A risk analyst peforming PCA wishes to explain80% of the variance. The first orthogonal factor has a volatility of 100, and the second 40, and the third 30. Assume there are no other factors. Which of the factors will be included in the final analysis?
A bank holds a portfolio ofcorporate bonds. Corporate bond spreads widen, resulting in a loss of value for the portfolio. This loss arises due to:
Which of the following statements are true?
I. Retail Risk Based Pricing involves using borrower specific data to arrive at both credit adjudication and pricing decisions
II. An integrated 'Risk Information Management Environment' includes two elements - people and processes
III. A Logical Data Model (LDM) lays down the relationships between data elements that an organization stores
IV. Reference Data and Metadata refer to the same thing
When building a operational loss distribution by combining a loss frequency distribution and a loss severity distribution, it is assumed that:
I. The severity of losses is conditional upon the numberof loss events
II. The frequency of losses is independent from the severity of the losses
III. Both the frequency and severity of loss events are dependent upon the state of internal controls in the bank
Under the standardized approach to determining operational risk capital, operations risk capital is equal to:
Under the standardized approach to calculating operational risk capital under Basel II, negative regulatory capital charges for any of the business units:
Which of the following risks and reasons justify the use of scenario analysis in operational riskmodeling:
I. Risks for which no internal loss data is available
II. Risks that are foreseeable but have no precedent, internally or externally
III. Risks for which objective assessments can be made by experts
IV. Risks that are known to exist, but for which no reliable external or internal losses can be analyzed
V. Reducing the complexity of having to fit statistical models to internal and external loss data
VI. Managing the capital estimation process as to produce estimates in line with management's desired capital buffers.
Which of the following is true in relation to the application of Extreme Value Theory when applied to operational risk measurement?
I. EVT focuses on extreme losses that are generally not covered by standard distribution assumptions
II. EVT considers the distribution of losses in the tails
III. The Peaks-over-thresholds (POT) and the generalized Pareto distributions are used to model extreme value distributions
IV. EVT is concerned with average losses beyond a given level of confidence
Which loss event type is the failure to timely deliver collateral classified as under the Basel II framework?
As the persistence parameter under EWMA is lowered, which of the following would be true:
A Bank Holding Company (BHC) is invested in an investment bank and a retail bank. The BHC defaults for certain if either the investment bank or the retail bank defaults. However, the BHC can also default on its own without either the investment bank or the retail bank defaulting. The investment bank and the retail bank's defaults are independent of each other, with a probability of default of 0.05 each. The BHC's probability of default is 0.11.
What is the probabilityof default of both the BHC and the investment bank? What is the probability of the BHC's default provided both the investment bank and the retail bank survive?
If the annual default hazard rate for a borrower is 10%, what is the probability that there is no default at the end of 5 years?
Under the CreditPortfolio View approach to credit risk modeling, which of the following best describes the conditional transition matrix:
Which of the following decisions need to be made as part of laying down a system for calculating VaR:
I. The confidence level and horizon
II. Whether portfolio valuation is based upon a delta-gamma approximation or a full revaluation
III. Whether the VaR is to be disclosed in the quarterly financial statements
IV. Whether a 10 day VaR will be calculated based on 10-day return periods, or for 1-day and scaled to 10 days
What would be the correct order of steps to addressing data quality problems in an organization?
Which of the following best describes Altman's Z-score
Loss provisioning is intended to cover:
There are two bonds in a portfolio, each with a market value of $50m. The probability of default of the two bonds are 0.03 and 0.08 respectively, over a one year horizon. If the default correlation is 25%, what is the one year expected loss on this portfolio?
Which of the following formulae describes Marginal VaR for a portfolio p, where V_i is the value of the i-th asset in the portfolio? (All other notation and symbols have their usual meaning.)
A)
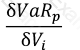
B)
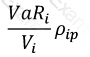
C)
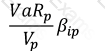
D)
All of the above
The risk that a counterparty fails to deliver its obligation upon settlement while having received the leg owed to it is called:
The VaR of a portfolio at the 99% confidence level is $250,000 when mean return is assumed to be zero. If the assumption of zero returns is changed to an assumption of returns of $10,000, what is the revised VaR?
According to the Basel framework, shareholders' equity and reserves are considered a part of:
Under the actuarial (or CreditRisk+) based modeling of defaults, what is the probability of 4 defaults in a retail portfolio where the number of expected defaults is2?
Which of the following statements are true:
I. Heavy tailed parametricdistributions are a good choice for severity modeling in operational risk.
II. Heavy tailed body-tail distributions are a good choice for severity modeling in operational risk.
III. Log-likelihood is a means to estimate parameters for a distribution.
IV. Body-tail distributions allow modeling small losses differently from large ones.
Which of the following statements are true:
I.Top down approaches help focus management attention on the frequency and severity of loss events, while bottom up approaches do not.
II. Top down approaches rely upon high level data while bottom up approaches need firm specific risk data to estimate risk.
III. Scenario analysis can help capture both qualitative and quantitative dimensions of operational risk.
Under thebasic indicator approach to determining operational risk capital, operational risk capital is equal to:
The sum of the stand alone economic capital of all the business units of a bank is:
If P be the transition matrix for 1 year, how can we find the transition matrix for 4 months?
A risk management function is best organized as:
A stock that follows the Weiner process has its future price determined by:
Which of the following are valid methods for selecting an appropriate model from the model space for severity estimation:
I. Cross-validation method
II. Bootstrap method
III. Complexity penalty method
IV. Maximum likelihood estimation method
For a FX forward contract, what would be the worst time for a counterparty to default (in terms of the maximum likely credit exposure)
The largest 10 lossesover a 250 day observation period are as follows. Calculate the expected shortfall at a 98% confidence level:
20m
19m
19m
17m
16m
13m
11m
10m
9m
9m
Which of the following will be a loss not covered by operational risk as defined under Basel II?
A zero coupon corporate bond maturing in an year has a probability of default of 5% and yields 12%. The recovery rate is zero. What is the risk free rate?
Which of the following is not an approach proposed by the Basel II framework to compute operational riskcapital?