physical keys to authorized users, such as lost, stolen, duplicated, or unreturned keys. An EAC token can provide more security, convenience, and flexibility than a physical key, as it can be easily activated, deactivated, or replaced, and it can also store additional information or perform other functions. Monitoring the opening of windows and doors, triggering alarms when intruders are detected, and locking down a facility during an emergency are not the abilities that an EAC token is best known for, as they are more related to the functions of other components of a physical security system, such as sensors, alarms, or locks. References: 2: CISSP For Dummies, 7th Edition, Chapter 9, page 253.
The use of strong authentication, the encryption of Personally Identifiable Information (PII) on database servers, application security reviews, and the encryption of data transmitted across networks provide
data integrity.
defense in depth.
data availability.
non-repudiation.
Defense in depth is a security strategy that involves applying multiple layers of protection to a system or network to prevent or mitigate attacks. The use of strong authentication, the encryption of Personally Identifiable Information (PII) on database servers, application security reviews, and the encryption of data transmitted across networks are examples of defense in depth measures that can enhance the security of the system or network.
A, C, and D are incorrect because they are not the best terms to describe the security strategy. Data integrity is a property of data that ensures its accuracy, consistency, and validity. Data availability is a property of data that ensures its accessibility and usability. Non-repudiation is a property of data that ensures its authenticity and accountability. While these properties are important for security, they are not the same as defense in depth.
When implementing controls in a heterogeneous end-point network for an organization, it is critical that
hosts are able to establish network communications.
users can make modifications to their security software configurations.
common software security components be implemented across all hosts.
firewalls running on each host are fully customizable by the user.
A heterogeneous end-point network is a network that consists of different types of devices, such as computers, tablets, smartphones, printers, etc., that connect to the network and communicate with each other. Each device, or host, may have different operating systems, applications, configurations, and security requirements. When implementing controls in a heterogeneous end-point network, it is critical that common software security components be implemented across all hosts. Common software security components are software programs or features that provide security functions, such as antivirus, firewall, encryption, authentication, etc. Implementing common software security components across all hosts ensures that the hosts have a consistent and minimum level of security protection, and that the hosts can interoperate securely with each other and with the network. Implementing common software security components across all hosts does not mean that the hosts have to be identical or have the same security settings. The hosts can still have different hardware, software, and security configurations, as long as they meet the security requirements and standards of the organization and the network. Implementing common software security components across all hosts is not the same as ensuring that hosts are able to establish network communications, allowing users to make modifications to their security software configurations, or making firewalls running on each host fully customizable by the user. These are other aspects of security management that may or may not be relevant or desirable for a heterogeneous end-point network, depending on the organization’s policies and objectives.
The process of mutual authentication involves a computer system authenticating a user and authenticating the
user to the audit process.
computer system to the user.
user's access to all authorized objects.
computer system to the audit process.
Mutual authentication is the process of verifying the identity of both parties in a communication. The computer system authenticates the user by verifying their credentials, such as username and password, biometrics, or tokens. The user authenticates the computer system by verifying its identity, such as a digital certificate, a trusted third party, or a challenge-response mechanism34. References: 3: CISSP All-in-One Exam Guide, Eighth Edition, Chapter 5, page 5154: CISSP For Dummies, 7th Edition, Chapter 5, page 151.
Which of the following is an effective method for avoiding magnetic media data remanence?
Degaussing
Encryption
Data Loss Prevention (DLP)
Authentication
Degaussing is an effective method for avoiding magnetic media data remanence, which is the residual representation of data that remains on a storage device after it has been erased or overwritten. Degaussing is a process of applying a strong magnetic field to the storage device, such as a hard disk or a tape, to erase the data and destroy the magnetic alignment of the media. Degaussing can ensure that the data is unrecoverable, even by forensic tools or techniques. Encryption, DLP, and authentication are not methods for avoiding magnetic media data remanence, as they do not erase the data from the storage device, but rather protect it from unauthorized access or disclosure. References: : CISSP All-in-One Exam Guide, Eighth Edition, Chapter 10, page 631. : CISSP For Dummies, 7th Edition, Chapter 9, page 251.
Multi-threaded applications are more at risk than single-threaded applications to
race conditions.
virus infection.
packet sniffing.
database injection.
Multi-threaded applications are more at risk than single-threaded applications to race conditions. A race condition is a type of concurrency error that occurs when two or more threads access or modify the same shared resource without proper synchronization or coordination. This may result in inconsistent, unpredictable, or erroneous outcomes, as the final result depends on the timing and order of the thread execution. Race conditions can compromise the security, reliability, and functionality of the application, and can lead to data corruption, memory leaks, deadlock, or privilege escalation12. References: 1: What is a Race Condition?32: Race Conditions - OWASP Cheat Sheet Series4
A disadvantage of an application filtering firewall is that it can lead to
a crash of the network as a result of user activities.
performance degradation due to the rules applied.
loss of packets on the network due to insufficient bandwidth.
Internet Protocol (IP) spoofing by hackers.
A disadvantage of an application filtering firewall is that it can lead to performance degradation due to the rules applied. An application filtering firewall is a type of firewall that inspects the content and context of the data packets at the application layer of the OSI model. It can block or allow traffic based on the application protocol, the source and destination addresses, the user identity, the time of day, and other criteria. An application filtering firewall provides a high level of security and control, but it also requires more processing power and memory than other types of firewalls. This can result in slower network performance and increased latency56. References: 5: Application Layer Filtering (ALF): What is it and How does it Fit into your Security Plan?76: Different types of Firewalls: Their advantages and disadvantages
In Business Continuity Planning (BCP), what is the importance of documenting business processes?
Provides senior management with decision-making tools
Establishes and adopts ongoing testing and maintenance strategies
Defines who will perform which functions during a disaster or emergency
Provides an understanding of the organization's interdependencies
Documenting business processes is an important step in Business Continuity Planning (BCP), as it provides an understanding of the organization’s interdependencies, such as the people, resources, systems, and functions that are involved in each process. This helps to identify the critical processes that need to be prioritized and protected, as well as the potential impact of a disruption on the organization’s operations and objectives12. References: 1: CISSP All-in-One Exam Guide, Eighth Edition, Chapter 10, page 10092: CISSP For Dummies, 7th Edition, Chapter 10, page 339.
The Hardware Abstraction Layer (HAL) is implemented in the
system software.
system hardware.
application software.
network hardware.
The Hardware Abstraction Layer (HAL) is implemented in the system software. The system software is the software that controls and manages the basic operations and functions of the computer system, such as the operating system, the device drivers, the firmware, and the BIOS. The HAL is a component of the system software that provides a common interface between the hardware and the software layers of the system. The HAL abstracts the details and differences of the hardware devices and components, and allows the software to interact with the hardware in a consistent and uniform way. The HAL also enables the system to support multiple hardware platforms and configurations without requiring changes in the software5 . References: 5: What is Hardware Abstraction Layer (HAL)? : Hardware Abstraction Layer (HAL) - GeeksforGeeks
Which of the following statements is TRUE for point-to-point microwave transmissions?
They are not subject to interception due to encryption.
Interception only depends on signal strength.
They are too highly multiplexed for meaningful interception.
They are subject to interception by an antenna within proximity.
They are subject to interception by an antenna within proximity. Point-to-point microwave transmissions are line-of-sight media, which means that they can be intercepted by any antenna that is in the direct path of the signal. The interception does not depend on encryption, multiplexing, or signal strength, as long as the antenna is close enough to receive the signal.
An internal Service Level Agreement (SLA) covering security is signed by senior managers and is in place. When should compliance to the SLA be reviewed to ensure that a good security posture is being delivered?
As part of the SLA renewal process
Prior to a planned security audit
Immediately after a security breach
At regularly scheduled meetings
Compliance to the SLA should be reviewed at regularly scheduled meetings, such as monthly or quarterly, to ensure that the security posture is being delivered as agreed. This allows both parties to monitor the performance, identify any issues or gaps, and take corrective actions if needed. Reviewing the SLA only as part of the renewal process, prior to a planned security audit, or immediately after a security breach is not sufficient, as it may result in missing or delaying the detection and resolution of security problems. References: 1: How to measure your SLA: 5 Metrics you should be Monitoring and Reporting23: Run your security awareness program like a marketer with these campaign kits4
Which of the following statements is TRUE of black box testing?
Only the functional specifications are known to the test planner.
Only the source code and the design documents are known to the test planner.
Only the source code and functional specifications are known to the test planner.
Only the design documents and the functional specifications are known to the test planner.
Black box testing is a method of software testing that does not require any knowledge of the internal structure or code of the software1. The test planner only knows the functional specifications, which describe what the software is supposed to do, and tests the software based on the expected inputs and outputs. Black box testing is useful for finding errors in the functionality, usability, or performance of the software, but it cannot detect errors in the code or design. White box testing, on the other hand, requires the test planner to have access to the source code and the design documents, and tests the software based on the internal logic and structure2. References: 1: CISSP All-in-One Exam Guide, Eighth Edition, Chapter 21, page 13132: CISSP For Dummies, 7th Edition, Chapter 8, page 215.
What should be the INITIAL response to Intrusion Detection System/Intrusion Prevention System (IDS/IPS) alerts?
Ensure that the Incident Response Plan is available and current.
Determine the traffic's initial source and block the appropriate port.
Disable or disconnect suspected target and source systems.
Verify the threat and determine the scope of the attack.
The initial response to Intrusion Detection System/Intrusion Prevention System (IDS/IPS) alerts should be to verify the threat and determine the scope of the attack, as this will help to confirm the validity and severity of the alert, and to identify the affected systems, networks, and data. This step is essential to avoid false positives, false negatives, and overreactions, and to prepare for the appropriate mitigation and recovery actions. Ensuring that the Incident Response Plan is available and current is a preparatory step that should be done before any IDS/IPS alert occurs, not after. Determining the traffic’s initial source and blocking the appropriate port, and disabling or disconnecting suspected target and source systems are possible mitigation steps that should be done after verifying the threat and determining the scope of the attack, not before . References: 5: IDS vs IPS - What’s the Difference & Which do You Need? - Comparitech 6: IDS vs. IPS: Definitions, Comparisons & Why You Need Both | Okta 7: IDS and IPS: Understanding Similarities and Differences - EC-Council
An auditor carrying out a compliance audit requests passwords that are encrypted in the system to verify that the passwords are compliant with policy. Which of the following is the BEST response to the auditor?
Provide the encrypted passwords and analysis tools to the auditor for analysis.
Analyze the encrypted passwords for the auditor and show them the results.
Demonstrate that non-compliant passwords cannot be created in the system.
Demonstrate that non-compliant passwords cannot be encrypted in the system.
The best response to the auditor is to demonstrate that the system enforces the password policy and does not allow non-compliant passwords to be created. This way, the auditor can verify the compliance without compromising the confidentiality or integrity of the encrypted passwords. Providing the encrypted passwords and analysis tools to the auditor (A) may expose the passwords to unauthorized access or modification. Analyzing the encrypted passwords for the auditor and showing them the results (B) may not be sufficient to convince the auditor of the compliance, as the results could be manipulated or falsified. Demonstrating that non-compliant passwords cannot be encrypted in the system (D) is not a valid response, as encryption does not depend on the compliance of the passwords. References: CISSP All-in-One Exam Guide, Eighth Edition, Chapter 5, page 241; Official (ISC)2 CISSP CBK Reference, Fifth Edition, Chapter 5, page 303.
Which of the following is the MOST important consideration when storing and processing Personally Identifiable Information (PII)?
Encrypt and hash all PII to avoid disclosure and tampering.
Store PII for no more than one year.
Avoid storing PII in a Cloud Service Provider.
Adherence to collection limitation laws and regulations.
The most important consideration when storing and processing PII is to adhere to the collection limitation laws and regulations that apply to the jurisdiction and context of the data processing. Collection limitation is a principle that states that PII should be collected only for a specific, legitimate, and lawful purpose, and only to the extent that is necessary for that purpose1. By following this principle, the data processor can minimize the amount of PII that is stored and processed, and reduce the risk of data breaches, misuse, or unauthorized access. Encrypting and hashing all PII, storing PII for no more than one year, and avoiding storing PII in a cloud service provider are also good practices for protecting PII, but they are not as important as adhering to the collection limitation laws and regulations. References: 1: CISSP All-in-One Exam Guide, Eighth Edition, Chapter 5, page 290.
Which one of the following security mechanisms provides the BEST way to restrict the execution of privileged procedures?
Role Based Access Control (RBAC)
Biometric access control
Federated Identity Management (IdM)
Application hardening
Role Based Access Control (RBAC) is the security mechanism that provides the best way to restrict the execution of privileged procedures. Privileged procedures are the actions or commands that require higher or special permissions or privileges to perform, such as changing system settings, installing software, or accessing sensitive data. RBAC is a security model that assigns permissions and privileges to roles, rather than to individual users. Roles are defined based on the functions or responsibilities of the users in an organization. Users are assigned to roles based on their qualifications or credentials. RBAC enforces the principle of least privilege, which means that users only have the minimum permissions and privileges necessary to perform their tasks. RBAC also simplifies the administration and management of access control, as it reduces the complexity and redundancy of assigning permissions and privileges to individual users. RBAC is not the same as biometric access control, federated identity management, or application hardening. Biometric access control is a security mechanism that uses physical or behavioral characteristics of the users, such as fingerprints, iris patterns, or voice recognition, to authenticate and authorize them. Federated identity management is a security mechanism that enables the sharing and recognition of identity information across different organizations or domains, using standards and protocols such as SAML, OAuth, or OpenID. Application hardening is a security mechanism that involves the modification or improvement of an application’s code, design, or configuration, to make it more resistant to attacks or vulnerabilities.
Which one of the following is a threat related to the use of web-based client side input validation?
Users would be able to alter the input after validation has occurred
The web server would not be able to validate the input after transmission
The client system could receive invalid input from the web server
The web server would not be able to receive invalid input from the client
A threat related to the use of web-based client side input validation is that users would be able to alter the input after validation has occurred. Client side input validation is performed on the user’s browser using JavaScript or other scripting languages. It can provide a faster and more user-friendly feedback to the user, but it can also be easily bypassed or manipulated by an attacker who disables JavaScript, uses a web proxy, or modifies the source code of the web page. Therefore, client side input validation should not be relied upon as the sole or primary method of preventing malicious or malformed input from reaching the web server. Server side input validation is also necessary to ensure the security and integrity of the web application56. References: 5: Input Validation - OWASP Cheat Sheet Series76: Input Validation vulnerabilities and how to fix them
Which of the following MUST be part of a contract to support electronic discovery of data stored in a cloud environment?
Integration with organizational directory services for authentication
Tokenization of data
Accommodation of hybrid deployment models
Identification of data location
Identification of data location is a must-have clause in a contract to support electronic discovery of data stored in a cloud environment. Electronic discovery, or e-discovery, is the process of identifying, preserving, collecting, processing, reviewing, and producing electronically stored information (ESI) that is relevant to a legal case or investigation1. In a cloud environment, where data may be stored in multiple locations, jurisdictions, or servers, it is essential to have a clear and contractual agreement on how and where the data can be accessed, retrieved, and produced for e-discovery purposes. Identification of data location can help ensure the availability, integrity, and admissibility of the data as evidence. Integration with organizational directory services for authentication, tokenization of data, and accommodation of hybrid deployment models are not mandatory clauses for e-discovery support, as they are more related to the security, privacy, and flexibility of the cloud service, rather than the legal aspects of data discovery. References: 1: CISSP All-in-One Exam Guide, Eighth Edition, Chapter 10, page 647.
What would be the PRIMARY concern when designing and coordinating a security assessment for an Automatic Teller Machine (ATM) system?
Physical access to the electronic hardware
Regularly scheduled maintenance process
Availability of the network connection
Processing delays
The primary concern when designing and coordinating a security assessment for an Automatic Teller Machine (ATM) system is the availability of the network connection. An ATM system relies on a network connection to communicate with the bank’s servers and process the transactions of the customers. If the network connection is disrupted, degraded, or compromised, the ATM system may not be able to function properly, or may expose the customers’ data or money to unauthorized access or theft. Therefore, a security assessment for an ATM system should focus on ensuring that the network connection is reliable, resilient, and secure, and that there are backup or alternative solutions in case of network failure12. References: 1: ATM Security: Best Practices for Automated Teller Machines32: ATM Security: A Comprehensive Guide4
What is the MOST effective countermeasure to a malicious code attack against a mobile system?
Sandbox
Change control
Memory management
Public-Key Infrastructure (PKI)
A sandbox is a security mechanism that isolates a potentially malicious code or application from the rest of the system, preventing it from accessing or modifying any sensitive data or resources1. A sandbox can be implemented at the operating system, application, or network level, and can provide a safe environment for testing, debugging, or executing untrusted code. A sandbox is the most effective countermeasure to a malicious code attack against a mobile system, as it can prevent the code from spreading, stealing, or destroying any information on the device. Change control, memory management, and PKI are not directly related to preventing or mitigating malicious code attacks on mobile systems. References: 1: CISSP All-in-One Exam Guide, Eighth Edition, Chapter 8, page 507.
Contingency plan exercises are intended to do which of the following?
Train personnel in roles and responsibilities
Validate service level agreements
Train maintenance personnel
Validate operation metrics
Contingency plan exercises are intended to train personnel in roles and responsibilities. Contingency plan exercises are simulated scenarios that test the preparedness and effectiveness of the contingency plan, which is a document that outlines the actions and procedures to be followed in the event of a disruption or disaster. Contingency plan exercises help to train the personnel involved in the contingency plan, such as the incident response team, the recovery team, and the business continuity team, in their roles and responsibilities, such as communication, coordination, decision making, and execution. Contingency plan exercises also help to identify and resolve any issues or gaps in the contingency plan, and to improve the skills and confidence of the personnel5 . References: 5: Contingency Plan Testing : Contingency Planning Guide for Federal Information Systems
An Intrusion Detection System (IDS) is generating alarms that a user account has over 100 failed login attempts per minute. A sniffer is placed on the network, and a variety of passwords for that user are noted. Which of the following is MOST likely occurring?
A dictionary attack
A Denial of Service (DoS) attack
A spoofing attack
A backdoor installation
A dictionary attack is a type of brute-force attack that attempts to guess a user’s password by trying a large number of possible words or phrases, often derived from a dictionary or a list of commonly used passwords. A dictionary attack can be detected by an Intrusion Detection System (IDS) if it generates a high number of failed login attempts per minute, as well as a variety of passwords for the same user. A sniffer can capture the network traffic and reveal the passwords being tried by the attacker34. References: 3: CISSP All-in-One Exam Guide, Eighth Edition, Chapter 6, page 6574: CISSP For Dummies, 7th Edition, Chapter 6, page 197.
How can a forensic specialist exclude from examination a large percentage of operating system files residing on a copy of the target system?
Take another backup of the media in question then delete all irrelevant operating system files.
Create a comparison database of cryptographic hashes of the files from a system with the same operating system and patch level.
Generate a message digest (MD) or secure hash on the drive image to detect tampering of the media being examined.
Discard harmless files for the operating system, and known installed programs.
A forensic specialist can exclude from examination a large percentage of operating system files residing on a copy of the target system by creating a comparison database of cryptographic hashes of the files from a system with the same operating system and patch level. This method is also known as known file filtering or file signature analysis. It allows the forensic specialist to quickly identify and eliminate the files that are part of the standard operating system installation and focus on the files that are unique or relevant to the investigation. This makes the process of exclusion much faster and more accurate than manually deleting or discarding files12. References: 1: Computer Forensics: Forensic Techniques, Part 1 [Updated 2019]32: Point Checklist: cissp book4
Which of the following is the FIRST action that a system administrator should take when it is revealed during a penetration test that everyone in an organization has unauthorized access to a server holding sensitive data?
Immediately document the finding and report to senior management.
Use system privileges to alter the permissions to secure the server
Continue the testing to its completion and then inform IT management
Terminate the penetration test and pass the finding to the server management team
If a system administrator discovers a serious security breach during a penetration test, such as unauthorized access to a server holding sensitive data, the first action that he or she should take is to immediately document the finding and report it to senior management. This is because senior management is ultimately responsible for the security of the organization and its assets, and they need to be aware of the situation and take appropriate actions to mitigate the risk and prevent further damage. Documenting the finding is also important to provide evidence and support for the report, and to comply with any legal or regulatory requirements. Using system privileges to alter the permissions to secure the server, continuing the testing to its completion, or terminating the penetration test and passing the finding to the server management team are not the first actions that a system administrator should take, as they may not address the root cause of the problem, may interfere with the ongoing testing, or may delay the notification of senior management.
By allowing storage communications to run on top of Transmission Control Protocol/Internet Protocol (TCP/IP) with a Storage Area Network (SAN), the
confidentiality of the traffic is protected.
opportunity to sniff network traffic exists.
opportunity for device identity spoofing is eliminated.
storage devices are protected against availability attacks.
By allowing storage communications to run on top of Transmission Control Protocol/Internet Protocol (TCP/IP) with a Storage Area Network (SAN), the opportunity to sniff network traffic exists. A SAN is a dedicated network that connects storage devices, such as disk arrays, tape libraries, or servers, to provide high-speed data access and transfer. A SAN may use different protocols or technologies to communicate with storage devices, such as Fibre Channel, iSCSI, or NFS. By allowing storage communications to run on top of TCP/IP, a common network protocol that supports internet and intranet communications, a SAN may leverage the existing network infrastructure and reduce costs and complexity. However, this also exposes the storage communications to the same risks and threats that affect the network communications, such as sniffing, spoofing, or denial-of-service attacks. Sniffing is the act of capturing or monitoring network traffic, which may reveal sensitive or confidential information, such as passwords, encryption keys, or data. By allowing storage communications to run on top of TCP/IP with a SAN, the confidentiality of the traffic is not protected, unless encryption or other security measures are applied. The opportunity for device identity spoofing is not eliminated, as an attacker may still impersonate a legitimate storage device or server by using a forged or stolen IP address or MAC address. The storage devices are not protected against availability attacks, as an attacker may still disrupt or overload the network or the storage devices by sending malicious or excessive packets or requests.
During an audit of system management, auditors find that the system administrator has not been trained. What actions need to be taken at once to ensure the integrity of systems?
A review of hiring policies and methods of verification of new employees
A review of all departmental procedures
A review of all training procedures to be undertaken
A review of all systems by an experienced administrator
During an audit of system management, if auditors find that the system administrator has not been trained, the immediate action that needs to be taken to ensure the integrity of systems is a review of all systems by an experienced administrator. This is to verify that the systems are configured, maintained, and secured properly, and that there are no errors, vulnerabilities, or breaches that could compromise the system’s availability, confidentiality, or integrity. A review of hiring policies, departmental procedures, or training procedures are not urgent actions, as they are more related to the long-term improvement of the system management process, rather than the current state of the systems . References: : CISSP All-in-One Exam Guide, Eighth Edition, Chapter 8, page 829. : CISSP For Dummies, 7th Edition, Chapter 8, page 267.
Which of the following can BEST prevent security flaws occurring in outsourced software development?
Contractual requirements for code quality
Licensing, code ownership and intellectual property rights
Certification of the quality and accuracy of the work done
Delivery dates, change management control and budgetary control
The best way to prevent security flaws occurring in outsourced software development is to establish contractual requirements for code quality that specify the security standards, guidelines, and best practices that the outsourced developers must follow. This way, the organization can ensure that the outsourced software meets the expected level of security and quality, and that any security flaws are detected and remediated before delivery. The other options are not as effective as contractual requirements for code quality, as they either do not address the security aspects of the software development (B and D), or do not prevent the security flaws from occurring in the first place ©. References: CISSP All-in-One Exam Guide, Eighth Edition, Chapter 8, page 472; Official (ISC)2 CISSP CBK Reference, Fifth Edition, Chapter 8, page 572.
Which of the following is ensured when hashing files during chain of custody handling?
Availability
Accountability
Integrity
Non-repudiation
Hashing files during chain of custody handling ensures integrity, which means that the files have not been altered or tampered with during the collection, preservation, or analysis of digital evidence1. Hashing is a process of applying a mathematical function to a file to generate a unique value, called a hash or a digest, that represents the file’s content. By comparing the hash values of the original and the copied files, the integrity of the files can be verified. Availability, accountability, and non-repudiation are not ensured by hashing files during chain of custody handling, as they are related to different aspects of information security. References: 1: CISSP All-in-One Exam Guide, Eighth Edition, Chapter 10, page 633.
Which of the following is the BEST way to verify the integrity of a software patch?
Cryptographic checksums
Version numbering
Automatic updates
Vendor assurance
The best way to verify the integrity of a software patch is to use cryptographic checksums. Cryptographic checksums are mathematical values that are computed from the data in the software patch using a hash function or an algorithm. Cryptographic checksums can be used to compare the original and the downloaded or installed version of the software patch, and to detect any alteration, corruption, or tampering of the data. Cryptographic checksums are also known as hashes, digests, or fingerprints, and they are often provided by the software vendor along with the software patch12. References: 1: What is a Checksum and How to Calculate a Checksum32: How to Verify File Integrity Using Hashes
What principle requires that changes to the plaintext affect many parts of the ciphertext?
Diffusion
Encapsulation
Obfuscation
Permutation
Diffusion is the principle that requires that changes to the plaintext affect many parts of the ciphertext. Diffusion is a property of a good encryption algorithm that aims to spread the influence of each plaintext bit over many ciphertext bits, so that a small change in the plaintext results in a large change in the ciphertext2. Diffusion can increase the security of the encryption by making it harder for an attacker to analyze the statistical patterns or correlations between the plaintext and the ciphertext. Encapsulation, obfuscation, and permutation are not principles that require that changes to the plaintext affect many parts of the ciphertext, as they are related to different aspects of encryption or security. References: 2: CISSP For Dummies, 7th Edition, Chapter 3, page 65.
When building a data center, site location and construction factors that increase the level of vulnerability to physical threats include
hardened building construction with consideration of seismic factors.
adequate distance from and lack of access to adjacent buildings.
curved roads approaching the data center.
proximity to high crime areas of the city.
When building a data center, site location and construction factors that increase the level of vulnerability to physical threats include proximity to high crime areas of the city. This factor increases the risk of theft, vandalism, sabotage, or other malicious acts that could damage or disrupt the data center operations. The other options are factors that decrease the level of vulnerability to physical threats, as they provide protection or deterrence against natural or human-made hazards. Hardened building construction with consideration of seismic factors (A) reduces the impact of earthquakes or other natural disasters. Adequate distance from and lack of access to adjacent buildings (B) prevents unauthorized entry or fire spread from neighboring structures. Curved roads approaching the data center © slow down the speed of vehicles and make it harder for attackers to ram or bomb the data center. References: CISSP All-in-One Exam Guide, Eighth Edition, Chapter 10, page 637; Official (ISC)2 CISSP CBK Reference, Fifth Edition, Chapter 10, page 699.
A Business Continuity Plan/Disaster Recovery Plan (BCP/DRP) will provide which of the following?
Guaranteed recovery of all business functions
Minimization of the need decision making during a crisis
Insurance against litigation following a disaster
Protection from loss of organization resources
Minimization of the need for decision making during a crisis is the main benefit that a Business Continuity Plan/Disaster Recovery Plan (BCP/DRP) will provide. A BCP/DRP is a set of policies, procedures, and resources that enable an organization to continue or resume its critical functions and operations in the event of a disruption or disaster. A BCP/DRP can provide several benefits, such as:
Minimization of the need for decision making during a crisis is the main benefit that a BCP/DRP will provide, because it can ensure that the organization and its staff have a clear and consistent guidance and direction on how to respond and act during a disruption or disaster, and avoid any confusion, uncertainty, or inconsistency that might worsen the situation or impact. A BCP/DRP can also help to reduce the stress and pressure on the organization and its staff during a crisis, and increase their confidence and competence in executing the plans.
The other options are not the benefits that a BCP/DRP will provide, but rather unrealistic or incorrect expectations or outcomes of a BCP/DRP. Guaranteed recovery of all business functions is not a benefit that a BCP/DRP will provide, because it is not possible or feasible to recover all business functions after a disruption or disaster, especially if the disruption or disaster is severe or prolonged. A BCP/DRP can only prioritize and recover the most critical or essential business functions, and may have to suspend or terminate the less critical or non-essential business functions. Insurance against litigation following a disaster is not a benefit that a BCP/DRP will provide, because it is not a guarantee or protection that the organization will not face any legal or regulatory consequences or liabilities after a disruption or disaster, especially if the disruption or disaster is caused by the organization’s negligence or misconduct. A BCP/DRP can only help to mitigate or reduce the legal or regulatory risks, and may have to comply with or report to the relevant authorities or parties. Protection from loss of organization resources is not a benefit that a BCP/DRP will provide, because it is not a prevention or avoidance of any damage or destruction of the organization’s assets or resources during a disruption or disaster, especially if the disruption or disaster is physical or natural. A BCP/DRP can only help to restore or replace the lost or damaged assets or resources, and may have to incur some costs or losses.
What would be the MOST cost effective solution for a Disaster Recovery (DR) site given that the organization’s systems cannot be unavailable for more than 24 hours?
Warm site
Hot site
Mirror site
Cold site
A warm site is the most cost effective solution for a disaster recovery (DR) site given that the organization’s systems cannot be unavailable for more than 24 hours. A DR site is a backup facility that can be used to restore the normal operation of the organization’s IT systems and infrastructure after a disruption or disaster. A DR site can have different levels of readiness and functionality, depending on the organization’s recovery objectives and budget. The main types of DR sites are:
A warm site is the most cost effective solution for a disaster recovery (DR) site given that the organization’s systems cannot be unavailable for more than 24 hours, because it can provide a balance between the recovery time and the recovery cost. A warm site can enable the organization to resume its critical functions and operations within a reasonable time frame, without spending too much on the DR site maintenance and operation. A warm site can also provide some flexibility and scalability for the organization to adjust its recovery strategies and resources according to its needs and priorities.
The other options are not the most cost effective solutions for a disaster recovery (DR) site given that the organization’s systems cannot be unavailable for more than 24 hours, but rather solutions that are either too costly or too slow for the organization’s recovery objectives and budget. A hot site is a solution that is too costly for a disaster recovery (DR) site given that the organization’s systems cannot be unavailable for more than 24 hours, because it requires the organization to invest a lot of money on the DR site equipment, software, and services, and to pay for the ongoing operational and maintenance costs. A hot site may be more suitable for the organization’s systems that cannot be unavailable for more than a few hours or minutes, or that have very high availability and performance requirements. A mirror site is a solution that is too costly for a disaster recovery (DR) site given that the organization’s systems cannot be unavailable for more than 24 hours, because it requires the organization to duplicate its entire primary site, with the same hardware, software, data, and applications, and to keep them online and synchronized at all times. A mirror site may be more suitable for the organization’s systems that cannot afford any downtime or data loss, or that have very strict compliance and regulatory requirements. A cold site is a solution that is too slow for a disaster recovery (DR) site given that the organization’s systems cannot be unavailable for more than 24 hours, because it requires the organization to spend a lot of time and effort on the DR site installation, configuration, and restoration, and to rely on other sources of backup data and applications. A cold site may be more suitable for the organization’s systems that can be unavailable for more than a few days or weeks, or that have very low criticality and priority.
What is the MOST important step during forensic analysis when trying to learn the purpose of an unknown application?
Disable all unnecessary services
Ensure chain of custody
Prepare another backup of the system
Isolate the system from the network
Isolating the system from the network is the most important step during forensic analysis when trying to learn the purpose of an unknown application. An unknown application is an application that is not recognized or authorized by the system or network administrator, and that may have been installed or executed without the user’s knowledge or consent. An unknown application may have various purposes, such as:
Forensic analysis is a process that involves examining and investigating the system or network for any evidence or traces of the unknown application, such as its origin, nature, behavior, and impact. Forensic analysis can provide several benefits, such as:
Isolating the system from the network is the most important step during forensic analysis when trying to learn the purpose of an unknown application, because it can ensure that the system is isolated and protected from any external or internal influences or interferences, and that the forensic analysis is conducted in a safe and controlled environment. Isolating the system from the network can also help to:
The other options are not the most important steps during forensic analysis when trying to learn the purpose of an unknown application, but rather steps that should be done after or along with isolating the system from the network. Disabling all unnecessary services is a step that should be done after isolating the system from the network, because it can ensure that the system is optimized and simplified for the forensic analysis, and that the system resources and functions are not consumed or affected by any irrelevant or redundant services. Ensuring chain of custody is a step that should be done along with isolating the system from the network, because it can ensure that the integrity and authenticity of the evidence are maintained and documented throughout the forensic process, and that the evidence can be traced and verified. Preparing another backup of the system is a step that should be done after isolating the system from the network, because it can ensure that the system data and configuration are preserved and replicated for the forensic analysis, and that the system can be restored and recovered in case of any damage or loss.
Which of the following is the FIRST step in the incident response process?
Determine the cause of the incident
Disconnect the system involved from the network
Isolate and contain the system involved
Investigate all symptoms to confirm the incident
Investigating all symptoms to confirm the incident is the first step in the incident response process. An incident is an event that violates or threatens the security, availability, integrity, or confidentiality of the IT systems or data. An incident response is a process that involves detecting, analyzing, containing, eradicating, recovering, and learning from an incident, using various methods and tools. An incident response can provide several benefits, such as:
Investigating all symptoms to confirm the incident is the first step in the incident response process, because it can ensure that the incident is verified and validated, and that the incident response is initiated and escalated. A symptom is a sign or an indication that an incident may have occurred or is occurring, such as an alert, a log, or a report. Investigating all symptoms to confirm the incident involves collecting and analyzing the relevant data and information from various sources, such as the IT systems, the network, the users, or the external parties, and determining whether an incident has actually happened or is happening, and how serious or urgent it is. Investigating all symptoms to confirm the incident can also help to:
The other options are not the first steps in the incident response process, but rather steps that should be done after or along with investigating all symptoms to confirm the incident. Determining the cause of the incident is a step that should be done after investigating all symptoms to confirm the incident, because it can ensure that the root cause and source of the incident are identified and analyzed, and that the incident response is directed and focused. Determining the cause of the incident involves examining and testing the affected IT systems and data, and tracing and tracking the origin and path of the incident, using various techniques and tools, such as forensics, malware analysis, or reverse engineering. Determining the cause of the incident can also help to:
Disconnecting the system involved from the network is a step that should be done along with investigating all symptoms to confirm the incident, because it can ensure that the system is isolated and protected from any external or internal influences or interferences, and that the incident response is conducted in a safe and controlled environment. Disconnecting the system involved from the network can also help to:
Isolating and containing the system involved is a step that should be done after investigating all symptoms to confirm the incident, because it can ensure that the incident is confined and restricted, and that the incident response is continued and maintained. Isolating and containing the system involved involves applying and enforcing the appropriate security measures and controls to limit or stop the activity and impact of the incident on the IT systems and data, such as firewall rules, access policies, or encryption keys. Isolating and containing the system involved can also help to:
A continuous information security-monitoring program can BEST reduce risk through which of the following?
Collecting security events and correlating them to identify anomalies
Facilitating system-wide visibility into the activities of critical user accounts
Encompassing people, process, and technology
Logging both scheduled and unscheduled system changes
A continuous information security monitoring program can best reduce risk through encompassing people, process, and technology. A continuous information security monitoring program is a process that involves maintaining the ongoing awareness of the security status, events, and activities of a system or network, by collecting, analyzing, and reporting the security data and information, using various methods and tools. A continuous information security monitoring program can provide several benefits, such as:
A continuous information security monitoring program can best reduce risk through encompassing people, process, and technology, because it can ensure that the continuous information security monitoring program is holistic and comprehensive, and that it covers all the aspects and elements of the system or network security. People, process, and technology are the three pillars of a continuous information security monitoring program, and they represent the following:
The other options are not the best ways to reduce risk through a continuous information security monitoring program, but rather specific or partial ways that can contribute to the risk reduction. Collecting security events and correlating them to identify anomalies is a specific way to reduce risk through a continuous information security monitoring program, but it is not the best way, because it only focuses on one aspect of the security data and information, and it does not address the other aspects, such as the security objectives and requirements, the security controls and measures, and the security feedback and improvement. Facilitating system-wide visibility into the activities of critical user accounts is a partial way to reduce risk through a continuous information security monitoring program, but it is not the best way, because it only covers one element of the system or network security, and it does not cover the other elements, such as the security threats and vulnerabilities, the security incidents and impacts, and the security response and remediation. Logging both scheduled and unscheduled system changes is a specific way to reduce risk through a continuous information security monitoring program, but it is not the best way, because it only focuses on one type of the security events and activities, and it does not focus on the other types, such as the security alerts and notifications, the security analysis and correlation, and the security reporting and documentation.
Which of the following types of business continuity tests includes assessment of resilience to internal and external risks without endangering live operations?
Walkthrough
Simulation
Parallel
White box
Simulation is the type of business continuity test that includes assessment of resilience to internal and external risks without endangering live operations. Business continuity is the ability of an organization to maintain or resume its critical functions and operations in the event of a disruption or disaster. Business continuity testing is the process of evaluating and validating the effectiveness and readiness of the business continuity plan (BCP) and the disaster recovery plan (DRP) through various methods and scenarios. Business continuity testing can provide several benefits, such as:
There are different types of business continuity tests, depending on the scope, purpose, and complexity of the test. Some of the common types are:
Simulation is the type of business continuity test that includes assessment of resilience to internal and external risks without endangering live operations, because it can simulate various types of risks, such as natural, human, or technical, and assess how the organization and its systems can cope and recover from them, without actually causing any harm or disruption to the live operations. Simulation can also help to identify and mitigate any potential risks that might affect the live operations, and to improve the resilience and preparedness of the organization and its systems.
The other options are not the types of business continuity tests that include assessment of resilience to internal and external risks without endangering live operations, but rather types that have other objectives or effects. Walkthrough is a type of business continuity test that does not include assessment of resilience to internal and external risks, but rather a review and discussion of the BCP and DRP, without any actual testing or practice. Parallel is a type of business continuity test that does not endanger live operations, but rather maintains them, while activating and operating the alternate site or system. Full interruption is a type of business continuity test that does endanger live operations, by shutting them down and transferring them to the alternate site or system.
An organization is found lacking the ability to properly establish performance indicators for its Web hosting solution during an audit. What would be the MOST probable cause?
Absence of a Business Intelligence (BI) solution
Inadequate cost modeling
Improper deployment of the Service-Oriented Architecture (SOA)
Insufficient Service Level Agreement (SLA)
Insufficient Service Level Agreement (SLA) would be the most probable cause for an organization to lack the ability to properly establish performance indicators for its Web hosting solution during an audit. A Web hosting solution is a service that provides the infrastructure, resources, and tools for hosting and maintaining a website or a web application on the internet. A Web hosting solution can offer various benefits, such as:
A Service Level Agreement (SLA) is a contract or an agreement that defines the expectations, responsibilities, and obligations of the parties involved in a service, such as the service provider and the service consumer. An SLA can include various components, such as:
Insufficient SLA would be the most probable cause for an organization to lack the ability to properly establish performance indicators for its Web hosting solution during an audit, because it could mean that the SLA does not include or specify the appropriate service level indicators or objectives for the Web hosting solution, or that the SLA does not provide or enforce the adequate service level reporting or penalties for the Web hosting solution. This could affect the ability of the organization to measure and assess the Web hosting solution quality, performance, and availability, and to identify and address any issues or risks in the Web hosting solution.
The other options are not the most probable causes for an organization to lack the ability to properly establish performance indicators for its Web hosting solution during an audit, but rather the factors that could affect or improve the Web hosting solution in other ways. Absence of a Business Intelligence (BI) solution is a factor that could affect the ability of the organization to analyze and utilize the data and information from the Web hosting solution, such as the web traffic, behavior, or conversion. A BI solution is a system that involves the collection, integration, processing, and presentation of the data and information from various sources, such as the Web hosting solution, to support the decision making and planning of the organization. However, absence of a BI solution is not the most probable cause for an organization to lack the ability to properly establish performance indicators for its Web hosting solution during an audit, because it does not affect the definition or specification of the performance indicators for the Web hosting solution, but rather the analysis or usage of the performance indicators for the Web hosting solution. Inadequate cost modeling is a factor that could affect the ability of the organization to estimate and optimize the cost and value of the Web hosting solution, such as the web hosting fees, maintenance costs, or return on investment. A cost model is a tool or a method that helps the organization to calculate and compare the cost and value of the Web hosting solution, and to identify and implement the best or most efficient Web hosting solution. However, inadequate cost modeling is not the most probable cause for an organization to lack the ability to properly establish performance indicators for its Web hosting solution during an audit, because it does not affect the definition or specification of the performance indicators for the Web hosting solution, but rather the estimation or optimization of the cost and value of the Web hosting solution. Improper deployment of the Service-Oriented Architecture (SOA) is a factor that could affect the ability of the organization to design and develop the Web hosting solution, such as the web services, components, or interfaces. A SOA is a software architecture that involves the modularization, standardization, and integration of the software components or services that provide the functionality or logic of the Web hosting solution. A SOA can offer various benefits, such as:
However, improper deployment of the SOA is not the most probable cause for an organization to lack the ability to properly establish performance indicators for its Web hosting solution during an audit, because it does not affect the definition or specification of the performance indicators for the Web hosting solution, but rather the design or development of the Web hosting solution.
When is a Business Continuity Plan (BCP) considered to be valid?
When it has been validated by the Business Continuity (BC) manager
When it has been validated by the board of directors
When it has been validated by all threat scenarios
When it has been validated by realistic exercises
A Business Continuity Plan (BCP) is considered to be valid when it has been validated by realistic exercises. A BCP is a part of a BCP/DRP that focuses on ensuring the continuous operation of the organization’s critical business functions and processes during and after a disruption or disaster. A BCP should include various components, such as:
A BCP is considered to be valid when it has been validated by realistic exercises, because it can ensure that the BCP is practical and applicable, and that it can achieve the desired outcomes and objectives in a real-life scenario. Realistic exercises are a type of testing, training, and exercises that involve performing and practicing the BCP with the relevant stakeholders, using simulated or hypothetical scenarios, such as a fire drill, a power outage, or a cyberattack. Realistic exercises can provide several benefits, such as:
The other options are not the criteria for considering a BCP to be valid, but rather the steps or parties that are involved in developing or approving a BCP. When it has been validated by the Business Continuity (BC) manager is not a criterion for considering a BCP to be valid, but rather a step that is involved in developing a BCP. The BC manager is the person who is responsible for overseeing and coordinating the BCP activities and processes, such as the business impact analysis, the recovery strategies, the BCP document, the testing, training, and exercises, and the maintenance and review. The BC manager can validate the BCP by reviewing and verifying the BCP components and outcomes, and ensuring that they meet the BCP standards and objectives. However, the validation by the BC manager is not enough to consider the BCP to be valid, as it does not test or demonstrate the BCP in a realistic scenario. When it has been validated by the board of directors is not a criterion for considering a BCP to be valid, but rather a party that is involved in approving a BCP. The board of directors is the group of people who are elected by the shareholders to represent their interests and to oversee the strategic direction and governance of the organization. The board of directors can approve the BCP by endorsing and supporting the BCP components and outcomes, and allocating the necessary resources and funds for the BCP. However, the approval by the board of directors is not enough to consider the BCP to be valid, as it does not test or demonstrate the BCP in a realistic scenario. When it has been validated by all threat scenarios is not a criterion for considering a BCP to be valid, but rather an unrealistic or impossible expectation for validating a BCP. A threat scenario is a description or a simulation of a possible or potential disruption or disaster that might affect the organization’s critical business functions and processes, such as a natural hazard, a human error, or a technical failure. A threat scenario can be used to test and validate the BCP by measuring and evaluating the BCP’s performance and effectiveness in responding and recovering from the disruption or disaster. However, it is not possible or feasible to validate the BCP by all threat scenarios, as there are too many or unknown threat scenarios that might occur, and some threat scenarios might be too severe or complex to simulate or test. Therefore, the BCP should be validated by the most likely or relevant threat scenarios, and not by all threat scenarios.
Which of the following is a PRIMARY advantage of using a third-party identity service?
Consolidation of multiple providers
Directory synchronization
Web based logon
Automated account management
Consolidation of multiple providers is the primary advantage of using a third-party identity service. A third-party identity service is a service that provides identity and access management (IAM) functions, such as authentication, authorization, and federation, for multiple applications or systems, using a single identity provider (IdP). A third-party identity service can offer various benefits, such as:
Consolidation of multiple providers is the primary advantage of using a third-party identity service, because it can simplify and streamline the IAM architecture and processes, by reducing the number of IdPs and IAM systems that are involved in managing the identities and access for multiple applications or systems. Consolidation of multiple providers can also help to avoid the issues or risks that might arise from having multiple IdPs and IAM systems, such as the inconsistency, redundancy, or conflict of the IAM policies and controls, or the inefficiency, vulnerability, or disruption of the IAM functions.
The other options are not the primary advantages of using a third-party identity service, but rather secondary or specific advantages for different aspects or scenarios of using a third-party identity service. Directory synchronization is an advantage of using a third-party identity service, but it is more relevant for the scenario where the organization has an existing directory service, such as LDAP or Active Directory, that stores and manages the user accounts and attributes, and wants to synchronize them with the third-party identity service, to enable the SSO or federation for the users. Web based logon is an advantage of using a third-party identity service, but it is more relevant for the aspect where the third-party identity service uses a web-based protocol, such as SAML or OAuth, to facilitate the SSO or federation for the users, by redirecting them to a web-based logon page, where they can enter their credentials or consent. Automated account management is an advantage of using a third-party identity service, but it is more relevant for the aspect where the third-party identity service provides the IAM functions, such as provisioning, deprovisioning, or updating, for the user accounts and access rights, using an automated or self-service mechanism, such as SCIM or JIT.
With what frequency should monitoring of a control occur when implementing Information Security Continuous Monitoring (ISCM) solutions?
Continuously without exception for all security controls
Before and after each change of the control
At a rate concurrent with the volatility of the security control
Only during system implementation and decommissioning
Monitoring of a control should occur at a rate concurrent with the volatility of the security control when implementing Information Security Continuous Monitoring (ISCM) solutions. ISCM is a process that involves maintaining the ongoing awareness of the security status, events, and activities of a system or network, by collecting, analyzing, and reporting the security data and information, using various methods and tools. ISCM can provide several benefits, such as:
A security control is a measure or mechanism that is implemented to protect the system or network from the security threats or risks, by preventing, detecting, or correcting the security incidents or impacts. A security control can have various types, such as administrative, technical, or physical, and various attributes, such as preventive, detective, or corrective. A security control can also have different levels of volatility, which is the degree or frequency of change or variation of the security control, due to various factors, such as the security requirements, the threat landscape, or the system or network environment.
Monitoring of a control should occur at a rate concurrent with the volatility of the security control when implementing ISCM solutions, because it can ensure that the ISCM solutions can capture and reflect the current and accurate state and performance of the security control, and can identify and report any issues or risks that might affect the security control. Monitoring of a control at a rate concurrent with the volatility of the security control can also help to optimize the ISCM resources and efforts, by allocating them according to the priority and urgency of the security control.
The other options are not the correct frequencies for monitoring of a control when implementing ISCM solutions, but rather incorrect or unrealistic frequencies that might cause problems or inefficiencies for the ISCM solutions. Continuously without exception for all security controls is an incorrect frequency for monitoring of a control when implementing ISCM solutions, because it is not feasible or necessary to monitor all security controls at the same and constant rate, regardless of their volatility or importance. Continuously monitoring all security controls without exception might cause the ISCM solutions to consume excessive or wasteful resources and efforts, and might overwhelm or overload the ISCM solutions with too much or irrelevant data and information. Before and after each change of the control is an incorrect frequency for monitoring of a control when implementing ISCM solutions, because it is not sufficient or timely to monitor the security control only when there is a change of the security control, and not during the normal operation of the security control. Monitoring the security control only before and after each change might cause the ISCM solutions to miss or ignore the security status, events, and activities that occur between the changes of the security control, and might delay or hinder the ISCM solutions from detecting and responding to the security issues or incidents that affect the security control. Only during system implementation and decommissioning is an incorrect frequency for monitoring of a control when implementing ISCM solutions, because it is not appropriate or effective to monitor the security control only during the initial or final stages of the system or network lifecycle, and not during the operational or maintenance stages of the system or network lifecycle. Monitoring the security control only during system implementation and decommissioning might cause the ISCM solutions to neglect or overlook the security status, events, and activities that occur during the regular or ongoing operation of the system or network, and might prevent or limit the ISCM solutions from improving and optimizing the security control.
What should be the FIRST action to protect the chain of evidence when a desktop computer is involved?
Take the computer to a forensic lab
Make a copy of the hard drive
Start documenting
Turn off the computer
Making a copy of the hard drive should be the first action to protect the chain of evidence when a desktop computer is involved. A chain of evidence, also known as a chain of custody, is a process that documents and preserves the integrity and authenticity of the evidence collected from a crime scene, such as a desktop computer. A chain of evidence should include information such as:
Making a copy of the hard drive should be the first action to protect the chain of evidence when a desktop computer is involved, because it can ensure that the original hard drive is not altered, damaged, or destroyed during the forensic analysis, and that the copy can be used as a reliable and admissible source of evidence. Making a copy of the hard drive should also involve using a write blocker, which is a device or a software that prevents any modification or deletion of the data on the hard drive, and generating a hash value, which is a unique and fixed identifier that can verify the integrity and consistency of the data on the hard drive.
The other options are not the first actions to protect the chain of evidence when a desktop computer is involved, but rather actions that should be done after or along with making a copy of the hard drive. Taking the computer to a forensic lab is an action that should be done after making a copy of the hard drive, because it can ensure that the computer is transported and stored in a secure and controlled environment, and that the forensic analysis is conducted by qualified and authorized personnel. Starting documenting is an action that should be done along with making a copy of the hard drive, because it can ensure that the chain of evidence is maintained and recorded throughout the forensic process, and that the evidence can be traced and verified. Turning off the computer is an action that should be done after making a copy of the hard drive, because it can ensure that the computer is powered down and disconnected from any network or device, and that the computer is protected from any further damage or tampering.
What is the PRIMARY reason for implementing change management?
Certify and approve releases to the environment
Provide version rollbacks for system changes
Ensure that all applications are approved
Ensure accountability for changes to the environment
Ensuring accountability for changes to the environment is the primary reason for implementing change management. Change management is a process that ensures that any changes to the system or network environment, such as the hardware, software, configuration, or documentation, are planned, approved, implemented, and documented in a controlled and consistent manner. Change management can provide several benefits, such as:
Ensuring accountability for changes to the environment is the primary reason for implementing change management, because it can ensure that the changes are authorized, justified, and traceable, and that the parties involved in the changes are responsible and accountable for their actions and results. Accountability can also help to deter or detect any unauthorized or malicious changes that might compromise the system or network environment.
The other options are not the primary reasons for implementing change management, but rather secondary or specific reasons for different aspects or phases of change management. Certifying and approving releases to the environment is a reason for implementing change management, but it is more relevant for the approval phase of change management, which is the phase that involves reviewing and validating the changes and their impacts, and granting or denying the permission to proceed with the changes. Providing version rollbacks for system changes is a reason for implementing change management, but it is more relevant for the implementation phase of change management, which is the phase that involves executing and monitoring the changes and their effects, and providing the backup and recovery options for the changes. Ensuring that all applications are approved is a reason for implementing change management, but it is more relevant for the application changes, which are the changes that affect the software components or services that provide the functionality or logic of the system or network environment.
Recovery strategies of a Disaster Recovery planning (DRIP) MUST be aligned with which of the following?
Hardware and software compatibility issues
Applications’ critically and downtime tolerance
Budget constraints and requirements
Cost/benefit analysis and business objectives
Recovery strategies of a Disaster Recovery planning (DRP) must be aligned with the cost/benefit analysis and business objectives. A DRP is a part of a BCP/DRP that focuses on restoring the normal operation of the organization’s IT systems and infrastructure after a disruption or disaster. A DRP should include various components, such as:
Recovery strategies of a DRP must be aligned with the cost/benefit analysis and business objectives, because it can ensure that the DRP is feasible and suitable, and that it can achieve the desired outcomes and objectives in a cost-effective and efficient manner. A cost/benefit analysis is a technique that compares the costs and benefits of different recovery strategies, and determines the optimal one that provides the best value for money. A business objective is a goal or a target that the organization wants to achieve through its IT systems and infrastructure, such as increasing the productivity, profitability, or customer satisfaction. A recovery strategy that is aligned with the cost/benefit analysis and business objectives can help to:
The other options are not the factors that the recovery strategies of a DRP must be aligned with, but rather factors that should be considered or addressed when developing or implementing the recovery strategies of a DRP. Hardware and software compatibility issues are factors that should be considered when developing the recovery strategies of a DRP, because they can affect the functionality and interoperability of the IT systems and infrastructure, and may require additional resources or adjustments to resolve them. Applications’ criticality and downtime tolerance are factors that should be addressed when implementing the recovery strategies of a DRP, because they can determine the priority and urgency of the recovery for different applications, and may require different levels of recovery objectives and resources. Budget constraints and requirements are factors that should be considered when developing the recovery strategies of a DRP, because they can limit the availability and affordability of the IT resources and funds for the recovery, and may require trade-offs or compromises to balance them.
Refer to the information below to answer the question.
During the investigation of a security incident, it is determined that an unauthorized individual accessed a system which hosts a database containing financial information.
If the intrusion causes the system processes to hang, which of the following has been affected?
System integrity
System availability
System confidentiality
System auditability
If the intrusion causes the system processes to hang, the system availability has been affected. The system availability is the property or the characteristic of the system that ensures that the system is accessible and functional when needed by the authorized users or entities, and that the system is protected from the unauthorized or the malicious denial or disruption of service. The system availability can be affected when the system processes hang, as it can prevent or delay the system from responding to the requests or performing the tasks, and it can cause the system to crash or freeze. The system availability can also be affected by other factors, such as the network congestion, the hardware failure, the power outage, or the malicious attacks, such as the distributed denial-of-service (DDoS) attack. System integrity, system confidentiality, and system auditability are not the properties or the characteristics of the system that have been affected, if the intrusion causes the system processes to hang, as they are related to the accuracy, the secrecy, or the accountability of the system, not the accessibility or the functionality of the system. References: CISSP All-in-One Exam Guide, Eighth Edition, Chapter 3, Security Architecture and Engineering, page 263. Official (ISC)2 CISSP CBK Reference, Fifth Edition, Chapter 3, Security Architecture and Engineering, page 279.
Which of the following is critical for establishing an initial baseline for software components in the operation and maintenance of applications?
Application monitoring procedures
Configuration control procedures
Security audit procedures
Software patching procedures
Configuration control procedures are critical for establishing an initial baseline for software components in the operation and maintenance of applications. Configuration control procedures are the processes and activities that ensure the integrity, consistency, and traceability of the software components throughout the SDLC. Configuration control procedures include identifying, documenting, storing, reviewing, approving, and updating the software components, as well as managing the changes and versions of the components. By establishing an initial baseline, the organization can have a reference point for measuring and evaluating the performance, quality, and security of the software components, and for applying and tracking the changes and updates to the components. The other options are not as critical as configuration control procedures, as they either do not establish an initial baseline (A and C), or do not apply to all software components (D). References: CISSP All-in-One Exam Guide, Eighth Edition, Chapter 8, page 468; Official (ISC)2 CISSP CBK Reference, Fifth Edition, Chapter 8, page 568.
Given the various means to protect physical and logical assets, match the access management area to the technology.


In the context of protecting physical and logical assets, the access management areas and the technologies can be matched as follows: - Facilities are the physical buildings or locations that house the organization’s assets, such as servers, computers, or documents. Facilities can be protected by using windows that are resistant to breakage, intrusion, or eavesdropping, and that can prevent the leakage of light or sound from inside the facilities. - Devices are the hardware or software components that enable the communication or processing of data, such as routers, switches, firewalls, or applications. Devices can be protected by using firewalls that can filter, block, or allow the network traffic based on the predefined rules or policies, and that can prevent unauthorized or malicious access or attacks to the devices or the data. - Information Systems are the systems that store, process, or transmit data, such as databases, servers, or applications. Information Systems can be protected by using authentication mechanisms that can verify the identity or the credentials of the users or the devices that request access to the information systems, and that can prevent impersonation or spoofing of the users or the devices. - Encryption is a technology that can be applied in various areas, such as Devices or Information Systems, to protect the confidentiality or the integrity of the data. Encryption can transform the data into an unreadable or unrecognizable form, using a secret key or an algorithm, and can prevent the interception, disclosure, or modification of the data by unauthorized parties.
During an audit, the auditor finds evidence of potentially illegal activity. Which of the following is the MOST appropriate action to take?
Immediately call the police
Work with the client to resolve the issue internally
Advise the person performing the illegal activity to cease and desist
Work with the client to report the activity to the appropriate authority
The most appropriate action to take when the auditor finds evidence of potentially illegal activity is to work with the client to report the activity to the appropriate authority. The auditor is a professional who performs an independent and objective examination of the system, the process, or the activity, to provide assurance, evaluation, or improvement. The auditor has a duty and a responsibility to report any evidence of potentially illegal activity that they find during the audit, as it can affect the security, the compliance, or the integrity of the system, the process, or the activity. The auditor should work with the client to report the activity to the appropriate authority, such as the law enforcement, the regulatory body, or the senior management, as it can ensure the cooperation, the communication, or the transparency between the auditor and the client, and it can follow the legal, the contractual, or the ethical obligations of the auditor and the client. The auditor should not immediately call the police, work with the client to resolve the issue internally, or advise the person performing the illegal activity to cease and desist, as they are not the most appropriate actions to take when the auditor finds evidence of potentially illegal activity, as they can bypass, undermine, or interfere with the cooperation, the communication, or the transparency between the auditor and the client, and they can violate the legal, the contractual, or the ethical obligations of the auditor and the client. References: CISSP All-in-One Exam Guide, Eighth Edition, Chapter 7, Security Operations, page 894. Official (ISC)2 CISSP CBK Reference, Fifth Edition, Chapter 7, Security Operations, page 910.
Without proper signal protection, embedded systems may be prone to which type of attack?
Brute force
Tampering
Information disclosure
Denial of Service (DoS)
The type of attack that embedded systems may be prone to without proper signal protection is information disclosure. Information disclosure is a type of attack that exposes or reveals sensitive or confidential information to unauthorized parties, such as attackers, competitors, or the public. Information disclosure can occur through various means, such as interception, leakage, or theft of the information. Embedded systems are systems that are integrated into other devices or machines, such as cars, medical devices, or industrial controllers, and perform specific functions or tasks. Embedded systems may communicate with other systems or devices through signals, such as radio frequency, infrared, or sound waves. Without proper signal protection, such as encryption, authentication, or shielding, embedded systems may be vulnerable to information disclosure, as the signals may be captured, analyzed, or modified by attackers, and the information contained in the signals may be compromised. Brute force, tampering, and denial of service are not the types of attack that embedded systems may be prone to without proper signal protection, as they are related to the guessing, alteration, or prevention of the access or functionality of the systems, not the exposure or revelation of the information. References: CISSP All-in-One Exam Guide, Eighth Edition, Chapter 3, Security Architecture and Engineering, page 311. Official (ISC)2 CISSP CBK Reference, Fifth Edition, Chapter 3, Security Architecture and Engineering, page 327.
Which of the following is the MOST beneficial to review when performing an IT audit?
Audit policy
Security log
Security policies
Configuration settings
The most beneficial item to review when performing an IT audit is the security log. The security log is a record of the events and activities that occur on a system or network, such as logins, logouts, file accesses, policy changes, or security incidents. The security log can provide valuable information for the auditor to assess the security posture, performance, and compliance of the system or network, and to identify any anomalies, vulnerabilities, or breaches that need to be addressed. The other options are not as beneficial as the security log, as they either do not provide enough information for the audit (A and C), or do not reflect the actual state of the system or network (D). References: CISSP All-in-One Exam Guide, Eighth Edition, Chapter 7, page 405; Official (ISC)2 CISSP CBK Reference, Fifth Edition, Chapter 7, page 465.
Which of the following is the PRIMARY benefit of a formalized information classification program?
It drives audit processes.
It supports risk assessment.
It reduces asset vulnerabilities.
It minimizes system logging requirements.
A formalized information classification program is a set of policies and procedures that define the categories, criteria, and responsibilities for classifying information assets according to their value, sensitivity, and criticality. The primary benefit of such a program is that it supports risk assessment, which is the process of identifying, analyzing, and evaluating the risks to the information assets and the organization. By classifying information assets, the organization can prioritize the protection of the most important and vulnerable assets, determine the appropriate security controls and measures, and allocate the necessary resources and budget. It drives audit processes, it reduces asset vulnerabilities, and it minimizes system logging requirements are all possible benefits of a formalized information classification program, but they are not the primary benefit of doing so. References: CISSP All-in-One Exam Guide, Eighth Edition, Chapter 1, Security and Risk Management, page 39. Official (ISC)2 CISSP CBK Reference, Fifth Edition, Chapter 1, Security and Risk Management, page 52.
Refer to the information below to answer the question.
In a Multilevel Security (MLS) system, the following sensitivity labels are used in increasing levels of sensitivity: restricted, confidential, secret, top secret. Table A lists the clearance levels for four users, while Table B lists the security classes of four different files.
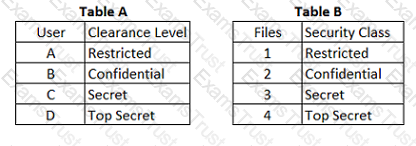
In a Bell-LaPadula system, which user cannot write to File 3?
User A
User B
User C
User D
In a Bell-LaPadula system, a user cannot write data to a file that has a lower security classification than their own. This is because of the star property (*property) of the Bell-LaPadula model, which states that a subject with a given security clearance may write data to an object if and only if the object’s security level is greater than or equal to the subject’s security level. This rule is also known as the no write-down rule, as it prevents the leakage of information from a higher level to a lower level. In this question, User D has a Top Secret clearance, and File 3 has a Secret security class. Therefore, User D cannot write to File 3, as they have a higher clearance than the security class of File 3, and they would violate the star property by writing down information to a lower level. User A, User B, and User C can write to File 3, as they have the same or lower clearances than the security class of File 3, and they would not violate the star property by writing up or across information to a higher or equal level. References: CISSP All-in-One Exam Guide, Eighth Edition, Chapter 4, Communication and Network Security, page 498. Official (ISC)2 CISSP CBK Reference, Fifth Edition, Chapter 4, Communication and Network Security, page 514.
What is the PRIMARY reason for ethics awareness and related policy implementation?
It affects the workflow of an organization.
It affects the reputation of an organization.
It affects the retention rate of employees.
It affects the morale of the employees.
The primary reason for ethics awareness and related policy implementation is to affect the reputation of an organization positively, by demonstrating its commitment to ethical principles, values, and standards in its business practices, services, and products. Ethics awareness and policy implementation can also help the organization avoid legal liabilities, fines, or sanctions for unethical conduct, and foster trust and loyalty among its customers, partners, and employees. The other options are not as important as affecting the reputation, as they either do not directly relate to ethics (A), or are secondary outcomes of ethics (C and D). References: CISSP All-in-One Exam Guide, Eighth Edition, Chapter 1, page 19; Official (ISC)2 CISSP CBK Reference, Fifth Edition, Chapter 1, page 28.
Refer to the information below to answer the question.
A large, multinational organization has decided to outsource a portion of their Information Technology (IT) organization to a third-party provider’s facility. This provider will be responsible for the design, development, testing, and support of several critical, customer-based applications used by the organization.
What additional considerations are there if the third party is located in a different country?
The organizational structure of the third party and how it may impact timelines within the organization
The ability of the third party to respond to the organization in a timely manner and with accurate information
The effects of transborder data flows and customer expectations regarding the storage or processing of their data
The quantity of data that must be provided to the third party and how it is to be used
The additional considerations that are there if the third party is located in a different country are the effects of transborder data flows and customer expectations regarding the storage or processing of their data. Transborder data flows are the movements or the transfers of data across the national or the regional borders, such as the internet, the cloud, or the outsourcing. Transborder data flows can have various effects on the security, the privacy, the compliance, or the sovereignty of the data, depending on the laws, the regulations, the standards, or the cultures of the different countries or regions involved. Customer expectations are the beliefs or the assumptions of the customers about the quality, the performance, or the satisfaction of the products or the services that they use or purchase. Customer expectations can vary depending on the needs, the preferences, or the values of the customers, and they can influence the reputation, the loyalty, or the profitability of the organization. The organization should consider the effects of transborder data flows and customer expectations regarding the storage or processing of their data, as they can affect the security, the privacy, the compliance, or the sovereignty of the data, and they can impact the reputation, the loyalty, or the profitability of the organization. The organization should also consider the legal, the contractual, the ethical, or the cultural implications of the transborder data flows and customer expectations, and they should communicate, negotiate, or align with the third party and the customers accordingly. The organization should not consider the organizational structure of the third party and how it may impact timelines within the organization, the ability of the third party to respond to the organization in a timely manner and with accurate information, or the quantity of data that must be provided to the third party and how it is to be used, as they are related to the management, the communication, or the provision of the data, not the effects of transborder data flows and customer expectations regarding the storage or processing of their data. References: CISSP All-in-One Exam Guide, Eighth Edition, Chapter 1, Security and Risk Management, page 59. Official (ISC)2 CISSP CBK Reference, Fifth Edition, Chapter 1, Security and Risk Management, page 74.
From a security perspective, which of the following is a best practice to configure a Domain Name Service (DNS) system?
Configure secondary servers to use the primary server as a zone forwarder.
Block all Transmission Control Protocol (TCP) connections.
Disable all recursive queries on the name servers.
Limit zone transfers to authorized devices.
From a security perspective, the best practice to configure a DNS system is to limit zone transfers to authorized devices. Zone transfers are the processes of replicating the DNS data from one server to another, usually from a primary server to a secondary server. Zone transfers can expose sensitive information about the network topology, hosts, and services to attackers, who can use this information to launch further attacks. Therefore, zone transfers should be restricted to only the devices that need them, and authenticated and encrypted to prevent unauthorized access or modification. The other options are not as good as limiting zone transfers, as they either do not provide sufficient security for the DNS system (A and B), or do not address the zone transfer issue ©. References: CISSP All-in-One Exam Guide, Eighth Edition, Chapter 4, page 156; Official (ISC)2 CISSP CBK Reference, Fifth Edition, Chapter 4, page 166.
Which of the following problems is not addressed by using OAuth (Open Standard to Authorization) 2.0 to integrate a third-party identity provider for a service?
Resource Servers are required to use passwords to authenticate end users.
Revocation of access of some users of the third party instead of all the users from the third party.
Compromise of the third party means compromise of all the users in the service.
Guest users need to authenticate with the third party identity provider.
The problem that is not addressed by using OAuth 2.0 to integrate a third-party identity provider for a service is that resource servers are required to use passwords to authenticate end users. OAuth 2.0 is a framework that enables a third-party application to obtain limited access to a protected resource on behalf of a resource owner, without exposing the resource owner’s credentials to the third-party application. OAuth 2.0 relies on an authorization server that acts as an identity provider and issues access tokens to the third-party application, based on the resource owner’s consent and the scope of the access request. OAuth 2.0 does not address the authentication of the resource owner or the end user by the resource server, which is the server that hosts the protected resource. The resource server may still require the resource owner or the end user to use passwords or other methods to authenticate themselves, before granting access to the protected resource. Revocation of access of some users of the third party instead of all the users from the third party, compromise of the third party means compromise of all the users in the service, and guest users need to authenticate with the third party identity provider are problems that are addressed by using OAuth 2.0 to integrate a third-party identity provider for a service, as they are related to the delegation, revocation, or granularity of the access control or the identity management. References: CISSP All-in-One Exam Guide, Eighth Edition, Chapter 5, Identity and Access Management, page 692. Official (ISC)2 CISSP CBK Reference, Fifth Edition, Chapter 5, Identity and Access Management, page 708.
Refer to the information below to answer the question.
A large organization uses unique identifiers and requires them at the start of every system session. Application access is based on job classification. The organization is subject to periodic independent reviews of access controls and violations. The organization uses wired and wireless networks and remote access. The organization also uses secure connections to branch offices and secure backup and recovery strategies for selected information and processes.
What MUST the access control logs contain in addition to the identifier?
Time of the access
Security classification
Denied access attempts
Associated clearance
The access control logs must contain the time of the access, in addition to the identifier. Access control logs are the records or the files that capture and store the information or the data related to the access control events or activities, such as the authentication, the authorization, the audit, or the accountability. Access control logs can help to monitor and analyze the access control performance and effectiveness, to detect and investigate any security incidents or breaches, and to provide evidence or proof for any legal or regulatory actions. The access control logs must contain the time of the access, as it can help to identify and verify when the access control event or activity occurred, and to correlate and compare it with other events or activities, such as the network traffic, the system activity, or the user behavior. The time of the access can also help to determine the duration and the frequency of the access control event or activity, and to measure and evaluate the access control efficiency and quality. The security classification, the denied access attempts, and the associated clearance are not the information that must be contained in the access control logs, as they are related to the level of sensitivity or protection of the data or the resource, the unsuccessful or rejected access control requests, or the level of authorization or permission of the user or the device, not the time of the access control event or activity. References: CISSP All-in-One Exam Guide, Eighth Edition, Chapter 5, Identity and Access Management, page 671. Official (ISC)2 CISSP CBK Reference, Fifth Edition, Chapter 5, Identity and Access Management, page 687.
Place the following information classification steps in sequential order.
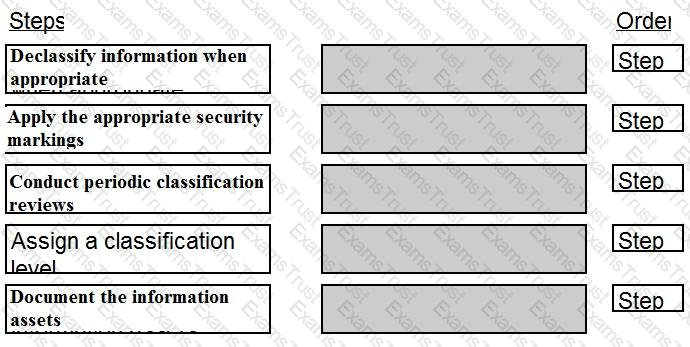

The following information classification steps should be placed in sequential order as follows:
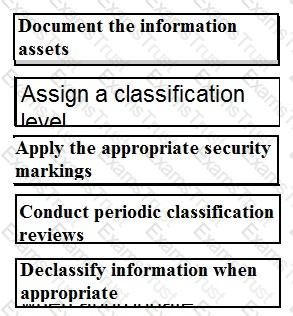
Information classification is a process or a method of categorizing the information assets based on their sensitivity, criticality, or value, and applying the appropriate security controls or measures to protect them. Information classification can help to ensure the confidentiality, the integrity, and the availability of the information assets, and to support the security, the compliance, or the business objectives of the organization. The information classification steps are the activities or the tasks that are involved in the information classification process, and they should be performed in a sequential order, as follows:
Which of the following is the BEST reason to review audit logs periodically?
Verify they are operating properly
Monitor employee productivity
Identify anomalies in use patterns
Meet compliance regulations
The best reason to review audit logs periodically is to identify anomalies in use patterns that may indicate unauthorized or malicious activities, such as intrusion attempts, data breaches, policy violations, or system errors. Audit logs record the events and actions that occur on a system or network, and can provide valuable information for security analysis, investigation, and response. The other options are not as good as identifying anomalies, as they either do not relate to security (B), or are not the primary purpose of audit logs (A and D). References: CISSP All-in-One Exam Guide, Eighth Edition, Chapter 7, page 405; Official (ISC)2 CISSP CBK Reference, Fifth Edition, Chapter 7, page 465.
What is the BEST first step for determining if the appropriate security controls are in place for protecting data at rest?
Identify regulatory requirements
Conduct a risk assessment
Determine business drivers
Review the security baseline configuration
A risk assessment is the best first step for determining if the appropriate security controls are in place for protecting data at rest. A risk assessment involves identifying the assets, threats, vulnerabilities, and impacts related to the data, as well as the likelihood and severity of potential breaches. Based on the risk assessment, the appropriate security controls can be selected and implemented to mitigate the risks to an acceptable level. References: CISSP All-in-One Exam Guide, Eighth Edition, Chapter 1: Security and Risk Management, p. 35; Official (ISC)2 CISSP CBK Reference, Fifth Edition, Domain 1: Security and Risk Management, p. 41.
Refer to the information below to answer the question.
A security practitioner detects client-based attacks on the organization’s network. A plan will be necessary to address these concerns.
What is the BEST reason for the organization to pursue a plan to mitigate client-based attacks?
Client privilege administration is inherently weaker than server privilege administration.
Client hardening and management is easier on clients than on servers.
Client-based attacks are more common and easier to exploit than server and network based attacks.
Client-based attacks have higher financial impact.
The best reason for the organization to pursue a plan to mitigate client-based attacks is that client-based attacks are more common and easier to exploit than server and network based attacks. Client-based attacks are the attacks that target the client applications or systems, such as web browsers, email clients, or media players, and that can exploit the vulnerabilities or weaknesses of the client software or configuration, or the user behavior or interaction. Client-based attacks are more common and easier to exploit than server and network based attacks, because the client applications or systems are more exposed and accessible to the attackers, the client software or configuration is more diverse and complex to secure, and the user behavior or interaction is more unpredictable and prone to errors or mistakes. Therefore, the organization needs to pursue a plan to mitigate client-based attacks, as they pose a significant security threat or risk to the organization’s data, systems, or network. Client privilege administration is inherently weaker than server privilege administration, client hardening and management is easier on clients than on servers, and client-based attacks have higher financial impact are not the best reasons for the organization to pursue a plan to mitigate client-based attacks, as they are not supported by the facts or evidence, or they are not relevant or specific to the client-side security. References: CISSP All-in-One Exam Guide, Eighth Edition, Chapter 8, Software Development Security, page 1050. Official (ISC)2 CISSP CBK Reference, Fifth Edition, Chapter 8, Software Development Security, page 1066.
A security manager has noticed an inconsistent application of server security controls resulting in vulnerabilities on critical systems. What is the MOST likely cause of this issue?
A lack of baseline standards
Improper documentation of security guidelines
A poorly designed security policy communication program
Host-based Intrusion Prevention System (HIPS) policies are ineffective
The most likely cause of the inconsistent application of server security controls resulting in vulnerabilities on critical systems is a lack of baseline standards. Baseline standards are the minimum level of security controls and measures that must be applied to the servers or other assets to ensure their protection and compliance. Baseline standards help to establish a consistent and uniform security posture across the organization, and to prevent or reduce the exposure to threats and risks. If there is a lack of baseline standards, the server security controls may vary in quality, effectiveness, or completeness, resulting in vulnerabilities on critical systems. Improper documentation of security guidelines, a poorly designed security policy communication program, and ineffective Host-based Intrusion Prevention System (HIPS) policies are not the most likely causes of this issue, as they do not directly affect the application of server security controls or the existence of baseline standards. References: CISSP All-in-One Exam Guide, Eighth Edition, Chapter 1, Security and Risk Management, page 35. Official (ISC)2 CISSP CBK Reference, Fifth Edition, Chapter 1, Security and Risk Management, page 48.
What physical characteristic does a retinal scan biometric device measure?
The amount of light reflected by the retina
The size, curvature, and shape of the retina
The pattern of blood vessels at the back of the eye
The pattern of light receptors at the back of the eye
A retinal scan is a biometric technique that uses unique patterns on a person’s retina blood vessels to identify them. The retina is a thin layer of tissue at the back of the eye that contains millions of light-sensitive cells and blood vessels. The retina converts the light rays that enter the eye into electrical signals that are sent to the brain for visual processing78
The pattern of blood vessels in the retina is not genetically determined and varies from person to person, even among identical twins. The retina also remains unchanged from birth until death, unless affected by some diseases or injuries. Therefore, the retina is considered to be one of the most accurate and reliable biometrics, apart from DNA78
A retinal scan is performed by projecting a low-energy infrared beam of light into a person’s eye as they look through the scanner’s eyepiece. The beam traces a standardized path on the retina, and the amount of light reflected by the blood vessels is measured. The pattern of variations in the reflection is digitized and stored in a database for comparison
When dealing with compliance with the Payment Card Industry-Data Security Standard (PCI-DSS), an organization that shares card holder information with a service provider MUST do which of the following?
Perform a service provider PCI-DSS assessment on a yearly basis.
Validate the service provider's PCI-DSS compliance status on a regular basis.
Validate that the service providers security policies are in alignment with those of the organization.
Ensure that the service provider updates and tests its Disaster Recovery Plan (DRP) on a yearly basis.
The action that an organization that shares card holder information with a service provider must do when dealing with compliance with the Payment Card Industry-Data Security Standard (PCI-DSS) is to validate the service provider’s PCI-DSS compliance status on a regular basis. PCI-DSS is a set of security standards that applies to any organization that stores, processes, or transmits card holder data, such as credit or debit card information. PCI-DSS aims to protect the card holder data from unauthorized access, use, disclosure, or theft, and to ensure the security and integrity of the payment transactions. If an organization shares card holder data with a service provider, such as a payment processor, a hosting provider, or a cloud provider, the organization is still responsible for the security and compliance of the card holder data, and must ensure that the service provider also meets the PCI-DSS requirements. The organization must validate the service provider’s PCI-DSS compliance status on a regular basis, by obtaining and reviewing the service provider’s PCI-DSS assessment reports, such as the Self-Assessment Questionnaire (SAQ), the Report on Compliance (ROC), or the Attestation of Compliance (AOC). Performing a service provider PCI-DSS assessment on a yearly basis, validating that the service provider’s security policies are in alignment with those of the organization, and ensuring that the service provider updates and tests its Disaster Recovery Plan (DRP) on a yearly basis are not the actions that an organization that shares card holder information with a service provider must do when dealing with compliance with PCI-DSS, as they are not sufficient or relevant to verify the service provider’s PCI-DSS compliance status or to protect the card holder data. References: CISSP All-in-One Exam Guide, Eighth Edition, Chapter 1, Security and Risk Management, page 49. Official (ISC)2 CISSP CBK Reference, Fifth Edition, Chapter 1, Security and Risk Management, page 64.
Refer to the information below to answer the question.
Desktop computers in an organization were sanitized for re-use in an equivalent security environment. The data was destroyed in accordance with organizational policy and all marking and other external indications of the sensitivity of the data that was formerly stored on the magnetic drives were removed.
Organizational policy requires the deletion of user data from Personal Digital Assistant (PDA) devices before disposal. It may not be possible to delete the user data if the device is malfunctioning. Which destruction method below provides the BEST assurance that the data has been removed?
Knurling
Grinding
Shredding
Degaussing
The best destruction method that provides the assurance that the data has been removed from a malfunctioning PDA device is shredding. Shredding is a method of physically destroying the media, such as flash memory cards, by cutting or tearing them into small pieces that make the data unrecoverable. Shredding can be effective in removing the data from a PDA device that cannot be deleted by software or firmware methods, as it does not depend on the functionality of the device or the media. Shredding can also prevent the reuse or the recycling of the media or the device, as it renders them unusable. Knurling, grinding, and degaussing are not the best destruction methods that provide the assurance that the data has been removed from a malfunctioning PDA device, as they are related to the methods of altering the surface, the shape, or the magnetic field of the media, not the methods of cutting or tearing the media into small pieces. References: CISSP All-in-One Exam Guide, Eighth Edition, Chapter 7, Security Operations, page 889. Official (ISC)2 CISSP CBK Reference, Fifth Edition, Chapter 7, Security Operations, page 905.
When implementing a secure wireless network, which of the following supports authentication and authorization for individual client endpoints.
Temporal Key Integrity Protocol (TKIP)
Wi-Fi Protected Access (WPA) Pre-Shared Key (PSK)
Wi-Fi Protected Access 2 (WPA2) Enterprise
Counter Mode with Cipher Block Chaining Message Authentication Code Protocol (CCMP)
When implementing a secure wireless network, the option that supports authentication and authorization for individual client endpoints is Wi-Fi Protected Access 2 (WPA2) Enterprise. WPA2 is a security protocol that provides encryption and authentication for wireless networks, based on the IEEE 802.11i standard. WPA2 has two modes: Personal and Enterprise. WPA2 Personal uses a Pre-Shared Key (PSK) that is shared among all the devices on the network, and does not require a separate authentication server. WPA2 Enterprise uses an Extensible Authentication Protocol (EAP) that authenticates each device individually, using a username and password or a certificate, and requires a Remote Authentication Dial-In User Service (RADIUS) server or another authentication server. WPA2 Enterprise provides more security and granularity than WPA2 Personal, as it can support different levels of access and permissions for different users or groups, and can prevent unauthorized or compromised devices from joining the network. Temporal Key Integrity Protocol (TKIP), Wi-Fi Protected Access (WPA) Pre-Shared Key (PSK), and Counter Mode with Cipher Block Chaining Message Authentication Code Protocol (CCMP) are not the options that support authentication and authorization for individual client endpoints, as they are related to the encryption or integrity of the wireless data, not the identity or access of the wireless devices. References: CISSP All-in-One Exam Guide, Eighth Edition, Chapter 4, Communication and Network Security, page 506. Official (ISC)2 CISSP CBK Reference, Fifth Edition, Chapter 4, Communication and Network Security, page 522.
Which one of the following affects the classification of data?
Assigned security label
Multilevel Security (MLS) architecture
Minimum query size
Passage of time
The passage of time is one of the factors that affects the classification of data. Data classification is the process of assigning a level of sensitivity or criticality to data based on its value, impact, and legal requirements. Data classification helps to determine the appropriate security controls and handling procedures for the data. However, data classification is not static, but dynamic, meaning that it can change over time depending on various factors. One of these factors is the passage of time, which can affect the relevance, usefulness, or sensitivity of the data. For example, data that is classified as confidential or secret at one point in time may become obsolete, outdated, or declassified at a later point in time, and thus require a lower level of protection. Conversely, data that is classified as public or unclassified at one point in time may become more valuable, sensitive, or regulated at a later point in time, and thus require a higher level of protection. Therefore, data classification should be reviewed and updated periodically to reflect the changes in the data over time.
The other options are not factors that affect the classification of data, but rather the outcomes or components of data classification. Assigned security label is the result of data classification, which indicates the level of sensitivity or criticality of the data. Multilevel Security (MLS) architecture is a system that supports data classification, which allows different levels of access to data based on the clearance and need-to-know of the users. Minimum query size is a parameter that can be used to enforce data classification, which limits the amount of data that can be retrieved or displayed at a time.
Which of the following is an effective control in preventing electronic cloning of Radio Frequency Identification (RFID) based access cards?
Personal Identity Verification (PIV)
Cardholder Unique Identifier (CHUID) authentication
Physical Access Control System (PACS) repeated attempt detection
Asymmetric Card Authentication Key (CAK) challenge-response
Asymmetric Card Authentication Key (CAK) challenge-response is an effective control in preventing electronic cloning of RFID based access cards. RFID based access cards are contactless cards that use radio frequency identification (RFID) technology to communicate with a reader and grant access to a physical or logical resource. RFID based access cards are vulnerable to electronic cloning, which is the process of copying the data and identity of a legitimate card to a counterfeit card, and using it to impersonate the original cardholder and gain unauthorized access. Asymmetric CAK challenge-response is a cryptographic technique that prevents electronic cloning by using public key cryptography and digital signatures to verify the authenticity and integrity of the card and the reader. Asymmetric CAK challenge-response works as follows:
Asymmetric CAK challenge-response prevents electronic cloning because the private keys of the card and the reader are never transmitted or exposed, and the signatures are unique and non-reusable for each transaction. Therefore, a cloned card cannot produce a valid signature without knowing the private key of the original card, and a rogue reader cannot impersonate a legitimate reader without knowing its private key.
The other options are not as effective as asymmetric CAK challenge-response in preventing electronic cloning of RFID based access cards. Personal Identity Verification (PIV) is a standard for federal employees and contractors to use smart cards for physical and logical access, but it does not specify the cryptographic technique for RFID based access cards. Cardholder Unique Identifier (CHUID) authentication is a technique that uses a unique number and a digital certificate to identify the card and the cardholder, but it does not prevent replay attacks or verify the reader’s identity. Physical Access Control System (PACS) repeated attempt detection is a technique that monitors and alerts on multiple failed or suspicious attempts to access a resource, but it does not prevent the cloning of the card or the impersonation of the reader.
An organization has doubled in size due to a rapid market share increase. The size of the Information Technology (IT) staff has maintained pace with this growth. The organization hires several contractors whose onsite time is limited. The IT department has pushed its limits building servers and rolling out workstations and has a backlog of account management requests.
Which contract is BEST in offloading the task from the IT staff?
Platform as a Service (PaaS)
Identity as a Service (IDaaS)
Desktop as a Service (DaaS)
Software as a Service (SaaS)
Identity as a Service (IDaaS) is the best contract in offloading the task of account management from the IT staff. IDaaS is a cloud-based service that provides identity and access management (IAM) functions, such as user authentication, authorization, provisioning, deprovisioning, password management, single sign-on (SSO), and multifactor authentication (MFA). IDaaS can help the organization to streamline and automate the account management process, reduce the workload and costs of the IT staff, and improve the security and compliance of the user accounts. IDaaS can also support the contractors who have limited onsite time, as they can access the organization’s resources remotely and securely through the IDaaS provider.
The other options are not as effective as IDaaS in offloading the task of account management from the IT staff, as they do not provide IAM functions. Platform as a Service (PaaS) is a cloud-based service that provides a platform for developing, testing, and deploying applications, but it does not manage the user accounts for the applications. Desktop as a Service (DaaS) is a cloud-based service that provides virtual desktops for users to access applications and data, but it does not manage the user accounts for the virtual desktops. Software as a Service (SaaS) is a cloud-based service that provides software applications for users to use, but it does not manage the user accounts for the software applications.
Which of the following is an initial consideration when developing an information security management system?
Identify the contractual security obligations that apply to the organizations
Understand the value of the information assets
Identify the level of residual risk that is tolerable to management
Identify relevant legislative and regulatory compliance requirements
When developing an information security management system (ISMS), an initial consideration is to understand the value of the information assets that the organization owns or processes. An information asset is any data, information, or knowledge that has value to the organization and supports its mission, objectives, and operations. Understanding the value of the information assets helps to determine the appropriate level of protection and investment for them, as well as the potential impact and consequences of losing, compromising, or disclosing them. Understanding the value of the information assets also helps to identify the stakeholders, owners, and custodians of the information assets, and their roles and responsibilities in the ISMS.
The other options are not initial considerations, but rather subsequent or concurrent considerations when developing an ISMS. Identifying the contractual security obligations that apply to the organizations is a consideration that depends on the nature, scope, and context of the information assets, as well as the relationships and agreements with the external parties. Identifying the level of residual risk that is tolerable to management is a consideration that depends on the risk appetite and tolerance of the organization, as well as the risk assessment and analysis of the information assets. Identifying relevant legislative and regulatory compliance requirements is a consideration that depends on the legal and ethical obligations and expectations of the organization, as well as the jurisdiction and industry of the information assets.
In a data classification scheme, the data is owned by the
system security managers
business managers
Information Technology (IT) managers
end users
In a data classification scheme, the data is owned by the business managers. Business managers are the persons or entities that have the authority and accountability for the creation, collection, processing, and disposal of a set of data. Business managers are also responsible for defining the purpose, value, and classification of the data, as well as the security requirements and controls for the data. Business managers should be able to determine the impact the information has on the mission of the organization, which means assessing the potential consequences of losing, compromising, or disclosing the data. The impact of the information on the mission of the organization is one of the main criteria for data classification, which helps to establish the appropriate level of protection and handling for the data.
The other options are not the data owners in a data classification scheme, but rather the other roles or functions related to data management. System security managers are the persons or entities that oversee the security of the information systems and networks that store, process, and transmit the data. They are responsible for implementing and maintaining the technical and physical security of the data, as well as monitoring and auditing the security performance and incidents. Information Technology (IT) managers are the persons or entities that manage the IT resources and services that support the business processes and functions that use the data. They are responsible for ensuring the availability, reliability, and scalability of the IT infrastructure and applications, as well as providing technical support and guidance to the users and stakeholders. End users are the persons or entities that access and use the data for their legitimate purposes and needs. They are responsible for complying with the security policies and procedures for the data, as well as reporting any security issues or violations.
When implementing a data classification program, why is it important to avoid too much granularity?
The process will require too many resources
It will be difficult to apply to both hardware and software
It will be difficult to assign ownership to the data
The process will be perceived as having value
When implementing a data classification program, it is important to avoid too much granularity, because the process will require too many resources. Data classification is the process of assigning a level of sensitivity or criticality to data based on its value, impact, and legal requirements. Data classification helps to determine the appropriate security controls and handling procedures for the data. However, data classification is not a simple or straightforward process, as it involves many factors, such as the nature, context, and scope of the data, the stakeholders, the regulations, and the standards. If the data classification program has too many levels or categories of data, it will increase the complexity, cost, and time of the process, and reduce the efficiency and effectiveness of the data protection. Therefore, data classification should be done with a balance between granularity and simplicity, and follow the principle of proportionality, which means that the level of protection should be proportional to the level of risk.
The other options are not the main reasons to avoid too much granularity in data classification, but rather the potential challenges or benefits of data classification. It will be difficult to apply to both hardware and software is a challenge of data classification, as it requires consistent and compatible methods and tools for labeling and protecting data across different types of media and devices. It will be difficult to assign ownership to the data is a challenge of data classification, as it requires clear and accountable roles and responsibilities for the creation, collection, processing, and disposal of data. The process will be perceived as having value is a benefit of data classification, as it demonstrates the commitment and awareness of the organization to protect its data assets and comply with its obligations.
Which of the following BEST describes the responsibilities of a data owner?
Ensuring quality and validation through periodic audits for ongoing data integrity
Maintaining fundamental data availability, including data storage and archiving
Ensuring accessibility to appropriate users, maintaining appropriate levels of data security
Determining the impact the information has on the mission of the organization
The best description of the responsibilities of a data owner is determining the impact the information has on the mission of the organization. A data owner is a person or entity that has the authority and accountability for the creation, collection, processing, and disposal of a set of data. A data owner is also responsible for defining the purpose, value, and classification of the data, as well as the security requirements and controls for the data. A data owner should be able to determine the impact the information has on the mission of the organization, which means assessing the potential consequences of losing, compromising, or disclosing the data. The impact of the information on the mission of the organization is one of the main criteria for data classification, which helps to establish the appropriate level of protection and handling for the data.
The other options are not the best descriptions of the responsibilities of a data owner, but rather the responsibilities of other roles or functions related to data management. Ensuring quality and validation through periodic audits for ongoing data integrity is a responsibility of a data steward, who is a person or entity that oversees the quality, consistency, and usability of the data. Maintaining fundamental data availability, including data storage and archiving is a responsibility of a data custodian, who is a person or entity that implements and maintains the technical and physical security of the data. Ensuring accessibility to appropriate users, maintaining appropriate levels of data security is a responsibility of a data controller, who is a person or entity that determines the purposes and means of processing the data.
Which of the following is MOST important when assigning ownership of an asset to a department?
The department should report to the business owner
Ownership of the asset should be periodically reviewed
Individual accountability should be ensured
All members should be trained on their responsibilities
When assigning ownership of an asset to a department, the most important factor is to ensure individual accountability for the asset. Individual accountability means that each person who has access to or uses the asset is responsible for its protection and proper handling. Individual accountability also implies that each person who causes or contributes to a security breach or incident involving the asset can be identified and held liable. Individual accountability can be achieved by implementing security controls such as authentication, authorization, auditing, and logging.
The other options are not as important as ensuring individual accountability, as they do not directly address the security risks associated with the asset. The department should report to the business owner is a management issue, not a security issue. Ownership of the asset should be periodically reviewed is a good practice, but it does not prevent misuse or abuse of the asset. All members should be trained on their responsibilities is a preventive measure, but it does not guarantee compliance or enforcement of the responsibilities.
A development operations team would like to start building new applications delegating the cybersecurity responsibility as much as possible to the service provider. Which of the following environments BEST fits their need?
Cloud Virtual Machines (VM)
Cloud application container within a Virtual Machine (VM)
On premises Virtual Machine (VM)
Self-hosted Virtual Machine (VM)
A cloud application container within a Virtual Machine (VM) is the environment that best fits the need of a development operations team that would like to start building new applications delegating the cybersecurity responsibility as much as possible to the service provider. A cloud application container within a VM is a type of cloud computing service that allows the development operations team to deploy and run their applications in isolated and lightweight environments that are hosted on a VM in the cloud. A cloud application container within a VM can provide several benefits to the development operations team, such as improving the portability, the scalability, the efficiency, and the performance of their applications. A cloud application container within a VM can also delegate the cybersecurity responsibility as much as possible to the service provider, as the service provider is responsible for managing and securing the underlying infrastructure, platform, and VM that host the application container. The development operations team only needs to focus on securing their application container and the data that is stored and processed within it, and rely on the service provider to provide the security controls and the protection for the rest of the cloud environment. References: CISSP All-in-One Exam Guide, Eighth Edition, Chapter 4: Communication and Network Security, page 154. CISSP Practice Exam | Boson, Question 15.
A developer begins employment with an information technology (IT) organization. On the first day, the developer works through the list of assigned projects and finds that some files within those projects aren't accessible, Other developers working on the same project have no trouble locating and working on the. What is the MOST likely explanation for the discrepancy in access?
The IT administrator had failed to grant the developer privileged access to the servers.
The project files were inadvertently deleted.
The new developer's computer had not been added to an access control list (ACL).
The new developer's user account was not associated with the right roles needed for the projects.
The most likely explanation for the discrepancy in access is that the new developer’s user account was not assigned the appropriate roles that correspond to the access rights for the project files. Roles are a way of grouping users based on their functions or responsibilities within an organization, and they can simplify the administration of access control policies. If the new developer’s user account was not associated with the right roles, he or she would not be able to access the files that other developers with the same roles can access. References: CISSP - Certified Information Systems Security Professional, Domain 5. Identity and Access Management (IAM), 5.1 Control physical and logical access to assets, 5.1.2 Manage identification and authentication of people, devices and services, 5.1.2.1 Identity management implementation; CISSP Exam Outline, Domain 5. Identity and Access Management (IAM), 5.1 Control physical and logical access to assets, 5.1.2 Manage identification and authentication of people, devices and services, 5.1.2.1 Identity management implementation
What is the MOST important goal of conducting security assessments?
To prepare the organization for an external audit, particularly by a regulatory entity
To discover unmitigated security vulnerabilities, and propose paths for mitigating them
To align the security program with organizational risk appetite
To demonstrate proper function of security controls and processes to senior management
The most important goal of conducting security assessments is to discover unmitigated security vulnerabilities, and propose paths for mitigating them. A security assessment is a process that involves evaluating and testing the security posture and performance of a system or network, and identifying and reporting any security vulnerabilities or issues that may pose a security risk. A security assessment can help to discover unmitigated security vulnerabilities, which are the security flaws or weaknesses that have not been detected, reported, or resolved, and that can be exploited by the adversaries to compromise the security of the system or network. A security assessment can also help to propose paths for mitigating the security vulnerabilities, which are the actions or measures that can be taken to eliminate, reduce, or transfer the security risk associated with the security vulnerabilities. Discovering unmitigated security vulnerabilities, and proposing paths for mitigating them, is the most important goal of conducting security assessments, as it can help to improve the security level and quality of the system or network, and to prevent or minimize the potential damage or loss caused by the security incidents or breaches . References: [CISSP CBK, Fifth Edition, Chapter 6, page 540]; [CISSP Practice Exam – FREE 20 Questions and Answers, Question 12].
Which of the following is the BEST method to gather evidence from a computer's hard drive?
Disk duplication
Disk replacement
Forensic signature
Forensic imaging
Forensic imaging is the best method to gather evidence from a computer’s hard drive, as it creates a bit-by-bit copy of the original drive, preserving the integrity and authenticity of the evidence. Disk duplication, disk replacement, and forensic signature are not valid methods for evidence collection, as they may alter or destroy the original data on the drive. References: CISSP All-in-One Exam Guide, Eighth Edition, Chapter 9: Law, Investigation, and Ethics, page 1008.
Which of the following is held accountable for the risk to organizational systems and data that result from outsourcing Information Technology (IT) systems and services?
The acquiring organization
The service provider
The risk executive (function)
The IT manager
The acquiring organization is held accountable for the risk to organizational systems and data that result from outsourcing Information Technology (IT) systems and services. Outsourcing is the practice of contracting out a business function or process to a third-party provider, such as a cloud service provider, a data center, or a managed service provider. Outsourcing can offer various benefits to the acquiring organization, such as cost reduction, efficiency improvement, scalability enhancement, and expertise access. However, outsourcing also introduces various risks to the organizational systems and data, such as loss of control, dependency, compliance issues, service quality issues, and security breaches. The acquiring organization is ultimately responsible and accountable for the risk management of the outsourced IT systems and services, as it owns the systems and data and bears the consequences of any adverse events. The acquiring organization should perform due diligence, risk assessment, contract negotiation, service level agreement, monitoring, and auditing of the service provider, and ensure that the service provider meets the security and performance requirements and standards of the acquiring organization. References: CISSP All-in-One Exam Guide, Eighth Edition, Chapter 1: Security and Risk Management, page 14. CISSP Testking ISC Exam Questions, Question 15.
What should be used to determine the risks associated with using Software as a Service (SaaS) for collaboration and email?
Cloud access security broker (CASB)
Open Web Application Security Project (OWASP)
Process for Attack Simulation and Threat Analysis (PASTA)
Common Security Framework (CSF)
The Common Security Framework (CSF) is a set of security standards, best practices, and tools developed by the Health Information Trust Alliance (HITRUST) to help organizations manage the risks and compliance requirements associated with using cloud services, such as Software as a Service (SaaS). The CSF covers 19 domains of security controls, such as access control, audit logging, encryption, incident management, and vulnerability management. The CSF also provides a certification program and a self-assessment tool for organizations to measure and demonstrate their adherence to the CSF requirements. The CSF is designed to be flexible, scalable, and customizable to suit the needs and objectives of different types and sizes of organizations. The CSF is not specific to the healthcare industry, although it incorporates some healthcare-related regulations and standards, such as the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA) and the Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard (PCI DSS). The CSF can be used to determine the risks associated with using SaaS for collaboration and email, as well as other cloud services and applications. References: CISSP All-in-One Exam Guide, Eighth Edition, Chapter 3: Security Engineering, page 169. Official (ISC)² CISSP CBK Reference, Fifth Edition, Domain 3: Security Architecture and Engineering, page 385.
Which of the following MOST applies to session initiation protocal (SIP) security?
It leverages Hypertext Transfer Protocol (HTTP) over Transport Layer Security (TLS).
It requires a Public Key Infrastructure (PKI).
It reuses security mechanisms derived from existing protocols.
It supports end-to-end security natively.
Session Initiation Protocol (SIP) is an application layer protocol that is used to establish, modify, and terminate multimedia sessions over the Internet. SIP does not support end-to-end security natively, but it reuses security mechanisms derived from existing protocols, such as Transport Layer Security (TLS), Secure Real-time Transport Protocol (SRTP), and Internet Protocol Security (IPsec). SIP does not leverage Hypertext Transfer Protocol (HTTP) over TLS, nor does it require a Public Key Infrastructure (PKI). References:
CISSP Official (ISC)2 Practice Tests, 3rd Edition, Domain 4: Communication and Network Security, Question 4.1.6
CISSP CBK, 5th Edition, Chapter 4: Communication and Network Security, Section: Secure Network Components and Communication Channels
The adoption of an enterprise-wide business continuity program requires Which of the following?
Good communication throughout the organization
Formation of Disaster Recovery (DP) project team
A completed Business Impact Analysis (BIA)
Well-documented information asset classification
The adoption of an enterprise-wide business continuity program requires good communication throughout the organization. A business continuity program is a set of policies, procedures, and plans that aim to ensure the continuity of critical business functions and processes in the event of a disruption or disaster. Good communication throughout the organization is essential for the adoption of a business continuity program, because it helps to raise awareness, gain support, coordinate activities, and share information among the stakeholders involved in the business continuity process. Formation of a disaster recovery project team, a completed business impact analysis, and well-documented information asset classification are not the requirements for the adoption of an enterprise-wide business continuity program, although they are important components of the business continuity process. A disaster recovery project team is a group of people who are responsible for planning, implementing, and testing the disaster recovery strategies and procedures for a specific business unit or function. A business impact analysis is a process of identifying and evaluating the potential impacts of a disruption or disaster on the business objectives, functions, and processes. An information asset classification is a process of assigning labels or categories to the information assets based on their value, sensitivity, and criticality to the organization. References: CISSP All-in-One Exam Guide, Eighth Edition, Chapter 7: Security Operations, page 747. Official (ISC)2 CISSP CBK Reference, Fifth Edition, Chapter 7: Security Operations, page 507.
When assessing web vulnerabilities, how can navigating the dark web add value to a penetration test?
The actual origin and tools used for the test can be hidden.
Information may be found on related breaches and hacking.
Vulnerabilities can be tested without impact on the tested environment.
Information may be found on hidden vendor patches.
The way that navigating the dark web can add value to a penetration test when assessing web vulnerabilities is that information may be found on related breaches and hacking. The dark web is a part of the internet that is not indexed or accessible by conventional search engines or browsers, and that requires special software or tools, such as Tor or I2P, to access. The dark web is often used for illegal or malicious activities, such as selling or buying drugs, weapons, or stolen data, or sharing or exchanging hacking tools, techniques, or information. Navigating the dark web can add value to a penetration test when assessing web vulnerabilities, as it can help to find information on related breaches and hacking, such as the vulnerabilities, exploits, or attacks that have been used or disclosed by hackers or cybercriminals against the target system or organization, or the data or credentials that have been stolen or compromised from the target system or organization. This information can help to identify or verify the existing or potential web vulnerabilities, to evaluate or prioritize the web vulnerabilities, or to simulate or replicate the web vulnerabilities or attacks. The actual origin and tools used for the test can be hidden, vulnerabilities can be tested without impact on the tested environment, or information may be found on hidden vendor patches are not the ways that navigating the dark web can add value to a penetration test when assessing web vulnerabilities, as they are not true or relevant. The actual origin and tools used for the test cannot be hidden by navigating the dark web, as this is not a function or a feature of the dark web. The actual origin and tools used for the test can be hidden by using other techniques or methods, such as proxy servers, virtual private networks, or encryption. Vulnerabilities cannot be tested without impact on the tested environment by navigating the dark web, as this is not a purpose or a benefit of the dark web. Vulnerabilities can be tested without impact on the tested environment by using other techniques or methods, such as sandboxing, virtualization, or simulation. Information on hidden vendor patches cannot be found by navigating the dark web, as this is not a type or a source of information that is available or accessible on the dark web. Information on hidden vendor patches can be found by using other techniques or methods, such as reverse engineering, vulnerability scanning, or vendor disclosure. References: Official (ISC)2 Guide to the CISSP CBK, Fifth Edition, Chapter 21: Software Development Security, page 2034.
A cybersecurity engineer has been tasked to research and implement an ultra-secure communications channel to protect the organization's most valuable intellectual property (IP). The primary directive in this initiative is to ensure there Is no possible way the communications can be intercepted without detection. Which of the following Is the only way to ensure this
‘outcome?
Diffie-Hellman key exchange
Symmetric key cryptography
[Public key infrastructure (PKI)
Quantum Key Distribution
The only way to ensure an ultra-secure communications channel that cannot be intercepted without detection is to use Quantum Key Distribution (QKD). QKD is a technique that uses the principles of quantum mechanics to generate and exchange cryptographic keys between two parties. QKD relies on the properties of quantum particles, such as photons or electrons, to encode and transmit the keys. QKD offers the following advantages for securing communications:
Which of the following events prompts a review of the disaster recovery plan (DRP)?
New members added to the steering committee
Completion of the security policy review
Change in senior management
Organizational merger
The event that prompts a review of the disaster recovery plan (DRP) is an organizational merger. A DRP is a plan that defines the procedures and actions to be taken in the event of a disaster or a disruption, to restore the normal operations and services of an organization as quickly as possible. A DRP covers the aspects such as the roles and responsibilities, the recovery strategies and objectives, the backup and restoration methods, the communication and coordination channels, and the testing and maintenance schedules of the disaster recovery process. An organizational merger is an event that involves the combination or integration of two or more organizations into one single organization, as a result of a business decision or a strategy. An organizational merger prompts a review of the DRP, as it can affect the scope, scale, and complexity of the DRP, and require the alignment, consolidation, or modification of the DRP. A review of the DRP can help to ensure that the DRP is updated and consistent with the current and future needs and requirements of the merged organization, and that the DRP is effective and efficient for the disaster recovery process. New members added to the steering committee, completion of the security policy review, and change in senior management are not events that prompt a review of the DRP. These are some of the factors or changes that may influence or impact the DRP, but they are not as significant or critical as an organizational merger. New members added to the steering committee are individuals who join or replace the existing members of the steering committee, which is a group of people who oversee and guide the DRP and the disaster recovery process. Completion of the security policy review is a process that evaluates and revises the security policy, which is a document that defines the security goals, principles, and rules of an organization. Change in senior management is a situation that involves the replacement or reassignment of the senior management or the executives of an organization, who are responsible for the strategic and operational decisions and actions of the organization. References: Official (ISC)2 CISSP CBK Reference, Fifth Edition, Domain 7, Security Operations, page 709. CISSP All-in-One Exam Guide, Eighth Edition, Chapter 7, Security Operations, page 674.
Using the cipher text and resultant clear text message to derive the non-alphabetic cipher key is an example of which method of cryptanalytic attack?
Frequency analysis
Ciphertext-only attack
Probable-plaintext attack
Known-plaintext attack
A known-plaintext attack is a type of cryptanalytic attack where the attacker has access to both the ciphertext and the corresponding plaintext, and tries to derive the key or the algorithm used to encrypt the message. This type of attack can be effective against some symmetric ciphers, such as substitution ciphers, where the key is non-alphabetic and the ciphertext is a permutation of the plaintext. For example, if the attacker knows that the plaintext “HELLO” corresponds to the ciphertext “QNUUX”, they can infer that the key is “Q-H, N-E, U-L, X-O”. A frequency analysis attack is a type of cryptanalytic attack where the attacker analyzes the frequency of letters or symbols in the ciphertext and compares them with the expected frequency of the language of the plaintext. A ciphertext-only attack is a type of cryptanalytic attack where the attacker only has access to the ciphertext and tries to guess the plaintext or the key by using statistical methods, brute force, or other techniques. A probable-plaintext attack is a type of cryptanalytic attack where the attacker has access to the ciphertext and some information about the probable plaintext, such as the format, the length, or some common words or phrases, and tries to recover the key or the algorithm used to encrypt the message. References: CISSP CBK Reference, 5th Edition, Chapter 8, page 421; CISSP All-in-One Exam Guide, 8th Edition, Chapter 8, page 395
Why are packet filtering routers used in low-risk environments?
They are high-resolution source discrimination and identification tools.
They are fast and flexible, and protect against Internet Protocol (IP) spoofing.
They are fast, flexible, and transparent.
They enforce strong user authentication and audit tog generation.
Packet filtering routers are used in low-risk environments because they offer speed, flexibility, and transparency in filtering traffic based on IP protocol, source/destination IP address, or port number without adding significant overhead or complexity. References: Unable to provide specific references due to browsing limitations.
What are the roles within a scrum methodoligy?
System owner, scrum master, and development team
prduct owner, scrum master, and scrum team
Scrum master, requirements manager, and development team
Scrum master, quality assurance team, and scrum team
The roles within a scrum methodology are product owner, scrum master, and scrum team. Scrum is an agile framework for developing, delivering, and sustaining complex products. The product owner is the person who represents the stakeholders and the business value of the product. The product owner is responsible for defining the product vision, managing the product backlog, and prioritizing the features. The scrum master is the person who facilitates the scrum process and ensures that the scrum team adheres to the scrum values, principles, and practices. The scrum master is responsible for removing impediments, coaching the team, and ensuring collaboration and communication. The scrum team is the group of people who work together to deliver the product increments. The scrum team is self-organizing, cross-functional, and accountable for the quality and timeliness of the product. References: CISSP All-in-One Exam Guide, Eighth Edition, Chapter 8: Software Development Security, page 393; [Official (ISC)2 CISSP CBK Reference, Fifth Edition, Chapter 8: Software Development Security, page 533]
Why are mobile devices something difficult to investigate in a forensic examination?
There are no forensics tools available for examination.
They may have proprietary software installed to protect them.
They may contain cryptographic protection.
They have password-based security at logon.
One of the reasons why mobile devices are difficult to investigate in a forensic examination is that they may contain cryptographic protection. Cryptographic protection is the use of encryption, hashing, or digital signatures to protect the confidentiality, integrity, or authenticity of data stored or transmitted on a device. Mobile devices, such as smartphones, tablets, or laptops, may use cryptographic protection to secure the data on the device, such as contacts, messages, photos, or documents, or the data in transit, such as emails, chats, or web browsing. Cryptographic protection can pose a challenge for forensic investigators, as they may need to obtain the keys, passwords, or biometrics to access the encrypted or signed data, or they may need to use specialized tools or techniques to bypass or break the cryptographic protection. Cryptographic protection can also affect the admissibility or reliability of the forensic evidence, as it may require additional verification or validation. References: CISSP All-in-One Exam Guide, Eighth Edition, Chapter 7: Security Operations, page 358; [Official (ISC)2 CISSP CBK Reference, Fifth Edition, Chapter 7: Security Operations, page 483]
What is the PRIMARY reason that a bit-level copy is more desirable than a file-level copy when replicating a hard drive's contents for an e-discovery investigation?
Files that have been deleted will be transferred.
The file and directory structure is retained.
File-level security settings will be preserved.
The corruption of files is less likely.
A bit-level copy is more desirable than a file-level copy when replicating a hard drive’s contents for an e-discovery investigation, because it preserves the data in the unallocated space and the slack space of the drive, which may contain deleted files or fragments of files that are relevant to the investigation. A file-level copy only copies the data that is accessible by the file system, and may miss important evidence. The file and directory structure, the file-level security settings, and the corruption of files are not affected by the choice of copy method, as long as the copy is done correctly. References: CISSP Official Study Guide, 9th Edition, page 1010; CISSP All-in-One Exam Guide, 8th Edition, page 1089
Which of the following is the GREATEST risk of relying only on Capability Maturity Models (CMM) for software to guide process improvement and assess capabilities of acquired software?
Organizations can only reach a maturity level 3 when using CMMs
CMMs do not explicitly address safety and security
CMMs can only be used for software developed in-house
CMMs are vendor specific and may be biased
The greatest risk of relying only on Capability Maturity Models (CMMs) for software to guide process improvement and assess capabilities of acquired software is that CMMs do not explicitly address safety and security. CMMs are frameworks that measure and improve the maturity and quality of the software development processes and products. CMMs define different levels of maturity, from initial to optimized, based on the presence and effectiveness of the key process areas, such as requirements management, project planning, configuration management, quality assurance, or risk management. CMMs can help to evaluate and improve the software development processes and products, but they do not explicitly address the safety and security aspects of the software. Safety and security are important attributes of the software, especially for critical or sensitive applications, such as medical, military, or financial applications. Safety and security require specific processes and practices, such as threat modeling, secure coding, vulnerability testing, or incident response, that are not covered by the CMMs. Therefore, relying only on CMMs for software may result in overlooking or neglecting the safety and security issues of the software, which may lead to serious consequences, such as harm, loss, or breach. Organizations can only reach a maturity level 3 when using CMMs, CMMs can only be used for software developed in-house, and CMMs are vendor specific and may be biased are not the greatest risks of relying only on CMMs for software. These are some of the limitations or challenges of using CMMs for software, but they are not as significant or critical as the lack of safety and security. Organizations can reach higher maturity levels than level 3 when using CMMs, depending on the implementation and assessment of the CMMs. CMMs can be used for software developed in-house or outsourced, depending on the scope and criteria of the CMMs. CMMs are not vendor specific and may not be biased, as they are based on industry standards and best practices, such as ISO/IEC 15504 or ISO/IEC 33001. References: Official (ISC)2 CISSP CBK Reference, Fifth Edition, Domain 8, Software Development Security, page 831. CISSP All-in-One Exam Guide, Eighth Edition, Chapter 8, Software Development Security, page 767.
Which of the following is the MOST effective method of detecting vulnerabilities in web-based applications early in the secure Software Development Life Cycle (SDLC)?
Web application vulnerability scanning
Application fuzzing
Code review
Penetration testing
The most effective method of detecting vulnerabilities in web-based applications early in the secure SDLC is code review. Code review is a process of examining and evaluating the source code of a web-based application to identify and correct any errors, defects, or weaknesses that may affect its functionality, quality, security, or performance. Code review can detect vulnerabilities in web-based applications early in the secure SDLC, as it can be performed during the development or testing phases, before the application is deployed or released. Code review can also improve the security posture of the web-based application, as it can reduce the attack surface, mitigate the risks, and comply with the standards and regulations. Web application vulnerability scanning, application fuzzing, or penetration testing are not the most effective methods of detecting vulnerabilities in web-based applications early in the secure SDLC, as they are performed later in the secure SDLC, usually after the application is deployed or released. Web application vulnerability scanning is a technique of using automated tools to scan and identify the common vulnerabilities or misconfigurations in a web-based application, such as SQL injection, cross-site scripting, or broken authentication. Application fuzzing is a technique of using random or malformed inputs to test the behavior and security of a web-based application, and to discover any errors, crashes, or vulnerabilities. Penetration testing is a technique of simulating a real-world attack on a web-based application, and to evaluate its security and resilience. References: Official (ISC)2 Guide to the CISSP CBK, Fifth Edition, Chapter 21: Software Development Security, page 2010.
Which of the following MUST be done before a digital forensics investigator may acquire digital evidence?
Inventory the digital evidence.
Isolate the digital evidence.
Verify that the investigator has the appropriate legal authority to proceed.
Perform hashing to verify the integrity of the digital evidence.
Before a digital forensics investigator may acquire digital evidence, which is the process of collecting and preserving the data from a digital device or system, the investigator must verify that he or she has the appropriate legal authority to proceed. This means that the investigator must have a valid search warrant, court order, consent, or other legal basis to access and seize the digital evidence, and must follow the relevant laws and regulations that govern the digital forensics process. Verifying the legal authority to proceed is essential to ensure that the digital evidence is admissible in court and that the investigator does not violate the privacy or property rights of the owner or user of the digital device or system. The other options are steps that are performed after the legal authority to proceed is verified, not before. References: Official (ISC)2 CISSP CBK Reference, Fifth Edition, Domain 7: Security Operations, pp. 1231-1232; CISSP All-in-One Exam Guide, Eighth Edition, Chapter 14: Security Operations, pp. 1389-1390.
A security practitioner needs to implementation solution to verify endpoint security protections and operating system (0S) versions. Which of the following is the BEST solution to implement?
An intrusion prevention system (IPS)
An intrusion prevention system (IPS)
Network Access Control (NAC)
A firewall
Network Access Control (NAC) is a solution that verifies the security posture and compliance of endpoints before granting them access to the network. NAC can check the endpoint security protections, such as antivirus, firewall, patch level, and OS version, and enforce policies based on the results. NAC can also quarantine or remediate non-compliant endpoints to prevent them from compromising the network security. NAC is the best solution to implement among the given options, as it provides both verification and enforcement of endpoint security. An intrusion prevention system (IPS) is a device that monitors network traffic and blocks or alerts on malicious or suspicious activities. An IPS does not verify the endpoint security protections or OS versions, nor does it enforce any policies on the endpoints. An IPS is a reactive rather than proactive solution. A firewall is a device that controls the network traffic based on predefined rules. A firewall does not verify the endpoint security protections or OS versions, nor does it enforce any policies on the endpoints. A firewall is a preventive rather than detective solution. An intrusion detection system (IDS) is a device that monitors network traffic and alerts on malicious or suspicious activities. An IDS does not verify the endpoint security protections or OS versions, nor does it enforce any policies on the endpoints. An IDS is a passive rather than active solution. References: CISSP All-in-One Exam Guide, Eighth Edition, Chapter 6: Security Assessment and Testing, p. 518-519. Official (ISC)2 CISSP CBK Reference, Fifth Edition, Domain 4: Communication and Network Security, p. 451-452.
A cloud service provider requires its customer organizations to enable maximum audit logging for its data storage service and to retain the logs for the period of three
months. The audit logging generates extremely high amount of logs. What is the MOST appropriate strategy for the log retention?
Keep last week's logs in an online storage and the rest in a near-line storage.
Keep all logs in an online storage.
Keep all logs in an offline storage.
Keep last week's logs in an online storage and the rest in an offline storage.
The most appropriate strategy for the log retention of a cloud service provider that requires its customer organizations to enable maximum audit logging for its data storage service and to retain the logs for the period of three months, given that the audit logging generates extremely high amount of logs, is to keep last week’s logs in an online storage and the rest in a near-line storage. Online storage is a type of storage that is directly accessible by the system or application, such as hard disk drives, solid state drives, or flash drives. Online storage is fast, convenient, and reliable, but it is also expensive and consumes more power. Near-line storage is a type of storage that is not directly accessible by the system or application, but can be made accessible within a short time, such as tape drives, optical disks, or removable media. Near-line storage is slower, less convenient, and less reliable than online storage, but it is also cheaper and consumes less power. By keeping last week’s logs in an online storage and the rest in a near-line storage, the cloud service provider can balance the trade-offs between performance, cost, and availability of the logs. The logs that are most likely to be accessed or analyzed are kept in the online storage, while the logs that are less likely to be accessed or analyzed are kept in the near-line storage. This way, the cloud service provider can meet the log retention requirement without wasting too much resources or compromising the security of the logs. Keeping all logs in an online storage, keeping all logs in an offline storage, or keeping last week’s logs in an online storage and the rest in an offline storage are not appropriate strategies for the log retention of the cloud service provider. Keeping all logs in an online storage would be too costly and inefficient, as it would consume too much disk space and power for logs that are rarely accessed or analyzed. Keeping all logs in an offline storage or keeping last week’s logs in an online storage and the rest in an offline storage would be too risky and inconvenient, as it would make the logs inaccessible or difficult to access in case of an audit, investigation, or incident response. Offline storage is a type of storage that is not accessible by the system or application, and requires manual intervention to access, such as archived tapes, disks, or media. References: Official (ISC)2 CISSP CBK Reference, Fifth Edition, Domain 7, Security Operations, page 697. CISSP All-in-One Exam Guide, Eighth Edition, Chapter 7, Security Operations, page 660.
What is a common mistake in records retention?
Having the organization legal department create a retention policy
Adopting a retention policy based on applicable organization requirements
Having the Human Resource (HR) department create a retention policy
Adopting a retention policy with the longest requirement period
A common mistake in records retention is adopting a retention policy with the longest requirement period, meaning that the records are kept for the maximum possible time, regardless of the legal or regulatory requirements, the business needs, or the risk assessment. Adopting a retention policy with the longest requirement period can have negative consequences, such as increasing the storage costs and complexity, reducing the efficiency and performance of the records management system, exposing the records to unauthorized access or disclosure, or violating the privacy or security of the records. Having the organization legal department create a retention policy, adopting a retention policy based on applicable organization requirements, and having the Human Resource (HR) department create a retention policy are not common mistakes in records retention, as they are either good practices or acceptable options for records retention, depending on the context and the scope of the records. References:
How can an attacker exploit overflow to execute arbitrary code?
Modify a function's return address.
Alter the address of the stack.
Substitute elements in the stack.
Move the stack pointer.
An attacker can exploit a buffer overflow to execute arbitrary code by modifying a function’s return address. A buffer overflow is a condition that occurs when a program attempts to write more data to a fixed-length memory space, or buffer, than it can hold. A buffer overflow can corrupt the adjacent memory locations, which may contain important data or instructions for the program. A function’s return address is the memory location that stores the address of the instruction that the program should return to after executing the function. An attacker can overwrite the return address with the address of a malicious code, which can be injected into the buffer or another location, and redirect the program flow to execute the malicious code. References: CISSP All-in-One Exam Guide, Eighth Edition, Chapter 8: Software Development Security, page 427; [Official (ISC)2 CISSP CBK Reference, Fifth Edition, Chapter 8: Software Development Security, page 567]
Which of the following would present the higher annualized loss expectancy (ALE)?
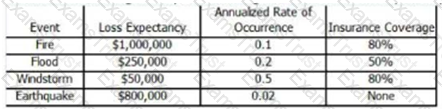
Fire
Earthquake
Windstorm
Flood
Earthquake would present the higher annualized loss expectancy (ALE) according to the table in the image. ALE is a metric that measures the expected loss per year due to a specific risk or threat. ALE is calculated by multiplying the single loss expectancy (SLE), which is the estimated cost of a single occurrence of the risk or threat, by the annualized rate of occurrence (ARO), which is the estimated frequency of the risk or threat occurring in a year. According to the table, the ALE for each event is as follows:
Therefore, earthquake has the highest ALE of $16,000, followed by fire, flood, and windstorm. Note that the insurance coverage does not affect the ALE calculation, as it only reduces the actual loss, not the expected loss. However, insurance coverage can be used to reduce the total cost of risk (TCOR), which is the sum of ALE and the cost of risk mitigation, such as insurance premiums, deductibles, and administrative costs. References:
When a flaw in Industrial control (ICS) software is discovered, what is the GREATEST impediment to deploying a patch?
Many IG systems have software that is no longer being maintained by the venders.
Compensating controls may impact IG performance.
Testing a patch in an IG may require more resources than the organization can commit.
vendors are required to validate the operability patches.
Industrial control systems (ICS) are critical for the operation of many sectors such as energy, transportation, manufacturing, and water. Patching ICS software is a challenging task because it may require extensive testing, validation, and coordination to ensure that the patch does not introduce new vulnerabilities, affect the functionality, performance, or availability of the system, or cause any adverse impacts on the physical processes or safety. Testing a patch in an ICS may require more resources than the organization can commit, such as time, personnel, equipment, or budget. Therefore, this is the greatest impediment to deploying a patch for ICS software. References: Recommended Practice for Patch Management of Control Systems, ICS Security Patching: Never, Next, Now, Patching and Change Management: CISSP Domain 7
Why would a system be structured to isolate different classes of information from one another and segregate them by user jurisdiction?
The organization can avoid e-discovery processes in the event of litigation.
The organization's infrastructure is clearly arranged and scope of responsibility is simplified.
The organization can vary its system policies to comply with conflicting national laws.
The organization is required to provide different services to various third-party organizations.
A system that is structured to isolate different classes of information from one another and segregate them by user jurisdiction can help the organization to vary its system policies to comply with conflicting national laws. Different classes of information may have different levels of sensitivity, confidentiality, or classification, and may require different security measures and controls to protect them. Different user jurisdictions may have different legal or regulatory requirements, standards, or expectations for the information, and may impose different obligations or restrictions on the organization. By isolating and segregating the information by class and jurisdiction, the organization can tailor its system policies to meet the specific needs and demands of each class and jurisdiction, and avoid any conflicts or violations of the national laws. The other options are not the reasons why a system would be structured to isolate different classes of information from one another and segregate them by user jurisdiction, as they either do not relate to the system structure, do not involve different classes or jurisdictions, or do not address the national laws. References: CISSP - Certified Information Systems Security Professional, Domain 1. Security and Risk Management, 1.6 Understand legal and regulatory issues that pertain to information security in a global context, 1.6.1 Understand and adhere to laws, regulations, and compliance requirements, 1.6.1.2 Data sovereignty; CISSP Exam Outline, Domain 1. Security and Risk Management, 1.6 Understand legal and regulatory issues that pertain to information security in a global context, 1.6.1 Understand and adhere to laws, regulations, and compliance requirements, 1.6.1.2 Data sovereignty
An organization operates a legacy Industrial Control System (ICS) to support its core business service, which carrot be replaced. Its management MUST be performed remotely through an administrative console software, which in tum depends on an old version of the Java Runtime Environment (JPE) known to be vulnerable to a number of attacks, How is this risk BEST managed?
Isolate the full ICS by moving It onto its own network segment
Air-gap and harden the host used for management purposes
Convince the management to decommission the ICS and mitigate to a modem technology
Deploy a restrictive proxy between all clients and the vulnerable management station
Air-gapping and hardening the host used for management purposes is the best way to manage the risk of a legacy Industrial Control System (ICS) that depends on a vulnerable version of the Java Runtime Environment (JRE). Air-gapping means disconnecting the host from any network or internet connection, so that it can only be accessed physically. Hardening means applying security patches, disabling unnecessary services, and configuring security settings to reduce the attack surface of the host. This way, the risk of remote exploitation of the JRE vulnerability is minimized, and the host is protected from other potential threats. Isolating the full ICS by moving it onto its own network segment may reduce the exposure of the system, but it does not eliminate the possibility of network-based attacks. Convincing the management to decommission the ICS and migrate to a modern technology may be the ideal solution, but it may not be feasible or cost-effective, especially if the ICS cannot be replaced. Deploying a restrictive proxy between all clients and the vulnerable management station may also help to filter and monitor the network traffic, but it does not address the root cause of the vulnerability, and it may introduce additional complexity and overhead to the system. References: CISSP All-in-One Exam Guide, Eighth Edition, Chapter 4: Security Architecture and Engineering, page 447. Official (ISC)2 CISSP CBK Reference, Fifth Edition, Chapter 4: Security Architecture and Engineering, page 321.
A Virtual Machine (VM) environment has five guest Operating Systems (OS) and provides strong isolation. What MUST an administrator review to audit a user’s access to data files?
Host VM monitor audit logs
Guest OS access controls
Host VM access controls
Guest OS audit logs
Guest OS audit logs are what an administrator must review to audit a user’s access to data files in a VM environment that has five guest OS and provides strong isolation. A VM environment is a system that allows multiple virtual machines (VMs) to run on a single physical machine, each with its own OS and applications. A VM environment can provide several benefits, such as:
A guest OS is the OS that runs on a VM, which is different from the host OS that runs on the physical machine. A guest OS can have its own security controls and mechanisms, such as access controls, encryption, authentication, and audit logs. Audit logs are records that capture and store the information about the events and activities that occur within a system or a network, such as the access and usage of the data files. Audit logs can provide a reactive and detective layer of security by enabling the monitoring and analysis of the system or network behavior, and facilitating the investigation and response of the incidents.
Guest OS audit logs are what an administrator must review to audit a user’s access to data files in a VM environment that has five guest OS and provides strong isolation, because they can provide the most accurate and relevant information about the user’s actions and interactions with the data files on the VM. Guest OS audit logs can also help the administrator to identify and report any unauthorized or suspicious access or disclosure of the data files, and to recommend or implement any corrective or preventive actions.
The other options are not what an administrator must review to audit a user’s access to data files in a VM environment that has five guest OS and provides strong isolation, but rather what an administrator might review for other purposes or aspects. Host VM monitor audit logs are records that capture and store the information about the events and activities that occur on the host VM monitor, which is the software or hardware component that manages and controls the VMs on the physical machine. Host VM monitor audit logs can provide information about the performance, status, and configuration of the VMs, but they cannot provide information about the user’s access to data files on the VMs. Guest OS access controls are rules and mechanisms that regulate and restrict the access and permissions of the users and processes to the resources and services on the guest OS. Guest OS access controls can provide a proactive and preventive layer of security by enforcing the principles of least privilege, separation of duties, and need to know. However, guest OS access controls are not what an administrator must review to audit a user’s access to data files, but rather what an administrator must configure and implement to protect the data files. Host VM access controls are rules and mechanisms that regulate and restrict the access and permissions of the users and processes to the VMs on the physical machine. Host VM access controls can provide a granular and dynamic layer of security by defining and assigning the roles and permissions according to the organizational structure and policies. However, host VM access controls are not what an administrator must review to audit a user’s access to data files, but rather what an administrator must configure and implement to protect the VMs.
In which of the following programs is it MOST important to include the collection of security process data?
Quarterly access reviews
Security continuous monitoring
Business continuity testing
Annual security training
Security continuous monitoring is the program in which it is most important to include the collection of security process data. Security process data is the data that reflects the performance, effectiveness, and compliance of the security processes, such as the security policies, standards, procedures, and guidelines. Security process data can include metrics, indicators, logs, reports, and assessments. Security process data can provide several benefits, such as:
Security continuous monitoring is the program in which it is most important to include the collection of security process data, because it is the program that involves maintaining the ongoing awareness of the security status, events, and activities of the system. Security continuous monitoring can enable the system to detect and respond to any security issues or incidents in a timely and effective manner, and to adjust and improve the security controls and processes accordingly. Security continuous monitoring can also help the system to comply with the security requirements and standards from the internal or external authorities or frameworks.
The other options are not the programs in which it is most important to include the collection of security process data, but rather programs that have other objectives or scopes. Quarterly access reviews are programs that involve reviewing and verifying the user accounts and access rights on a quarterly basis. Quarterly access reviews can ensure that the user accounts and access rights are valid, authorized, and up to date, and that any inactive, expired, or unauthorized accounts or rights are removed or revoked. However, quarterly access reviews are not the programs in which it is most important to include the collection of security process data, because they are not focused on the security status, events, and activities of the system, but rather on the user accounts and access rights. Business continuity testing is a program that involves testing and validating the business continuity plan (BCP) and the disaster recovery plan (DRP) of the system. Business continuity testing can ensure that the system can continue or resume its critical functions and operations in case of a disruption or disaster, and that the system can meet the recovery objectives and requirements. However, business continuity testing is not the program in which it is most important to include the collection of security process data, because it is not focused on the security status, events, and activities of the system, but rather on the continuity and recovery of the system. Annual security training is a program that involves providing and updating the security knowledge and skills of the system users and staff on an annual basis. Annual security training can increase the security awareness and competence of the system users and staff, and reduce the human errors or risks that might compromise the system security. However, annual security training is not the program in which it is most important to include the collection of security process data, because it is not focused on the security status, events, and activities of the system, but rather on the security education and training of the system users and staff.
Which of the following is of GREATEST assistance to auditors when reviewing system configurations?
Change management processes
User administration procedures
Operating System (OS) baselines
System backup documentation
Operating System (OS) baselines are of greatest assistance to auditors when reviewing system configurations. OS baselines are standard or reference configurations that define the desired and secure state of an OS, including the settings, parameters, patches, and updates. OS baselines can provide several benefits, such as:
OS baselines are of greatest assistance to auditors when reviewing system configurations, because they can enable the auditors to evaluate and verify the current and actual state of the OS against the desired and secure state of the OS. OS baselines can also help the auditors to identify and report any gaps, issues, or risks in the OS configurations, and to recommend or implement any corrective or preventive actions.
The other options are not of greatest assistance to auditors when reviewing system configurations, but rather of assistance for other purposes or aspects. Change management processes are processes that ensure that any changes to the system configurations are planned, approved, implemented, and documented in a controlled and consistent manner. Change management processes can improve the security and reliability of the system configurations by preventing or reducing the errors, conflicts, or disruptions that might occur due to the changes. However, change management processes are not of greatest assistance to auditors when reviewing system configurations, because they do not define the desired and secure state of the system configurations, but rather the procedures and controls for managing the changes. User administration procedures are procedures that define the roles, responsibilities, and activities for creating, modifying, deleting, and managing the user accounts and access rights. User administration procedures can enhance the security and accountability of the user accounts and access rights by enforcing the principles of least privilege, separation of duties, and need to know. However, user administration procedures are not of greatest assistance to auditors when reviewing system configurations, because they do not define the desired and secure state of the system configurations, but rather the rules and tasks for administering the users. System backup documentation is documentation that records the information and details about the system backup processes, such as the backup frequency, type, location, retention, and recovery. System backup documentation can increase the availability and resilience of the system by ensuring that the system data and configurations can be restored in case of a loss or damage. However, system backup documentation is not of greatest assistance to auditors when reviewing system configurations, because it does not define the desired and secure state of the system configurations, but rather the backup and recovery of the system configurations.
Which of the following could cause a Denial of Service (DoS) against an authentication system?
Encryption of audit logs
No archiving of audit logs
Hashing of audit logs
Remote access audit logs
Remote access audit logs could cause a Denial of Service (DoS) against an authentication system. A DoS attack is a type of attack that aims to disrupt or degrade the availability or performance of a system or a network by overwhelming it with excessive or malicious traffic or requests. An authentication system is a system that verifies the identity and credentials of the users or entities that want to access the system or network resources or services. An authentication system can use various methods or factors to authenticate the users or entities, such as passwords, tokens, certificates, biometrics, or behavioral patterns.
Remote access audit logs are records that capture and store the information about the events and activities that occur when the users or entities access the system or network remotely, such as via the internet, VPN, or dial-up. Remote access audit logs can provide a reactive and detective layer of security by enabling the monitoring and analysis of the remote access behavior, and facilitating the investigation and response of the incidents.
Remote access audit logs could cause a DoS against an authentication system, because they could consume a large amount of disk space, memory, or bandwidth on the authentication system, especially if the remote access is frequent, intensive, or malicious. This could affect the performance or functionality of the authentication system, and prevent or delay the legitimate users or entities from accessing the system or network resources or services. For example, an attacker could launch a DoS attack against an authentication system by sending a large number of fake or invalid remote access requests, and generating a large amount of remote access audit logs that fill up the disk space or memory of the authentication system, and cause it to crash or slow down.
The other options are not the factors that could cause a DoS against an authentication system, but rather the factors that could improve or protect the authentication system. Encryption of audit logs is a technique that involves using a cryptographic algorithm and a key to transform the audit logs into an unreadable or unintelligible format, that can only be reversed or decrypted by authorized parties. Encryption of audit logs can enhance the security and confidentiality of the audit logs by preventing unauthorized access or disclosure of the sensitive information in the audit logs. However, encryption of audit logs could not cause a DoS against an authentication system, because it does not affect the availability or performance of the authentication system, but rather the integrity or privacy of the audit logs. No archiving of audit logs is a practice that involves not storing or transferring the audit logs to a separate or external storage device or location, such as a tape, disk, or cloud. No archiving of audit logs can reduce the security and availability of the audit logs by increasing the risk of loss or damage of the audit logs, and limiting the access or retrieval of the audit logs. However, no archiving of audit logs could not cause a DoS against an authentication system, because it does not affect the availability or performance of the authentication system, but rather the availability or preservation of the audit logs. Hashing of audit logs is a technique that involves using a hash function, such as MD5 or SHA, to generate a fixed-length and unique value, called a hash or a digest, that represents the audit logs. Hashing of audit logs can improve the security and integrity of the audit logs by verifying the authenticity or consistency of the audit logs, and detecting any modification or tampering of the audit logs. However, hashing of audit logs could not cause a DoS against an authentication system, because it does not affect the availability or performance of the authentication system, but rather the integrity or verification of the audit logs.
Which of the following is a PRIMARY benefit of using a formalized security testing report format and structure?
Executive audiences will understand the outcomes of testing and most appropriate next steps for corrective actions to be taken
Technical teams will understand the testing objectives, testing strategies applied, and business risk associated with each vulnerability
Management teams will understand the testing objectives and reputational risk to the organization
Technical and management teams will better understand the testing objectives, results of each test phase, and potential impact levels
Technical and management teams will better understand the testing objectives, results of each test phase, and potential impact levels is the primary benefit of using a formalized security testing report format and structure. Security testing is a process that involves evaluating and verifying the security posture, vulnerabilities, and threats of a system or a network, using various methods and techniques, such as vulnerability assessment, penetration testing, code review, and compliance checks. Security testing can provide several benefits, such as:
A security testing report is a document that summarizes and communicates the findings and recommendations of the security testing process to the relevant stakeholders, such as the technical and management teams. A security testing report can have various formats and structures, depending on the scope, purpose, and audience of the report. However, a formalized security testing report format and structure is one that follows a standard and consistent template, such as the one proposed by the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) in the Special Publication 800-115, Technical Guide to Information Security Testing and Assessment. A formalized security testing report format and structure can have several components, such as:
Technical and management teams will better understand the testing objectives, results of each test phase, and potential impact levels is the primary benefit of using a formalized security testing report format and structure, because it can ensure that the security testing report is clear, comprehensive, and consistent, and that it provides the relevant and useful information for the technical and management teams to make informed and effective decisions and actions regarding the system or network security.
The other options are not the primary benefits of using a formalized security testing report format and structure, but rather secondary or specific benefits for different audiences or purposes. Executive audiences will understand the outcomes of testing and most appropriate next steps for corrective actions to be taken is a benefit of using a formalized security testing report format and structure, but it is not the primary benefit, because it is more relevant for the executive summary component of the report, which is a brief and high-level overview of the report, rather than the entire report. Technical teams will understand the testing objectives, testing strategies applied, and business risk associated with each vulnerability is a benefit of using a formalized security testing report format and structure, but it is not the primary benefit, because it is more relevant for the methodology and results components of the report, which are more technical and detailed parts of the report, rather than the entire report. Management teams will understand the testing objectives and reputational risk to the organization is a benefit of using a formalized security testing report format and structure, but it is not the primary benefit, because it is more relevant for the introduction and conclusion components of the report, which are more contextual and strategic parts of the report, rather than the entire report.
All of the following items should be included in a Business Impact Analysis (BIA) questionnaire EXCEPT questions that
determine the risk of a business interruption occurring
determine the technological dependence of the business processes
Identify the operational impacts of a business interruption
Identify the financial impacts of a business interruption
A Business Impact Analysis (BIA) is a process that identifies and evaluates the potential effects of natural and man-made disasters on business operations. The BIA questionnaire is a tool that collects information from business process owners and stakeholders about the criticality, dependencies, recovery objectives, and resources of their processes. The BIA questionnaire should include questions that:
The BIA questionnaire should not include questions that determine the risk of a business interruption occurring, as this is part of the risk assessment process, which is a separate activity from the BIA. The risk assessment process identifies and analyzes the threats and vulnerabilities that could cause a business interruption, and estimates the likelihood and impact of such events. The risk assessment process also evaluates the existing controls and mitigation strategies, and recommends additional measures to reduce the risk to an acceptable level.
A company whose Information Technology (IT) services are being delivered from a Tier 4 data center, is preparing a companywide Business Continuity Planning (BCP). Which of the following failures should the IT manager be concerned with?
Application
Storage
Power
Network
A company whose IT services are being delivered from a Tier 4 data center should be most concerned with application failures when preparing a companywide BCP. A BCP is a document that describes how an organization will continue its critical business functions in the event of a disruption or disaster. A BCP should include a risk assessment, a business impact analysis, a recovery strategy, and a testing and maintenance plan.
A Tier 4 data center is the highest level of data center classification, according to the Uptime Institute. A Tier 4 data center has the highest level of availability, reliability, and fault tolerance, as it has multiple and independent paths for power and cooling, and redundant and backup components for all systems. A Tier 4 data center has an uptime rating of 99.995%, which means it can only experience 0.4 hours of downtime per year. Therefore, the likelihood of a power, storage, or network failure in a Tier 4 data center is very low, and the impact of such a failure would be minimal, as the data center can quickly switch to alternative sources or routes.
However, a Tier 4 data center cannot prevent or mitigate application failures, which are caused by software bugs, configuration errors, or malicious attacks. Application failures can affect the functionality, performance, or security of the IT services, and cause data loss, corruption, or breach. Therefore, the IT manager should be most concerned with application failures when preparing a BCP, and ensure that the applications are properly designed, tested, updated, and monitored.
Which of the following actions will reduce risk to a laptop before traveling to a high risk area?
Examine the device for physical tampering
Implement more stringent baseline configurations
Purge or re-image the hard disk drive
Change access codes
Purging or re-imaging the hard disk drive of a laptop before traveling to a high risk area will reduce the risk of data compromise or theft in case the laptop is lost, stolen, or seized by unauthorized parties. Purging or re-imaging the hard disk drive will erase all the data and applications on the laptop, leaving only the operating system and the essential software. This will minimize the exposure of sensitive or confidential information that could be accessed by malicious actors. Purging or re-imaging the hard disk drive should be done using secure methods that prevent data recovery, such as overwriting, degaussing, or physical destruction.
The other options will not reduce the risk to the laptop as effectively as purging or re-imaging the hard disk drive. Examining the device for physical tampering will only detect if the laptop has been compromised after the fact, but will not prevent it from happening. Implementing more stringent baseline configurations will improve the security settings and policies of the laptop, but will not protect the data if the laptop is bypassed or breached. Changing access codes will make it harder for unauthorized users to log in to the laptop, but will not prevent them from accessing the data if they use other methods, such as booting from a removable media or removing the hard disk drive.
When assessing an organization’s security policy according to standards established by the International Organization for Standardization (ISO) 27001 and 27002, when can management responsibilities be defined?
Only when assets are clearly defined
Only when standards are defined
Only when controls are put in place
Only procedures are defined
When assessing an organization’s security policy according to standards established by the ISO 27001 and 27002, management responsibilities can be defined only when standards are defined. Standards are the specific rules, guidelines, or procedures that support the implementation of the security policy. Standards define the minimum level of security that must be achieved by the organization, and provide the basis for measuring compliance and performance. Standards also assign roles and responsibilities to different levels of management and staff, and specify the reporting and escalation procedures.
Management responsibilities are the duties and obligations that managers have to ensure the effective and efficient execution of the security policy and standards. Management responsibilities include providing leadership, direction, support, and resources for the security program, establishing and communicating the security objectives and expectations, ensuring compliance with the legal and regulatory requirements, monitoring and reviewing the security performance and incidents, and initiating corrective and preventive actions when needed.
Management responsibilities cannot be defined without standards, as standards provide the framework and criteria for defining what managers need to do and how they need to do it. Management responsibilities also depend on the scope and complexity of the security policy and standards, which may vary depending on the size, nature, and context of the organization. Therefore, standards must be defined before management responsibilities can be defined.
The other options are not correct, as they are not prerequisites for defining management responsibilities. Assets are the resources that need to be protected by the security policy and standards, but they do not determine the management responsibilities. Controls are the measures that are implemented to reduce the security risks and achieve the security objectives, but they do not determine the management responsibilities. Procedures are the detailed instructions that describe how to perform the security tasks and activities, but they do not determine the management responsibilities.
Intellectual property rights are PRIMARY concerned with which of the following?
Owner’s ability to realize financial gain
Owner’s ability to maintain copyright
Right of the owner to enjoy their creation
Right of the owner to control delivery method
Intellectual property rights are primarily concerned with the owner’s ability to realize financial gain from their creation. Intellectual property is a category of intangible assets that are the result of human creativity and innovation, such as inventions, designs, artworks, literature, music, software, etc. Intellectual property rights are the legal rights that grant the owner the exclusive control over the use, reproduction, distribution, and modification of their intellectual property. Intellectual property rights aim to protect the owner’s interests and incentives, and to reward them for their contribution to the society and economy.
The other options are not the primary concern of intellectual property rights, but rather the secondary or incidental benefits or aspects of them. The owner’s ability to maintain copyright is a means of enforcing intellectual property rights, but not the end goal of them. The right of the owner to enjoy their creation is a personal or moral right, but not a legal or economic one. The right of the owner to control the delivery method is a specific or technical aspect of intellectual property rights, but not a general or fundamental one.
An important principle of defense in depth is that achieving information security requires a balanced focus on which PRIMARY elements?
Development, testing, and deployment
Prevention, detection, and remediation
People, technology, and operations
Certification, accreditation, and monitoring
An important principle of defense in depth is that achieving information security requires a balanced focus on the primary elements of people, technology, and operations. People are the users, administrators, managers, and other stakeholders who are involved in the security process. They need to be aware, trained, motivated, and accountable for their security roles and responsibilities. Technology is the hardware, software, network, and other tools that are used to implement the security controls and measures. They need to be selected, configured, updated, and monitored according to the security standards and best practices. Operations are the policies, procedures, processes, and activities that are performed to achieve the security objectives and requirements. They need to be documented, reviewed, audited, and improved continuously to ensure their effectiveness and efficiency.
The other options are not the primary elements of defense in depth, but rather the phases, functions, or outcomes of the security process. Development, testing, and deployment are the phases of the security life cycle, which describes how security is integrated into the system development process. Prevention, detection, and remediation are the functions of the security management, which describes how security is maintained and improved over time. Certification, accreditation, and monitoring are the outcomes of the security evaluation, which describes how security is assessed and verified against the criteria and standards.
Which of the following represents the GREATEST risk to data confidentiality?
Network redundancies are not implemented
Security awareness training is not completed
Backup tapes are generated unencrypted
Users have administrative privileges
Generating backup tapes unencrypted represents the greatest risk to data confidentiality, as it exposes the data to unauthorized access or disclosure if the tapes are lost, stolen, or intercepted. Backup tapes are often stored off-site or transported to remote locations, which increases the chances of them falling into the wrong hands. If the backup tapes are unencrypted, anyone who obtains them can read the data without any difficulty. Therefore, backup tapes should always be encrypted using strong algorithms and keys, and the keys should be protected and managed separately from the tapes.
The other options do not pose as much risk to data confidentiality as generating backup tapes unencrypted. Network redundancies are not implemented will affect the availability and reliability of the network, but not necessarily the confidentiality of the data. Security awareness training is not completed will increase the likelihood of human errors or negligence that could compromise the data, but not as directly as generating backup tapes unencrypted. Users have administrative privileges will grant users more access and control over the system and the data, but not as widely as generating backup tapes unencrypted.
What is the MOST important consideration from a data security perspective when an organization plans to relocate?
Ensure the fire prevention and detection systems are sufficient to protect personnel
Review the architectural plans to determine how many emergency exits are present
Conduct a gap analysis of a new facilities against existing security requirements
Revise the Disaster Recovery and Business Continuity (DR/BC) plan
When an organization plans to relocate, the most important consideration from a data security perspective is to conduct a gap analysis of the new facilities against the existing security requirements. A gap analysis is a process that identifies and evaluates the differences between the current state and the desired state of a system or a process. In this case, the gap analysis would compare the security controls and measures implemented in the old and new locations, and identify any gaps or weaknesses that need to be addressed. The gap analysis would also help to determine the costs and resources needed to implement the necessary security improvements in the new facilities.
The other options are not as important as conducting a gap analysis, as they do not directly address the data security risks associated with relocation. Ensuring the fire prevention and detection systems are sufficient to protect personnel is a safety issue, not a data security issue. Reviewing the architectural plans to determine how many emergency exits are present is also a safety issue, not a data security issue. Revising the Disaster Recovery and Business Continuity (DR/BC) plan is a good practice, but it is not a preventive measure, rather a reactive one. A DR/BC plan is a document that outlines how an organization will recover from a disaster and resume its normal operations. A DR/BC plan should be updated regularly, not only when relocating.
Which of the following types of technologies would be the MOST cost-effective method to provide a reactive control for protecting personnel in public areas?
Install mantraps at the building entrances
Enclose the personnel entry area with polycarbonate plastic
Supply a duress alarm for personnel exposed to the public
Hire a guard to protect the public area
Supplying a duress alarm for personnel exposed to the public is the most cost-effective method to provide a reactive control for protecting personnel in public areas. A duress alarm is a device that allows a person to signal for help in case of an emergency, such as an attack, a robbery, or a medical condition. A duress alarm can be activated by pressing a button, pulling a cord, or speaking a code word. A duress alarm can alert security personnel, law enforcement, or other responders to the location and nature of the emergency, and initiate appropriate actions. A duress alarm is a reactive control because it responds to an incident after it has occurred, rather than preventing it from happening.
The other options are not as cost-effective as supplying a duress alarm, as they involve more expensive or complex technologies or resources. Installing mantraps at the building entrances is a preventive control that restricts the access of unauthorized persons to the facility, but it also requires more space, maintenance, and supervision. Enclosing the personnel entry area with polycarbonate plastic is a preventive control that protects the personnel from physical attacks, but it also reduces the visibility and ventilation of the area. Hiring a guard to protect the public area is a deterrent control that discourages potential attackers, but it also involves paying wages, benefits, and training costs.
At what level of the Open System Interconnection (OSI) model is data at rest on a Storage Area Network (SAN) located?
Link layer
Physical layer
Session layer
Application layer
Data at rest on a Storage Area Network (SAN) is located at the physical layer of the Open System Interconnection (OSI) model. The OSI model is a conceptual framework that describes how data is transmitted and processed across different layers of a network. The OSI model consists of seven layers: application, presentation, session, transport, network, data link, and physical. The physical layer is the lowest layer of the OSI model, and it is responsible for the transmission and reception of raw bits over a physical medium, such as cables, wires, or optical fibers. The physical layer defines the physical characteristics of the medium, such as voltage, frequency, modulation, connectors, etc. The physical layer also deals with the physical topology of the network, such as bus, ring, star, mesh, etc.
A Storage Area Network (SAN) is a dedicated network that provides access to consolidated and block-level data storage. A SAN consists of storage devices, such as disks, tapes, or arrays, that are connected to servers or clients via a network infrastructure, such as switches, routers, or hubs. A SAN allows multiple servers or clients to share the same storage devices, and it provides high performance, availability, scalability, and security for data storage. Data at rest on a SAN is located at the physical layer of the OSI model, because it is stored as raw bits on the physical medium of the storage devices, and it is accessed by the servers or clients through the physical medium of the network infrastructure.
Which of the following factors contributes to the weakness of Wired Equivalent Privacy (WEP) protocol?
WEP uses a small range Initialization Vector (IV)
WEP uses Message Digest 5 (MD5)
WEP uses Diffie-Hellman
WEP does not use any Initialization Vector (IV)
WEP uses a small range Initialization Vector (IV) is the factor that contributes to the weakness of Wired Equivalent Privacy (WEP) protocol. WEP is a security protocol that provides encryption and authentication for wireless networks, such as Wi-Fi. WEP uses the RC4 stream cipher to encrypt the data packets, and the CRC-32 checksum to verify the data integrity. WEP also uses a shared secret key, which is concatenated with a 24-bit Initialization Vector (IV), to generate the keystream for the RC4 encryption. WEP has several weaknesses and vulnerabilities, such as:
WEP has been deprecated and replaced by more secure protocols, such as Wi-Fi Protected Access (WPA) or Wi-Fi Protected Access II (WPA2), which use stronger encryption and authentication methods, such as the Temporal Key Integrity Protocol (TKIP), the Advanced Encryption Standard (AES), or the Extensible Authentication Protocol (EAP).
The other options are not factors that contribute to the weakness of WEP, but rather factors that are irrelevant or incorrect. WEP does not use Message Digest 5 (MD5), which is a hash function that produces a 128-bit output from a variable-length input. WEP does not use Diffie-Hellman, which is a method for generating a shared secret key between two parties. WEP does use an Initialization Vector (IV), which is a 24-bit value that is concatenated with the secret key.
In a Transmission Control Protocol/Internet Protocol (TCP/IP) stack, which layer is responsible for negotiating and establishing a connection with another node?
Transport layer
Application layer
Network layer
Session layer
The transport layer of the Transmission Control Protocol/Internet Protocol (TCP/IP) stack is responsible for negotiating and establishing a connection with another node. The TCP/IP stack is a simplified version of the OSI model, and it consists of four layers: application, transport, internet, and link. The transport layer is the third layer of the TCP/IP stack, and it is responsible for providing reliable and efficient end-to-end data transfer between two nodes on a network. The transport layer uses protocols, such as Transmission Control Protocol (TCP) or User Datagram Protocol (UDP), to segment, sequence, acknowledge, and reassemble the data packets, and to handle error detection and correction, flow control, and congestion control. The transport layer also provides connection-oriented or connectionless services, depending on the protocol used.
TCP is a connection-oriented protocol, which means that it establishes a logical connection between two nodes before exchanging data, and it maintains the connection until the data transfer is complete. TCP uses a three-way handshake to negotiate and establish a connection with another node. The three-way handshake works as follows:
UDP is a connectionless protocol, which means that it does not establish or maintain a connection between two nodes, but rather sends data packets independently and without any guarantee of delivery, order, or integrity. UDP does not use a handshake or any other mechanism to negotiate and establish a connection with another node, but rather relies on the application layer to handle any connection-related issues.
Which of the following is the BEST network defense against unknown types of attacks or stealth attacks in progress?
Intrusion Prevention Systems (IPS)
Intrusion Detection Systems (IDS)
Stateful firewalls
Network Behavior Analysis (NBA) tools
Network Behavior Analysis (NBA) tools are the best network defense against unknown types of attacks or stealth attacks in progress. NBA tools are devices or software that monitor and analyze the network traffic and activities, and detect any anomalies or deviations from the normal or expected behavior. NBA tools use various techniques, such as statistical analysis, machine learning, artificial intelligence, or heuristics, to establish a baseline of the network behavior, and to identify any outliers or indicators of compromise. NBA tools can provide several benefits, such as:
The other options are not the best network defense against unknown types of attacks or stealth attacks in progress, but rather network defenses that have other limitations or drawbacks. Intrusion Prevention Systems (IPS) are devices or software that monitor and block the network traffic and activities that match the predefined signatures or rules of known attacks. IPS can provide a proactive and preventive layer of security, but they cannot detect or stop unknown types of attacks or stealth attacks that do not match any signatures or rules, or that can evade or disable the IPS. Intrusion Detection Systems (IDS) are devices or software that monitor and alert the network traffic and activities that match the predefined signatures or rules of known attacks. IDS can provide a reactive and detective layer of security, but they cannot detect or alert unknown types of attacks or stealth attacks that do not match any signatures or rules, or that can evade or disable the IDS. Stateful firewalls are devices or software that filter and control the network traffic and activities based on the state and context of the network sessions, such as the source and destination IP addresses, port numbers, protocol types, and sequence numbers. Stateful firewalls can provide a granular and dynamic layer of security, but they cannot filter or control unknown types of attacks or stealth attacks that use valid or spoofed network sessions, or that can exploit or bypass the firewall rules.
Which of the following operates at the Network Layer of the Open System Interconnection (OSI) model?
Packet filtering
Port services filtering
Content filtering
Application access control
Packet filtering operates at the network layer of the Open System Interconnection (OSI) model. The OSI model is a conceptual framework that describes how data is transmitted and processed across different layers of a network. The OSI model consists of seven layers: application, presentation, session, transport, network, data link, and physical. The network layer is the third layer from the bottom of the OSI model, and it is responsible for routing and forwarding data packets between different networks or subnets. The network layer uses logical addresses, such as IP addresses, to identify the source and destination of the data packets, and it uses protocols, such as IP, ICMP, or ARP, to perform the routing and forwarding functions.
Packet filtering is a technique that controls the access to a network or a host by inspecting the incoming and outgoing data packets and applying a set of rules or policies to allow or deny them. Packet filtering can be performed by devices, such as routers, firewalls, or proxies, that operate at the network layer of the OSI model. Packet filtering typically examines the network layer header of the data packets, such as the source and destination IP addresses, the protocol type, or the fragmentation flags, and compares them with the predefined rules or policies. Packet filtering can also examine the transport layer header of the data packets, such as the source and destination port numbers, the TCP flags, or the sequence numbers, and compare them with the rules or policies. Packet filtering can provide a basic level of security and performance for a network or a host, but it also has some limitations, such as the inability to inspect the payload or the content of the data packets, the vulnerability to spoofing or fragmentation attacks, or the complexity and maintenance of the rules or policies.
The other options are not techniques that operate at the network layer of the OSI model, but rather at other layers. Port services filtering is a technique that controls the access to a network or a host by inspecting the transport layer header of the data packets and applying a set of rules or policies to allow or deny them based on the port numbers or the services. Port services filtering operates at the transport layer of the OSI model, which is the fourth layer from the bottom. Content filtering is a technique that controls the access to a network or a host by inspecting the application layer payload or the content of the data packets and applying a set of rules or policies to allow or deny them based on the keywords, URLs, file types, or other criteria. Content filtering operates at the application layer of the OSI model, which is the seventh and the topmost layer. Application access control is a technique that controls the access to a network or a host by inspecting the application layer identity or the credentials of the users or the processes and applying a set of rules or policies to allow or deny them based on the roles, permissions, or other attributes. Application access control operates at the application layer of the OSI model, which is the seventh and the topmost layer.
Which of the following is used by the Point-to-Point Protocol (PPP) to determine packet formats?
Layer 2 Tunneling Protocol (L2TP)
Link Control Protocol (LCP)
Challenge Handshake Authentication Protocol (CHAP)
Packet Transfer Protocol (PTP)
Link Control Protocol (LCP) is used by the Point-to-Point Protocol (PPP) to determine packet formats. PPP is a data link layer protocol that provides a standard method for transporting network layer packets over point-to-point links, such as serial lines, modems, or dial-up connections. PPP supports various network layer protocols, such as IP, IPX, or AppleTalk, and it can encapsulate them in a common frame format. PPP also provides features such as authentication, compression, error detection, and multilink aggregation. LCP is a subprotocol of PPP that is responsible for establishing, configuring, maintaining, and terminating the point-to-point connection. LCP negotiates and agrees on various options and parameters for the PPP link, such as the maximum transmission unit (MTU), the authentication method, the compression method, the error detection method, and the packet format. LCP uses a series of messages, such as configure-request, configure-ack, configure-nak, configure-reject, terminate-request, terminate-ack, code-reject, protocol-reject, echo-request, echo-reply, and discard-request, to communicate and exchange information between the PPP peers.
The other options are not used by PPP to determine packet formats, but rather for other purposes. Layer 2 Tunneling Protocol (L2TP) is a tunneling protocol that allows the creation of virtual private networks (VPNs) over public networks, such as the Internet. L2TP encapsulates PPP frames in IP datagrams and sends them across the tunnel between two L2TP endpoints. L2TP does not determine the packet format of PPP, but rather uses it as a payload. Challenge Handshake Authentication Protocol (CHAP) is an authentication protocol that is used by PPP to verify the identity of the remote peer before allowing access to the network. CHAP uses a challenge-response mechanism that involves a random number (nonce) and a hash function to prevent replay attacks. CHAP does not determine the packet format of PPP, but rather uses it as a transport. Packet Transfer Protocol (PTP) is not a valid option, as there is no such protocol with this name. There is a Point-to-Point Protocol over Ethernet (PPPoE), which is a protocol that encapsulates PPP frames in Ethernet frames and allows the use of PPP over Ethernet networks. PPPoE does not determine the packet format of PPP, but rather uses it as a payload.
An external attacker has compromised an organization’s network security perimeter and installed a sniffer onto an inside computer. Which of the following is the MOST effective layer of security the organization could have implemented to mitigate the attacker’s ability to gain further information?
Implement packet filtering on the network firewalls
Install Host Based Intrusion Detection Systems (HIDS)
Require strong authentication for administrators
Implement logical network segmentation at the switches
Implementing logical network segmentation at the switches is the most effective layer of security the organization could have implemented to mitigate the attacker’s ability to gain further information. Logical network segmentation is the process of dividing a network into smaller subnetworks or segments based on criteria such as function, location, or security level. Logical network segmentation can be implemented at the switches, which are devices that operate at the data link layer of the OSI model and forward data packets based on the MAC addresses. Logical network segmentation can provide several benefits, such as:
Logical network segmentation can mitigate the attacker’s ability to gain further information by limiting the visibility and access of the sniffer to the segment where it is installed. A sniffer is a tool that captures and analyzes the data packets that are transmitted over a network. A sniffer can be used for legitimate purposes, such as troubleshooting, testing, or monitoring the network, or for malicious purposes, such as eavesdropping, stealing, or modifying the data. A sniffer can only capture the data packets that are within its broadcast domain, which is the set of devices that can communicate with each other without a router. By implementing logical network segmentation at the switches, the organization can create multiple broadcast domains and isolate the sensitive or critical data from the compromised segment. This way, the attacker can only see the data packets that belong to the same segment as the sniffer, and not the data packets that belong to other segments. This can prevent the attacker from gaining further information or accessing other resources on the network.
The other options are not the most effective layers of security the organization could have implemented to mitigate the attacker’s ability to gain further information, but rather layers that have other limitations or drawbacks. Implementing packet filtering on the network firewalls is not the most effective layer of security, because packet filtering only examines the network layer header of the data packets, such as the source and destination IP addresses, and does not inspect the payload or the content of the data. Packet filtering can also be bypassed by using techniques such as IP spoofing or fragmentation. Installing Host Based Intrusion Detection Systems (HIDS) is not the most effective layer of security, because HIDS only monitors and detects the activities and events on a single host, and does not prevent or respond to the attacks. HIDS can also be disabled or evaded by the attacker if the host is compromised. Requiring strong authentication for administrators is not the most effective layer of security, because authentication only verifies the identity of the users or processes, and does not protect the data in transit or at rest. Authentication can also be defeated by using techniques such as phishing, keylogging, or credential theft.
An input validation and exception handling vulnerability has been discovered on a critical web-based system. Which of the following is MOST suited to quickly implement a control?
Add a new rule to the application layer firewall
Block access to the service
Install an Intrusion Detection System (IDS)
Patch the application source code
Adding a new rule to the application layer firewall is the most suited to quickly implement a control for an input validation and exception handling vulnerability on a critical web-based system. An input validation and exception handling vulnerability is a type of vulnerability that occurs when a web-based system does not properly check, filter, or sanitize the input data that is received from the users or other sources, or does not properly handle the errors or exceptions that are generated by the system. An input validation and exception handling vulnerability can lead to various attacks, such as:
An application layer firewall is a device or software that operates at the application layer of the OSI model and inspects the application layer payload or the content of the data packets. An application layer firewall can provide various functions, such as:
Adding a new rule to the application layer firewall is the most suited to quickly implement a control for an input validation and exception handling vulnerability on a critical web-based system, because it can prevent or reduce the impact of the attacks by filtering or blocking the malicious or invalid input data that exploit the vulnerability. For example, a new rule can be added to the application layer firewall to:
Adding a new rule to the application layer firewall can be done quickly and easily, without requiring any changes or patches to the web-based system, which can be time-consuming and risky, especially for a critical system. Adding a new rule to the application layer firewall can also be done remotely and centrally, without requiring any physical access or installation on the web-based system, which can be inconvenient and costly, especially for a distributed system.
The other options are not the most suited to quickly implement a control for an input validation and exception handling vulnerability on a critical web-based system, but rather options that have other limitations or drawbacks. Blocking access to the service is not the most suited option, because it can cause disruption and unavailability of the service, which can affect the business operations and customer satisfaction, especially for a critical system. Blocking access to the service can also be a temporary and incomplete solution, as it does not address the root cause of the vulnerability or prevent the attacks from occurring again. Installing an Intrusion Detection System (IDS) is not the most suited option, because IDS only monitors and detects the attacks, and does not prevent or respond to them. IDS can also generate false positives or false negatives, which can affect the accuracy and reliability of the detection. IDS can also be overwhelmed or evaded by the attacks, which can affect the effectiveness and efficiency of the detection. Patching the application source code is not the most suited option, because it can take a long time and require a lot of resources and testing to identify, fix, and deploy the patch, especially for a complex and critical system. Patching the application source code can also introduce new errors or vulnerabilities, which can affect the functionality and security of the system. Patching the application source code can also be difficult or impossible, if the system is proprietary or legacy, which can affect the feasibility and compatibility of the patch.
What is the purpose of an Internet Protocol (IP) spoofing attack?
To send excessive amounts of data to a process, making it unpredictable
To intercept network traffic without authorization
To disguise the destination address from a target’s IP filtering devices
To convince a system that it is communicating with a known entity
The purpose of an Internet Protocol (IP) spoofing attack is to convince a system that it is communicating with a known entity. IP spoofing is a technique that involves creating and sending IP packets with a forged source IP address, which is usually the IP address of a trusted or authorized host. IP spoofing can be used for various malicious purposes, such as:
The purpose of IP spoofing is to convince a system that it is communicating with a known entity, because it allows the attacker to evade detection, avoid responsibility, and exploit trust relationships.
The other options are not the main purposes of IP spoofing, but rather the possible consequences or methods of IP spoofing. To send excessive amounts of data to a process, making it unpredictable is a possible consequence of IP spoofing, as it can cause a DoS or DDoS attack. To intercept network traffic without authorization is a possible method of IP spoofing, as it can be used to hijack or intercept a TCP session. To disguise the destination address from a target’s IP filtering devices is not a valid option, as IP spoofing involves forging the source address, not the destination address.
A manufacturing organization wants to establish a Federated Identity Management (FIM) system with its 20 different supplier companies. Which of the following is the BEST solution for the manufacturing organization?
Trusted third-party certification
Lightweight Directory Access Protocol (LDAP)
Security Assertion Markup language (SAML)
Cross-certification
Security Assertion Markup Language (SAML) is the best solution for the manufacturing organization that wants to establish a Federated Identity Management (FIM) system with its 20 different supplier companies. FIM is a process that allows the sharing and recognition of identities across different organizations that have a trust relationship. FIM enables the users of one organization to access the resources or services of another organization without having to create or maintain multiple accounts or credentials. FIM can provide several benefits, such as:
SAML is a standard protocol that supports FIM by allowing the exchange of authentication and authorization information between different parties. SAML uses XML-based messages, called assertions, to convey the identity, attributes, and entitlements of a user to a service provider. SAML defines three roles for the parties involved in FIM:
SAML works as follows:
SAML is the best solution for the manufacturing organization that wants to establish a FIM system with its 20 different supplier companies, because it can enable the seamless and secure access to the resources or services across the different organizations, without requiring the users to create or maintain multiple accounts or credentials. SAML can also provide interoperability and compatibility between different platforms and technologies, as it is based on a standard and open protocol.
The other options are not the best solutions for the manufacturing organization that wants to establish a FIM system with its 20 different supplier companies, but rather solutions that have other limitations or drawbacks. Trusted third-party certification is a process that involves a third party, such as a certificate authority (CA), that issues and verifies digital certificates that contain the public key and identity information of a user or an entity. Trusted third-party certification can provide authentication and encryption for the communication between different parties, but it does not provide authorization or entitlement information for the access to the resources or services. Lightweight Directory Access Protocol (LDAP) is a protocol that allows the access and management of directory services, such as Active Directory, that store the identity and attribute information of users and entities. LDAP can provide a centralized and standardized way to store and retrieve identity and attribute information, but it does not provide a mechanism to exchange or federate the information across different organizations. Cross-certification is a process that involves two or more CAs that establish a trust relationship and recognize each other’s certificates. Cross-certification can extend the trust and validity of the certificates across different domains or organizations, but it does not provide a mechanism to exchange or federate the identity, attribute, or entitlement information.
Which of the following BEST describes an access control method utilizing cryptographic keys derived from a smart card private key that is embedded within mobile devices?
Derived credential
Temporary security credential
Mobile device credentialing service
Digest authentication
Derived credential is the best description of an access control method utilizing cryptographic keys derived from a smart card private key that is embedded within mobile devices. A smart card is a device that contains a microchip that stores a private key and a digital certificate that are used for authentication and encryption. A smart card is typically inserted into a reader that is attached to a computer or a terminal, and the user enters a personal identification number (PIN) to unlock the smart card and access the private key and the certificate. A smart card can provide a high level of security and convenience for the user, as it implements a two-factor authentication method that combines something the user has (the smart card) and something the user knows (the PIN).
However, a smart card may not be compatible or convenient for mobile devices, such as smartphones or tablets, that do not have a smart card reader or a USB port. To address this issue, a derived credential is a solution that allows the user to use a mobile device as an alternative to a smart card for authentication and encryption. A derived credential is a cryptographic key and a certificate that are derived from the smart card private key and certificate, and that are stored on the mobile device. A derived credential works as follows:
A derived credential can provide a secure and convenient way to use a mobile device as an alternative to a smart card for authentication and encryption, as it implements a two-factor authentication method that combines something the user has (the mobile device) and something the user is (the biometric feature). A derived credential can also comply with the standards and policies for the use of smart cards, such as the Personal Identity Verification (PIV) or the Common Access Card (CAC) programs.
The other options are not the best descriptions of an access control method utilizing cryptographic keys derived from a smart card private key that is embedded within mobile devices, but rather descriptions of other methods or concepts. Temporary security credential is a method that involves issuing a short-lived credential, such as a token or a password, that can be used for a limited time or a specific purpose. Temporary security credential can provide a flexible and dynamic way to grant access to the users or entities, but it does not involve deriving a cryptographic key from a smart card private key. Mobile device credentialing service is a concept that involves providing a service that can issue, manage, or revoke credentials for mobile devices, such as certificates, tokens, or passwords. Mobile device credentialing service can provide a centralized and standardized way to control the access of mobile devices, but it does not involve deriving a cryptographic key from a smart card private key. Digest authentication is a method that involves using a hash function, such as MD5, to generate a digest or a fingerprint of the user’s credentials, such as the username and password, and sending it to the server for verification. Digest authentication can provide a more secure way to authenticate the user than the basic authentication, which sends the credentials in plain text, but it does not involve deriving a cryptographic key from a smart card private key.
Users require access rights that allow them to view the average salary of groups of employees. Which control would prevent the users from obtaining an individual employee’s salary?
Limit access to predefined queries
Segregate the database into a small number of partitions each with a separate security level
Implement Role Based Access Control (RBAC)
Reduce the number of people who have access to the system for statistical purposes
Limiting access to predefined queries is the control that would prevent the users from obtaining an individual employee’s salary, if they only require access rights that allow them to view the average salary of groups of employees. A query is a request for information from a database, which can be expressed in a structured query language (SQL) or a graphical user interface (GUI). A query can specify the criteria, conditions, and operations for selecting, filtering, sorting, grouping, and aggregating the data from the database. A predefined query is a query that has been created and stored in advance by the database administrator or the data owner, and that can be executed by the authorized users without any modification. A predefined query can provide several benefits, such as:
Limiting access to predefined queries is the control that would prevent the users from obtaining an individual employee’s salary, if they only require access rights that allow them to view the average salary of groups of employees, because it can ensure that the users can only access the data that is relevant and necessary for their tasks, and that they cannot access or manipulate the data that is beyond their scope or authority. For example, a predefined query can be created and stored that calculates and displays the average salary of groups of employees based on certain criteria, such as department, position, or experience. The users who need to view this information can execute this predefined query, but they cannot modify it or create their own queries that might reveal the individual employee’s salary or other sensitive data.
The other options are not the controls that would prevent the users from obtaining an individual employee’s salary, if they only require access rights that allow them to view the average salary of groups of employees, but rather controls that have other purposes or effects. Segregating the database into a small number of partitions each with a separate security level is a control that would improve the performance and security of the database by dividing it into smaller and manageable segments that can be accessed and processed independently and concurrently. However, this control would not prevent the users from obtaining an individual employee’s salary, if they have access to the partition that contains the salary data, and if they can create or modify their own queries. Implementing Role Based Access Control (RBAC) is a control that would enforce the access rights and permissions of the users based on their roles or functions within the organization, rather than their identities or attributes. However, this control would not prevent the users from obtaining an individual employee’s salary, if their roles or functions require them to access the salary data, and if they can create or modify their own queries. Reducing the number of people who have access to the system for statistical purposes is a control that would reduce the risk and impact of unauthorized access or disclosure of the sensitive data by minimizing the exposure and distribution of the data. However, this control would not prevent the users from obtaining an individual employee’s salary, if they are among the people who have access to the system, and if they can create or modify their own queries.
What is the BEST approach for controlling access to highly sensitive information when employees have the same level of security clearance?
Audit logs
Role-Based Access Control (RBAC)
Two-factor authentication
Application of least privilege
Applying the principle of least privilege is the best approach for controlling access to highly sensitive information when employees have the same level of security clearance. The principle of least privilege is a security concept that states that every user or process should have the minimum amount of access rights and permissions that are necessary to perform their tasks or functions, and nothing more. The principle of least privilege can provide several benefits, such as:
Applying the principle of least privilege is the best approach for controlling access to highly sensitive information when employees have the same level of security clearance, because it can ensure that the employees can only access the information that is relevant and necessary for their tasks or functions, and that they cannot access or manipulate the information that is beyond their scope or authority. For example, if the highly sensitive information is related to a specific project or department, then only the employees who are involved in that project or department should have access to that information, and not the employees who have the same level of security clearance but are not involved in that project or department.
The other options are not the best approaches for controlling access to highly sensitive information when employees have the same level of security clearance, but rather approaches that have other purposes or effects. Audit logs are records that capture and store the information about the events and activities that occur within a system or a network, such as the access and usage of the sensitive data. Audit logs can provide a reactive and detective layer of security by enabling the monitoring and analysis of the system or network behavior, and facilitating the investigation and response of the incidents. However, audit logs cannot prevent or reduce the access or disclosure of the sensitive information, but rather provide evidence or clues after the fact. Role-Based Access Control (RBAC) is a method that enforces the access rights and permissions of the users based on their roles or functions within the organization, rather than their identities or attributes. RBAC can provide a granular and dynamic layer of security by defining and assigning the roles and permissions according to the organizational structure and policies. However, RBAC cannot control the access to highly sensitive information when employees have the same level of security clearance and the same role or function within the organization, but rather rely on other criteria or mechanisms. Two-factor authentication is a technique that verifies the identity of the users by requiring them to provide two pieces of evidence or factors, such as something they know (e.g., password, PIN), something they have (e.g., token, smart card), or something they are (e.g., fingerprint, face). Two-factor authentication can provide a strong and preventive layer of security by preventing unauthorized access to the system or network by the users who do not have both factors. However, two-factor authentication cannot control the access to highly sensitive information when employees have the same level of security clearance and the same two factors, but rather rely on other criteria or mechanisms.
Which security access policy contains fixed security attributes that are used by the system to determine a
user’s access to a file or object?
Mandatory Access Control (MAC)
Access Control List (ACL)
Discretionary Access Control (DAC)
Authorized user control
The security access policy that contains fixed security attributes that are used by the system to determine a user’s access to a file or object is Mandatory Access Control (MAC). MAC is a type of access control model that assigns permissions to users and objects based on their security labels, which indicate their level of sensitivity or trustworthiness. MAC is enforced by the system or the network, rather than by the owner or the creator of the object, and it cannot be modified or overridden by the users. MAC can provide some benefits for security, such as enhancing the confidentiality and the integrity of the data, preventing unauthorized access or disclosure, and supporting the audit and compliance activities. MAC is commonly used in military or government environments, where the data is classified according to its level of sensitivity, such as top secret, secret, confidential, or unclassified. The users are granted security clearance based on their level of trustworthiness, such as their background, their role, or their need to know. The users can only access the objects that have the same or lower security classification than their security clearance, and the objects can only be accessed by the users that have the same or higher security clearance than their security classification. This is based on the concept of no read up and no write down, which requires that a user can only read data of lower or equal sensitivity level, and can only write data of higher or equal sensitivity level. MAC contains fixed security attributes that are used by the system to determine a user’s access to a file or object, by using the following methods:
An organization has outsourced its financial transaction processing to a Cloud Service Provider (CSP) who will provide them with Software as a Service (SaaS). If there was a data breach who is responsible for monetary losses?
The Data Protection Authority (DPA)
The Cloud Service Provider (CSP)
The application developers
The data owner
The data owner is the person who has the authority and responsibility for the data stored, processed, or transmitted by an Information System (IS). The data owner is responsible for the monetary losses if there was a data breach, as the data owner is accountable for the security, quality, and integrity of the data, as well as for defining the classification, sensitivity, retention, and disposal of the data. The Data Protection Authority (DPA) is not responsible for the monetary losses, but for the enforcement of the data protection laws and regulations. The Cloud Service Provider (CSP) is not responsible for the monetary losses, but for the provision of the cloud services and the protection of the cloud infrastructure. The application developers are not responsible for the monetary losses, but for the development and maintenance of the software applications. References: CISSP All-in-One Exam Guide, Eighth Edition, Chapter 1: Security and Risk Management, page 48; Official (ISC)2 Guide to the CISSP CBK, Fifth Edition, Chapter 1: Security and Risk Management, page 40.
Which of the following is the GREATEST benefit of implementing a Role Based Access Control (RBAC)
system?
Integration using Lightweight Directory Access Protocol (LDAP)
Form-based user registration process
Integration with the organizations Human Resources (HR) system
A considerably simpler provisioning process
The greatest benefit of implementing a Role Based Access Control (RBAC) system is a considerably simpler provisioning process. Provisioning is the process of creating, modifying, or deleting the user accounts and access rights on a system or a network. Provisioning can be a complex and tedious task, especially in large or dynamic organizations that have many users, systems, and resources. RBAC is a type of access control model that assigns permissions to users based on their roles or functions within the organization, rather than on their individual identities or attributes. RBAC can simplify the provisioning process by reducing the administrative overhead and ensuring the consistency and accuracy of the user accounts and access rights. RBAC can also provide some benefits for security, such as enforcing the principle of least privilege, facilitating the separation of duties, and supporting the audit and compliance activities. Integration using Lightweight Directory Access Protocol (LDAP), form-based user registration process, and integration with the organizations Human Resources (HR) system are not the greatest benefits of implementing a RBAC system, although they may be related or useful features. Integration using LDAP is a technique that uses a standard protocol to communicate and exchange information with a directory service, such as Active Directory or OpenLDAP. LDAP can provide some benefits for access control, such as centralizing and standardizing the user accounts and access rights, supporting the authentication and authorization mechanisms, and enabling the interoperability and scalability of the systems or the network. However, integration using LDAP is not a benefit of RBAC, as it is not a feature or a requirement of RBAC, and it can be used with other access control models, such as discretionary access control (DAC) or mandatory access control (MAC). Form-based user registration process is a technique that uses a web-based form to collect and validate the user information and preferences, such as name, email, password, or role. Form-based user registration process can provide some benefits for access control, such as simplifying and automating the user account creation, enhancing the user experience and satisfaction, and supporting the self-service and delegation capabilities. However, form-based user registration process is not a benefit of RBAC, as it is not a feature or a requirement of RBAC, and it can be used with other access control models, such as DAC or MAC. Integration with the organizations HR system is a technique that uses a software application or a service to synchronize and update the user accounts and access rights with the HR data, such as employee records, job titles, or organizational units. Integration with the organizations HR system can provide some benefits for access control, such as streamlining and automating the provisioning process, improving the accuracy and timeliness of the user accounts and access rights, and supporting the identity lifecycle management activities. However, integration with the organizations HR system is not a benefit of RBAC, as it is not a feature or a requirement of RBAC, and it can be used with other access control models, such as DAC or MAC.
What does a Synchronous (SYN) flood attack do?
Forces Transmission Control Protocol /Internet Protocol (TCP/IP) connections into a reset state
Establishes many new Transmission Control Protocol / Internet Protocol (TCP/IP) connections
Empties the queue of pending Transmission Control Protocol /Internet Protocol (TCP/IP) requests
Exceeds the limits for new Transmission Control Protocol /Internet Protocol (TCP/IP) connections
A SYN flood attack does exceed the limits for new TCP/IP connections. A SYN flood attack is a type of denial-of-service attack that sends a large number of SYN packets to a server, without completing the TCP three-way handshake. The server allocates resources for each SYN packet and waits for the final ACK packet, which never arrives. This consumes the server’s memory and processing power, and prevents it from accepting new legitimate connections. The other options are not accurate descriptions of what a SYN flood attack does. References: SYN flood - Wikipedia; SYN flood DDoS attack | Cloudflare.
What does electronic vaulting accomplish?
It protects critical files.
It ensures the fault tolerance of Redundant Array of Independent Disks (RAID) systems
It stripes all database records
It automates the Disaster Recovery Process (DRP)
Section: Security Operations
The security accreditation task of the System Development Life Cycle (SDLC) process is completed at the end of which phase?
System acquisition and development
System operations and maintenance
System initiation
System implementation
The security accreditation task of the System Development Life Cycle (SDLC) process is completed at the end of the system implementation phase. The SDLC is a framework that describes the stages and activities involved in the development, deployment, and maintenance of a system. The SDLC typically consists of the following phases: system initiation, system acquisition and development, system implementation, system operations and maintenance, and system disposal. The security accreditation task is the process of formally authorizing a system to operate in a specific environment, based on the security requirements, controls, and risks. The security accreditation task is part of the security certification and accreditation (C&A) process, which also includes the security certification task, which is the process of technically evaluating and testing the security controls and functionality of a system. The security accreditation task is completed at the end of the system implementation phase, which is the phase where the system is installed, configured, integrated, and tested in the target environment. The security accreditation task involves reviewing the security certification results and documentation, such as the security plan, the security assessment report, and the plan of action and milestones, and making a risk-based decision to grant, deny, or conditionally grant the authorization to operate (ATO) the system. The security accreditation task is usually performed by a senior official, such as the authorizing official (AO) or the designated approving authority (DAA), who has the authority and responsibility to accept the security risks and approve the system operation. The security accreditation task is not completed at the end of the system acquisition and development, system operations and maintenance, or system initiation phases. The system acquisition and development phase is the phase where the system requirements, design, and development are defined and executed, and the security controls are selected and implemented. The system operations and maintenance phase is the phase where the system is used and supported in the operational environment, and the security controls are monitored and updated. The system initiation phase is the phase where the system concept, scope, and objectives are established, and the security categorization and planning are performed.
Which of the following is MOST effective in detecting information hiding in Transmission Control Protocol/internet Protocol (TCP/IP) traffic?
Stateful inspection firewall
Application-level firewall
Content-filtering proxy
Packet-filter firewall
An application-level firewall is the most effective in detecting information hiding in TCP/IP traffic. Information hiding is a technique that conceals data or messages within other data or messages, such as using steganography, covert channels, or encryption. An application-level firewall is a type of firewall that operates at the application layer of the OSI model, and inspects the content and context of the network packets, such as the headers, payloads, or protocols. An application-level firewall can help to detect information hiding in TCP/IP traffic, as it can analyze the data for any anomalies, inconsistencies, or violations of the expected format or behavior. A stateful inspection firewall, a content-filtering proxy, and a packet-filter firewall are not as effective in detecting information hiding in TCP/IP traffic, as they operate at lower layers of the OSI model, and only inspect the state, content, or header of the network packets, respectively. References: CISSP All-in-One Exam Guide, Eighth Edition, Chapter 6: Communication and Network Security, page 731; Official (ISC)2 Guide to the CISSP CBK, Fifth Edition, Chapter 4: Communication and Network Security, page 511.
What is the MAIN reason for testing a Disaster Recovery Plan (DRP)?
To ensure Information Technology (IT) staff knows and performs roles assigned to each of them
To validate backup sites’ effectiveness
To find out what does not work and fix it
To create a high level DRP awareness among Information Technology (IT) staff
The main reason for testing a DRP is to identify and correct any gaps, errors, or weaknesses in the plan before a real disaster occurs. Testing a DRP also helps to ensure that the plan is feasible, effective, and aligned with the organization’s objectives and requirements. Testing a DRP can also help to train and familiarize the IT staff with their roles and responsibilities in the event of a disaster, but this is not the primary purpose of testing. References: CISSP All-in-One Exam Guide, Eighth Edition, Chapter 9: Business Continuity and Disaster Recovery Planning, page 1019; Official (ISC)2 Guide to the CISSP CBK, Fifth Edition, Chapter 8: Security Operations, page 1020.
When in the Software Development Life Cycle (SDLC) MUST software security functional requirements be defined?
After the system preliminary design has been developed and the data security categorization has been performed
After the vulnerability analysis has been performed and before the system detailed design begins
After the system preliminary design has been developed and before the data security categorization begins
After the business functional analysis and the data security categorization have been performed
Software security functional requirements must be defined after the business functional analysis and the data security categorization have been performed in the Software Development Life Cycle (SDLC). The SDLC is a process that involves planning, designing, developing, testing, deploying, operating, and maintaining a system, using various models and methodologies, such as waterfall, spiral, agile, or DevSecOps. The SDLC can be divided into several phases, each with its own objectives and activities, such as:
Software security functional requirements are the specific and measurable security features and capabilities that the system must provide to meet the security objectives and requirements. Software security functional requirements are derived from the business functional analysis and the data security categorization, which are two tasks that are performed in the system initiation phase of the SDLC. The business functional analysis is the process of identifying and documenting the business functions and processes that the system must support and enable, such as the inputs, outputs, workflows, and tasks. The data security categorization is the process of determining the security level and impact of the system and its data, based on the confidentiality, integrity, and availability criteria, and applying the appropriate security controls and measures. Software security functional requirements must be defined after the business functional analysis and the data security categorization have been performed, because they can ensure that the system design and development are consistent and compliant with the security objectives and requirements, and that the system security is aligned and integrated with the business functions and processes.
The other options are not the phases of the SDLC when the software security functional requirements must be defined, but rather phases that involve other tasks or activities related to the system design and development. After the system preliminary design has been developed and the data security categorization has been performed is not the phase when the software security functional requirements must be defined, but rather the phase when the system architecture and components are designed, based on the system scope and objectives, and the data security categorization is verified and validated. After the vulnerability analysis has been performed and before the system detailed design begins is not the phase when the software security functional requirements must be defined, but rather the phase when the system design and components are evaluated and tested for the security effectiveness and compliance, and the system detailed design is developed, based on the system architecture and components. After the system preliminary design has been developed and before the data security categorization begins is not the phase when the software security functional requirements must be defined, but rather the phase when the system architecture and components are designed, based on the system scope and objectives, and the data security categorization is initiated and planned.
Which of the following is the BEST method to prevent malware from being introduced into a production environment?
Purchase software from a limited list of retailers
Verify the hash key or certificate key of all updates
Do not permit programs, patches, or updates from the Internet
Test all new software in a segregated environment
Testing all new software in a segregated environment is the best method to prevent malware from being introduced into a production environment. Malware is any malicious software that can harm or compromise the security, availability, integrity, or confidentiality of a system or data. Malware can be introduced into a production environment through various sources, such as software downloads, updates, patches, or installations. Testing all new software in a segregated environment involves verifying and validating the functionality and security of the software before deploying it to the production environment, using a separate system or network that is isolated and protected from the production environment. Testing all new software in a segregated environment can provide several benefits, such as:
The other options are not the best methods to prevent malware from being introduced into a production environment, but rather methods that can reduce or mitigate the risk of malware, but not eliminate it. Purchasing software from a limited list of retailers is a method that can reduce the risk of malware from being introduced into a production environment, but not prevent it. This method involves obtaining software only from trusted and reputable sources, such as official vendors or distributors, that can provide some assurance of the quality and security of the software. However, this method does not guarantee that the software is free of malware, as it may still contain hidden or embedded malware, or it may be tampered with or compromised during the delivery or installation process. Verifying the hash key or certificate key of all updates is a method that can reduce the risk of malware from being introduced into a production environment, but not prevent it. This method involves checking the authenticity and integrity of the software updates, patches, or installations, by comparing the hash key or certificate key of the software with the expected or published value, using cryptographic techniques and tools. However, this method does not guarantee that the software is free of malware, as it may still contain malware that is not detected or altered by the hash key or certificate key, or it may be subject to a man-in-the-middle attack or a replay attack that can intercept or modify the software or the key. Not permitting programs, patches, or updates from the Internet is a method that can reduce the risk of malware from being introduced into a production environment, but not prevent it. This method involves restricting or blocking the access or download of software from the Internet, which is a common and convenient source of malware, by applying and enforcing the appropriate security policies and controls, such as firewall rules, antivirus software, or web filters. However, this method does not guarantee that the software is free of malware, as it may still be obtained or infected from other sources, such as removable media, email attachments, or network shares.
Which of the following is a web application control that should be put into place to prevent exploitation of Operating System (OS) bugs?
Check arguments in function calls
Test for the security patch level of the environment
Include logging functions
Digitally sign each application module
Testing for the security patch level of the environment is the web application control that should be put into place to prevent exploitation of Operating System (OS) bugs. OS bugs are errors or defects in the code or logic of the OS that can cause the OS to malfunction or behave unexpectedly. OS bugs can be exploited by attackers to gain unauthorized access, disrupt business operations, or steal or leak sensitive data. Testing for the security patch level of the environment is the web application control that should be put into place to prevent exploitation of OS bugs, because it can provide several benefits, such as:
The other options are not the web application controls that should be put into place to prevent exploitation of OS bugs, but rather web application controls that can prevent or mitigate other types of web application attacks or issues. Checking arguments in function calls is a web application control that can prevent or mitigate buffer overflow attacks, which are attacks that exploit the vulnerability of the web application code that does not properly check the size or length of the input data that is passed to a function or a variable, and overwrite the adjacent memory locations with malicious code or data. Including logging functions is a web application control that can prevent or mitigate unauthorized access or modification attacks, which are attacks that exploit the lack of or weak authentication or authorization mechanisms of the web applications, and access or modify the web application data or functionality without proper permission or verification. Digitally signing each application module is a web application control that can prevent or mitigate code injection or tampering attacks, which are attacks that exploit the vulnerability of the web application code that does not properly validate or sanitize the input data that is executed or interpreted by the web application, and inject or modify the web application code with malicious code or data.
What is the BEST approach to addressing security issues in legacy web applications?
Debug the security issues
Migrate to newer, supported applications where possible
Conduct a security assessment
Protect the legacy application with a web application firewall
Migrating to newer, supported applications where possible is the best approach to addressing security issues in legacy web applications. Legacy web applications are web applications that are outdated, unsupported, or incompatible with the current technologies and standards. Legacy web applications may have various security issues, such as:
Migrating to newer, supported applications where possible is the best approach to addressing security issues in legacy web applications, because it can provide several benefits, such as:
The other options are not the best approaches to addressing security issues in legacy web applications, but rather approaches that can mitigate or remediate the security issues, but not eliminate or prevent them. Debugging the security issues is an approach that can mitigate the security issues in legacy web applications, but not the best approach, because it involves identifying and fixing the errors or defects in the code or logic of the web applications, which may be difficult or impossible to do for the legacy web applications that are outdated or unsupported. Conducting a security assessment is an approach that can remediate the security issues in legacy web applications, but not the best approach, because it involves evaluating and testing the security effectiveness and compliance of the web applications, using various techniques and tools, such as audits, reviews, scans, or penetration tests, and identifying and reporting any security weaknesses or gaps, which may not be sufficient or feasible to do for the legacy web applications that are incompatible or obsolete. Protecting the legacy application with a web application firewall is an approach that can mitigate the security issues in legacy web applications, but not the best approach, because it involves deploying and configuring a web application firewall, which is a security device or software that monitors and filters the web traffic between the web applications and the users or clients, and blocks or allows the web requests or responses based on the predefined rules or policies, which may not be effective or efficient to do for the legacy web applications that have weak or outdated encryption or authentication mechanisms.
A Java program is being developed to read a file from computer A and write it to computer B, using a third computer C. The program is not working as expected. What is the MOST probable security feature of Java preventing the program from operating as intended?
Least privilege
Privilege escalation
Defense in depth
Privilege bracketing
The most probable security feature of Java preventing the program from operating as intended is least privilege. Least privilege is a principle that states that a subject (such as a user, a process, or a program) should only have the minimum amount of access or permissions that are necessary to perform its function or task. Least privilege can help to reduce the attack surface and the potential damage of a system or network, by limiting the exposure and impact of a subject in case of a compromise or misuse.
Java implements the principle of least privilege through its security model, which consists of several components, such as:
In this question, the Java program is being developed to read a file from computer A and write it to computer B, using a third computer C. This means that the Java program needs to have the permissions to perform the file I/O and the network communication operations, which are considered as sensitive or risky actions by the Java security model. However, if the Java program is running on computer C with the default or the minimal security permissions, such as in the Java Security Sandbox, then it will not be able to perform these operations, and the program will not work as expected. Therefore, the most probable security feature of Java preventing the program from operating as intended is least privilege, which limits the access or permissions of the Java program based on its source, signer, or policy.
The other options are not the security features of Java preventing the program from operating as intended, but rather concepts or techniques that are related to security in general or in other contexts. Privilege escalation is a technique that allows a subject to gain higher or unauthorized access or permissions than what it is supposed to have, by exploiting a vulnerability or a flaw in a system or network. Privilege escalation can help an attacker to perform malicious actions or to access sensitive resources or data, by bypassing the security controls or restrictions. Defense in depth is a concept that states that a system or network should have multiple layers or levels of security, to provide redundancy and resilience in case of a breach or an attack. Defense in depth can help to protect a system or network from various threats and risks, by using different types of security measures and controls, such as the physical, the technical, or the administrative ones. Privilege bracketing is a technique that allows a subject to temporarily elevate or lower its access or permissions, to perform a specific function or task, and then return to its original or normal level. Privilege bracketing can help to reduce the exposure and impact of a subject, by minimizing the time and scope of its higher or lower access or permissions.
Which of the following is the PRIMARY risk with using open source software in a commercial software construction?
Lack of software documentation
License agreements requiring release of modified code
Expiration of the license agreement
Costs associated with support of the software
The primary risk with using open source software in a commercial software construction is license agreements requiring release of modified code. Open source software is software that uses publicly available source code, which can be seen, modified, and distributed by anyone. Open source software has some advantages, such as being affordable and flexible, but it also has some disadvantages, such as being potentially insecure or unsupported.
One of the main disadvantages of using open source software in a commercial software construction is the license agreements that govern the use and distribution of the open source software. License agreements are legal contracts that specify the rights and obligations of the parties involved in the software, such as the original authors, the developers, and the users. License agreements can vary in terms of their terms and conditions, such as the scope, the duration, or the fees of the software.
Some of the common types of license agreements for open source software are:
The primary risk with using open source software in a commercial software construction is license agreements requiring release of modified code, which are usually associated with copyleft licenses. This means that if a commercial software construction uses or incorporates open source software that is licensed under a copyleft license, then it must also release its own source code and any modifications or derivatives of it, under the same or compatible copyleft license. This can pose a significant risk for the commercial software construction, as it may lose its competitive advantage, intellectual property, or revenue, by disclosing its source code and allowing others to use, modify, or distribute it.
The other options are not the primary risks with using open source software in a commercial software construction, but rather secondary or minor risks that may or may not apply to the open source software. Lack of software documentation is a secondary risk with using open source software in a commercial software construction, as it may affect the quality, usability, or maintainability of the open source software, but it does not necessarily affect the rights or obligations of the commercial software construction. Expiration of the license agreement is a minor risk with using open source software in a commercial software construction, as it may affect the availability or continuity of the open source software, but it is unlikely to happen, as most open source software licenses are perpetual or indefinite. Costs associated with support of the software is a secondary risk with using open source software in a commercial software construction, as it may affect the reliability, security, or performance of the open source software, but it can be mitigated or avoided by choosing the open source software that has adequate or alternative support options.
The configuration management and control task of the certification and accreditation process is incorporated in which phase of the System Development Life Cycle (SDLC)?
System acquisition and development
System operations and maintenance
System initiation
System implementation
The configuration management and control task of the certification and accreditation process is incorporated in the system acquisition and development phase of the System Development Life Cycle (SDLC). The SDLC is a process that involves planning, designing, developing, testing, deploying, operating, and maintaining a system, using various models and methodologies, such as waterfall, spiral, agile, or DevSecOps. The SDLC can be divided into several phases, each with its own objectives and activities, such as:
The certification and accreditation process is a process that involves assessing and verifying the security and compliance of a system, and authorizing and approving the system operation and maintenance, using various standards and frameworks, such as NIST SP 800-37 or ISO/IEC 27001. The certification and accreditation process can be divided into several tasks, each with its own objectives and activities, such as:
The configuration management and control task of the certification and accreditation process is incorporated in the system acquisition and development phase of the SDLC, because it can ensure that the system design and development are consistent and compliant with the security objectives and requirements, and that the system changes are controlled and documented. Configuration management and control is a process that involves establishing and maintaining the baseline and the inventory of the system components and resources, such as hardware, software, data, or documentation, and tracking and recording any modifications or updates to the system components and resources, using various techniques and tools, such as version control, change control, or configuration audits. Configuration management and control can provide several benefits, such as:
The other options are not the phases of the SDLC that incorporate the configuration management and control task of the certification and accreditation process, but rather phases that involve other tasks of the certification and accreditation process. System operations and maintenance is a phase of the SDLC that incorporates the security monitoring task of the certification and accreditation process, because it can ensure that the system operation and maintenance are consistent and compliant with the security objectives and requirements, and that the system security is updated and improved. System initiation is a phase of the SDLC that incorporates the security categorization and security planning tasks of the certification and accreditation process, because it can ensure that the system scope and objectives are defined and aligned with the security objectives and requirements, and that the security plan and policy are developed and documented. System implementation is a phase of the SDLC that incorporates the security assessment and security authorization tasks of the certification and accreditation process, because it can ensure that the system deployment and installation are evaluated and verified for the security effectiveness and compliance, and that the system operation and maintenance are authorized and approved based on the risk and impact analysis and the security objectives and requirements.
Copyright © 2014-2025 Examstrust. All Rights Reserved
